Related Research Articles

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and or nails.

The human leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.

Curtis Montague Schilling is an American former Major League Baseball right-handed pitcher who is a commentator for conservative media outlet BlazeTV. He helped lead the Philadelphia Phillies to a World Series appearance in 1993, and won championships in 2001 with the Arizona Diamondbacks and in 2004 and 2007 with the Boston Red Sox, being named the World Series MVP in 2001. Schilling retired with a career postseason record of 11–2, and his .846 postseason winning percentage is a major-league record among pitchers with at least ten decisions. He is a member of the 3,000 strikeout club and has the highest strikeout-to-walk ratio of any of its inactive members. He is tied for third for the most 300-strikeout seasons.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
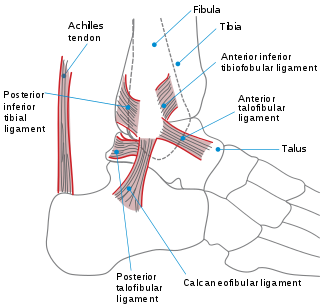
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

The 2004 American League Championship Series was the Major League Baseball playoff series to decide the American League champion for the 2004 season, and the right to play in the 2004 World Series. A rematch of the 2003 American League Championship Series, it was played between the Boston Red Sox, who had won the AL wild card and defeated the Anaheim Angels in the American League Division Series, and the New York Yankees, who had won the AL East with the best record in the AL, defeated the Minnesota Twins. The Red Sox became the first team in MLB history to come back from a 0–3 series deficit to win a best-of-seven series. In fact, the history of North American professional sports has seen no NBA team ever win a series after falling behind 3-0 and only four NHL teams have ever done so. Prior to the 2004 ALCS, no MLB team had so much as forced a Game 7 under those circumstances – and only one team since 2004 has been able to do so.
Otoplasty denotes the surgical and non-surgical procedures for correcting the deformities and defects of the pinna, and for reconstructing a defective, or deformed, or absent external ear, consequent to congenital conditions and trauma. The otoplastic surgeon corrects the defect or deformity by creating an external ear that is of natural proportions, contour, and appearance, usually achieved by the reshaping, the moving, and the augmenting of the cartilaginous support framework of the pinna. Moreover, the occurrence of congenital ear deformities occasionally overlaps with other medical conditions.
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.

Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee, or preserved before reconstruction through an arthroscopic procedure. ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
The Broström operation is a repair of ligaments on lateral ankle. It is designed to address ankle instability. More importantly, it is primarily used to repair the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) in the ankle. It is thought that the majority of patients regain most function in their ankles. The recovery time for the procedure varies according to the patient but usually takes a minimum of 3–6 months.

The sole is the bottom of the foot.

The 2004 Boston Red Sox season was the 104th season in the franchise's Major League Baseball history. Managed by Terry Francona, the Red Sox finished with a 98–64 record, three games behind the New York Yankees in the American League East. The Red Sox qualified for the postseason as the AL wild card, swept the Anaheim Angels in the ALDS, and faced the Yankees in the ALCS for the second straight year. After losing the first three games to the Yankees and trailing in the ninth inning of the fourth game, the Red Sox became the first team in major league history to come back from a three-game postseason deficit, defeating the Yankees in seven games. The Red Sox then swept the St. Louis Cardinals in the World Series, capturing their first championship since 1918.
A compartment syndrome is an increased pressure within a muscular compartment that compromises the circulation to the muscles.

A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated.
In surgery, a surgical incision is a cut made through the skin and soft tissue to facilitate an operation or procedure. Often, multiple incisions are possible for an operation. In general, a surgical incision is made as small and unobtrusive as possible to facilitate safe and timely operating conditions.
References
- ↑ Curry, Jack (October 24, 2004). "A Doctor is Keeping Schilling in Stitches". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 October 2017.
- ↑ Nelson, Murry R. (2013). American sports a history of icons, idols, and ideas. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO. p. 1163. ISBN 978-0313397530.
- ↑ "Doctors sewed skin to tissue on Schilling's leg". ESPN. October 21, 2004. Retrieved 22 October 2017.