Related Research Articles

Joubert syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, an area of the brain that controls balance and coordination.

Colpocephaly is a cephalic disorder involving the disproportionate enlargement of the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles and is usually diagnosed early after birth due to seizures. It is a nonspecific finding and is associated with multiple neurological syndromes, including agenesis of the corpus callosum, Chiari malformation, lissencephaly, and microcephaly. Although the exact cause of colpocephaly is not known yet, it is commonly believed to occur as a result of neuronal migration disorders during early brain development, intrauterine disturbances, perinatal injuries, and other central nervous system disorders. Individuals with colpocephaly have various degrees of motor disabilities, visual defects, spasticity, and moderate to severe intellectual disability. No specific treatment for colpocephaly exists, but patients may undergo certain treatments to improve their motor function or intellectual disability.

The corpus callosum, also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about ten centimetres in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections.

MASA syndrome is a rare X-linked recessive neurological disorder on the L1 disorder spectrum belonging in the group of hereditary spastic paraplegias a paraplegia known to increase stiffness spasticity in the lower limbs. This syndrome also has two other names, CRASH syndrome and Gareis-Mason syndrome.
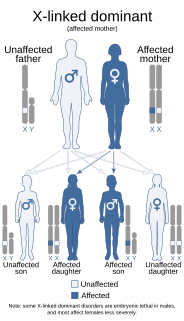
Aicardi syndrome is a rare genetic malformation syndrome characterized by the partial or complete absence of a key structure in the brain called the corpus callosum, the presence of retinal abnormalities, and seizures in the form of infantile spasms.
Optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH) is a medical condition arising from the underdevelopment of the optic nerve(s). This condition is the most common congenital optic nerve anomaly. The optic disc appears abnormally small, because not all the optic nerve axons have developed properly. It is often associated with endocrinopathies, developmental delay, and brain malformations. The optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting visual signals from the retina to the brain, has approximately 1.2 million nerve fibers in the average person. In those diagnosed with ONH, however, there are noticeably fewer nerves.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum. It occurs when the development of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain, in the embryo is disrupted. The result of this is that the fibers that would otherwise form the corpus callosum are instead longitudinally oriented along the ipsilateral ventricular wall and form structures called Probst bundles.
In medicine, agenesis refers to the failure of an organ to develop during embryonic growth and development due to the absence of primordial tissue. Many forms of agenesis are referred to by individual names, depending on the organ affected:
Hypoplasia is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells. Hypoplasia is similar to aplasia, but less severe. It is technically not the opposite of hyperplasia. Hypoplasia is a congenital condition, while hyperplasia generally refers to excessive cell growth later in life.
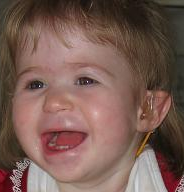
1p36 deletion syndrome is a congenital genetic disorder characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disability, delayed growth, hypotonia, seizures, limited speech ability, malformations, hearing and vision impairment, and distinct facial features. The symptoms may vary, depending on the exact location of the chromosomal deletion.
Saal Bulas syndrome is listed as a "rare disease" by the Office of Rare Diseases (ORD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This means that Saal Bulas syndrome, or a subtype of Saal Bulas syndrome, affects fewer than 200,000 people in the US population.
Vici syndrome, also called immunodeficiency with cleft lip/palate, cataract, hypopigmentation and absent corpus callosum, is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by albinism, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cataracts, cardiomyopathy, severe psychomotor retardation, seizures, immunodeficiency and recurrent severe infections. To date, about 50 cases have been reported.
Warren S. Brown is director of the Travis Research Institute and professor of psychology in the Graduate School of Psychology at Fuller Theological Seminary. Brown received his doctorate in Experimental Physiological Psychology from the University of Southern California (1971). Prior to Fuller, Brown spent 11 years as a research scientist at the UCLA Brain Research Institute. He was a founding member of the National Organization for Disorders of the Corpus Callosum, the International Research Consortium on the Corpus Callosum and Cerebral Connectivity (IRC5), and the International Society for Science and Religion. Brown and his wife founded the annual "Warren and Janet Brown Scholarship" at Fuller that supports students in neuropsychological research.

Acrocallosal syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by corpus callosum agenesis, polydactyly, multiple dysmorphic features, motor and intellectual disabilities, and other symptoms. The syndrome was first described by Albert Schinzel in 1979.
FG syndrome (FGS) is a rare genetic syndrome caused by one or more recessive genes located on the X chromosome and causing physical anomalies and developmental delays. FG syndrome was named after the first letters of the surnames of the first patients noted with the disease. First reported by American geneticists John M. Opitz and Elisabeth G. Kaveggia in 1974, its major clinical features include intellectual disability, hyperactivity, hypotonia, and a characteristic facial appearance including macrocephaly.
Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome is a condition characterized by orbital cysts, microphthalmia, porencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and facial skin tags.
Genitopatellar syndrome is a rare disorder with characteristic craniofacial features, congenital flexion contractures of the lower limbs, absent or abnormal patellae, urogenital anomalies, and severe psychomotor retardation. In 2012, it was shown that mutations in the gene KAT6B cause the syndrome.

Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome (GLH) or cerebellotrigeminal-dermal dysplasia is a rare neurocutaneous (Phakomatosis) disorder affecting the trigeminal nerve and causing several other neural and physical abnormalities. Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome has been diagnosed in only 34 people. Cases of Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome may be under-reported as other diseases share the characteristics of cerebellar malformation shown in Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome. Gómez–López-Hernández syndrome was first characterized in 1979.

Andermann syndrome, also known as agenesis of corpus callosum with neuronopathy (ACCPN) and Charlevoix disease, among other names, is a very rare neurodegenerative genetic disorder that damages the nerves used to control muscles and related to sensation and is often associated with agenesis of the corpus collosum.
Toriello–Carey syndrome is a genetic disorder that is characterized by Pierre Robin sequence and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Children with the disorder also possess a characteristic facial phenotype.
References
- ↑ Shapiro Syndrome, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD), National Institutes of Health