Related Research Articles
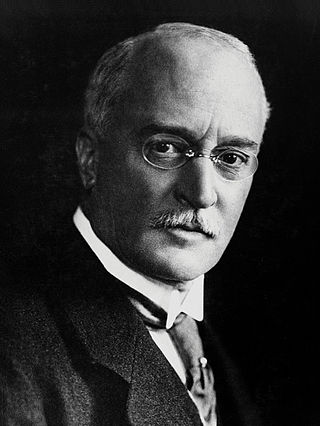
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.

Louis IV, called the Bavarian, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328 until his death in 1347.

The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 15 Nazis, four police officers, and one bystander.

Rudolf Ludwig Mössbauer was a German physicist best known for his 1957 discovery of 'recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence', for which he was awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics. This effect, called the Mössbauer effect, is the basis for Mössbauer spectroscopy.

The Technical University of Munich is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences.

Erwin Neher is a German biophysicist, specializing in the field of cell physiology. For significant contribution in the field, in 1991 he was awarded, along with Bert Sakmann, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for "their discoveries concerning the function of single ion channels in cells".

Roderich Fick was a German architect most prominent during the Nazi regime.

Friedrich Ludwig "Fritz" Bauer was a German pioneer of computer science and professor at the Technical University of Munich.
Ulmus × arbusculaE. Wolf [: "bushy" ] is a putative hybrid of Ulmus scabra and Ulmus pumila raised from seed collected from a large wych elm in the St. Petersburg Botanic Garden in 1902. A similar crossing was cloned ('FL025') by the Istituto per la Protezione delle Piante (IPP), Florence, as part of the Italian elm breeding programme circa 2000.
Roy A. Batchelor is Professor Emeritus in Political Economy and Statistics in Bayes Business School, City, University of London.

Otto Rudolf Salvisberg was a Swiss architect.

Gotthold Julius Rudolph Sohm was a German jurist and Church historian as well as a theologian. He published works concerning Roman and German law, Canon law and Church History.
Transbase is a relational database management system, developed and maintained by Transaction Software GmbH, Munich. The development of Transbase was started in the 1980s by Rudolf Bayer under the name "Merkur" at the department of Computer Science of the Technical University of Munich (TUM).
Violetta Elsa Plincke was a Waldorf teacher and lecturer on education who contributed much to the establishment of Steiner education in Britain.
Dorothea Maria Irene Liebermann-Meffert was a German surgeon and professor of surgery at the Technical University of Munich.

Rupert Huber is a German physicist and university professor. Huber is known for his research in terahertz technology and semiconductor physics.
Robert Suckale was a German art historian, medievalist and professor at the Technical University of Berlin.
Volker Markl is a German computer scientist and database systems researcher.
Alfons Kemper is a German computer scientist and a full professor for database systems at the Technical University of Munich.

The TUM School of Computation, Information and Technology (CIT) is a school of the Technical University of Munich, established in 2022 by the merger of three former departments. As of 2022, it is structured into the Department of Mathematics, the Department of Computer Engineering, the Department of Computer Science, and the Department of Electrical Engineering.
References
- ↑ Rudolf Bayer at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ GI-Fellow citation, retrieved 2012-03-09.