Related Research Articles

TiVo is a digital video recorder (DVR) developed and marketed by Xperi and introduced in 1999. TiVo provides an on-screen guide of scheduled broadcast programming television programs, whose features include "OnePass" schedules which record every new episode of a series, and "WishList" searches which allow the user to find and record shows that match their interests by title, actor, director, category, or keyword. TiVo also provides a range of features when the TiVo DVR is connected to a home network, including film and TV show downloads, advanced search, online scheduling, and at one time, personal photo viewing and local music playback.
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.

A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
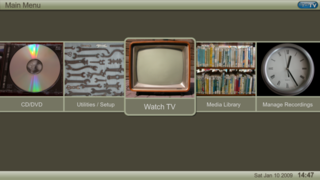
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.
OpenMAX, often shortened as "OMX", is a non-proprietary and royalty-free cross-platform set of C-language programming interfaces. It provides abstractions for routines that are especially useful for processing of audio, video, and still images. It is intended for low power and embedded system devices that need to efficiently process large amounts of multimedia data in predictable ways, such as video codecs, graphics libraries, and other functions for video, image, audio, voice and speech.
A home theater PC (HTPC) or media center computer is a convergent device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that focuses on video, photo, audio playback, and sometimes video recording functionality. Since the mid-2000s, other types of consumer electronics, including game consoles and dedicated media devices, have crossed over to manage video and music content. The term "media center" also refers to specialized application software designed to run on standard personal computers.
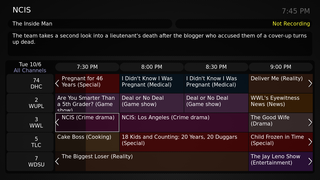
Electronic programming guides (EPGs) and interactive programming guides (IPGs) are menu-based systems that provide users of television, radio and other media applications with continuously updated menus that display scheduling information for current and upcoming broadcast programming. Some guides also feature backward scrolling to promote their catch up content. They are commonly known as guides or TV guides.

MediaPortal is an open-source media player and digital video recorder software project, often considered an alternative to Windows Media Center. It provides a 10-foot user interface for performing typical PVR/TiVo functionality, including playing, pausing, and recording live TV; playing DVDs, videos, and music; viewing pictures; and other functions. Plugins allow it to perform additional tasks, such as watching online video, listening to music from online services such as Last.fm, and launching other applications such as games. It interfaces with the hardware commonly found in HTPCs, such as TV tuners, infrared receivers, and LCD displays.
Flash Video is a container file format used to deliver digital video content over the Internet using Adobe Flash Player version 6 and newer. Flash Video content may also be embedded within SWF files. There are two different Flash Video file formats: FLV and F4V. The audio and video data within FLV files are encoded in the same way as SWF files. The F4V file format is based on the ISO base media file format, starting with Flash Player 9 update 3. Both formats are supported in Adobe Flash Player and developed by Adobe Systems. FLV was originally developed by Macromedia. In the early 2000s, Flash Video was the de facto standard for web-based streaming video. Users include Hulu, VEVO, Yahoo! Video, metacafe, Reuters.com, and many other news providers.

Windows Media Center (WMC) is a digital video recorder and media player created by Microsoft. Media Center was first introduced to Windows in 2002 on Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE). It was included in Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista, as well as all editions of Windows 7 except Starter and Home Basic. It was also available on Windows 8 Pro and Windows 8.1 Pro as a paid add-on, before being discontinued in Windows 10, although it can reportedly be unofficially reinstalled using a series of Command Prompt commands.

Gracenote, Inc. is a company owned by Nielsen Holdings that provides music, video and sports metadata and automatic content recognition (ACR) technologies to entertainment services and companies, worldwide. Formerly CDDB, Gracenote maintains and licenses an Internet-accessible database containing information about the contents of audio compact discs and vinyl records.
This is a comparison of digital video recorder (DVR), also known as personal video recorder (PVR), software packages. Note: this is may be considered a comparison of DVB software, not all listed packages have recording capabilities.

GB-PVR was a PVR application, running on Microsoft Windows, whose main function was scheduling TV recordings and playing back live TV. GB-PVR is no longer under active development and has been superseded by NextPVR, also known as nPVR.
ProgDVB is a freeware/shareware software used to watch digital TV channels and listen to radio on computers. It supports DVB-S (satellite), DVB-S2, DVB-C (cable), DVB-T (terrestrial) and IPTV sources.

Zap2it is an American website and affiliate network that provides local television listings for areas of the United States and Canada. The site is produced by Nexstar Media Group. Zap2it affiliates include Wave Broadband, Cox, Dish Network, Disney, Sinclair Broadcast Group, The New York Times, the Los Angeles Times, and The Washington Post.
Software categories are groups of software. They allow software to be understood in terms of those categories, instead of the particularities of each package. Different classification schemes consider different aspects of software.
VBox Home TV gateway is a network-enabled live TV tuner and PVR HDTV set-top-box produced by VBox Communications Ltd.
References
- ↑ "Schedules Direct". Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-08-10.
- ↑ "Schedules Direct Membership" . Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ↑ "Approved Applications List" . Retrieved 2012-02-03.