
A pump is a device that moves fluids, or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.

A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

An air compressor is a pneumatic device that converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. By one of several methods, an air compressor forces more and more air into a storage tank, increasing the pressure. When the tank's pressure reaches its engineered upper limit, the air compressor shuts off. The compressed air, then, is held in the tank until called into use. The energy contained in the compressed air can be used for a variety of applications, utilizing the kinetic energy of the air as it is released and the tank depressurizes. When tank pressure reaches its lower limit, the air compressor turns on again and re-pressurizes the tank. An air compressor must be differentiated from a pump because it works for any gas/air, while pumps work on a liquid.

Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine.

A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.

A butterfly valve is a valve that isolates or regulates the flow of a fluid. The closing mechanism is a disk that rotates.
Ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about 100 nanopascals. UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximately 40 km, so the gas is in free molecular flow, and gas molecules will collide with the chamber walls many times before colliding with each other. Almost all molecular interactions therefore take place on various surfaces in the chamber.

A rotary valve is a type of valve in which the rotation of a passage or passages in a transverse plug regulates the flow of liquid or gas through the attached pipes. The common stopcock is the simplest form of rotary valve. Rotary valves have been applied in numerous applications, including:

Bulk material handling is an engineering field that is centered on the design of equipment used for the handling of dry materials. Bulk materials are those dry materials which are powdery, granular or lumpy in nature, and are stored in heaps. Examples of bulk materials are minerals, ores, coal, cereals, woodchips, sand, gravel, clay, cement, ash, salt, chemicals, grain, sugar, flour and stone in loose bulk form. It can also relate to the handling of mixed wastes. Bulk material handling is an essential part of all industries that process bulk ingredients, including: food, beverage, confectionery, pet food, animal feed, tobacco, chemical, agricultural, polymer, plastic, rubber, ceramic, electronics, metals, minerals, paint, paper, textiles and more.
A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes solid particulates such as dust, pollen, mold, and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines.

A dust collector is a system used to enhance the quality of air released from industrial and commercial processes by collecting dust and other impurities from air or gas. Designed to handle high-volume dust loads, a dust collector system consists of a blower, dust filter, a filter-cleaning system, and a dust receptacle or dust removal system. It is distinguished from air purifiers, which use disposable filters to remove dust.
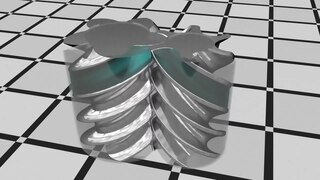
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.

An oil filter is a filter designed to remove contaminants from engine oil, transmission oil, lubricating oil, or hydraulic oil. Their chief use is in internal-combustion engines for motor vehicles, powered aircraft, railway locomotives, ships and boats, and static engines such as generators and pumps. Other vehicle hydraulic systems, such as those in automatic transmissions and power steering, are often equipped with an oil filter. Gas turbine engines, such as those on jet aircraft, also require the use of oil filters. Oil filters are used in many different types of hydraulic machinery. The oil industry itself employs filters for oil production, oil pumping, and oil recycling. Modern engine oil filters tend to be "full-flow" (inline) or "bypass".

Vibratory bowl feeders are common devices used to feed individual component parts for assembly on industrial production lines. They are used when a randomly sorted bulk package of small components must be fed into another machine one-by-one, oriented in a particular direction.
Vertical roller mill is a type of grinder used to grind materials into extremely fine powder for use in mineral dressing processes, paints, pyrotechnics, cements and ceramics. It is an energy efficient alternative for a ball mill.
Double dump valves, also known as double flap valves or double flap gates, are a type of airlock valve commonly used in industrial applications as a component in bulk material handling applications. Double dump valves are primarily used to discharge chunky or fibrous, bulk materials from hoppers, bins, and cyclones operating under positive or negative pressure. Double dump valves are used to discharge a flow of material while at the same time serving as an airlock transition point to preserve the pressure differential above and below the valve. This type of material handling valve is ideal for use with bulky or abrasive materials that would tend to jam or damage a rotary feeder.
Trickle valves, also known as vacuum valves, are commonly used in industrial dust collection applications to maintain an airlock seal on a dust collector hopper while allowing bulk solid material to be automatically discharged. These valves are typically a less expensive alternative to more commonly used rotary airlocks. Unlike rotary airlock valves which are driven by either an electric motor or a gas or air-powered motor, trickle valves require no external power source and are therefore well-suited for use in mechanical trenchers, where a dust-free environment in the pinnacle truss and axle bore is required for smooth operation. Trickle values were originally developed for this purpose.

A rotary union is a union that allows for rotation of the united parts. It is thus a device that provides a seal between a stationary supply passage and a rotating part to permit the flow of a fluid into and/or out of the rotating part. Fluids typically used with rotary joints and rotating unions include various heat transfer media and fluid power media such as steam, water, thermal oil, hydraulic fluid, and coolants. A rotary union is sometimes referred to as a rotating union, rotary valve, swivel union,rotorseal, rotary couplings, rotary joint, rotating joints, hydraulic coupling, pneumatic rotary union, through bore rotary union, air rotary union, electrical rotary union, or vacuum rotary union
Endless-piston principle is a dispensing variation of rotating positive displacement pumps. Their operating principle can be compared with an endless piston that conveys the product from the suction side to the discharge side, building up a differential pressure in the process.
A spark extinguishing system is used for preventive fire protection. A spark extinguishing system can detect and eliminate ignition sources before a fire or dust explosion occurs. Systems for grinding, chopping, drying, cooling and pressing materials including their pneumatic or mechanical transport and extraction systems and facilities for separation or storage purposes, also dust collectors, filters, cyclones, silos, and hoppers are especially at risk.














