
Raja Sher Singh Attariwala, OBI was a royal military commander and a member of the Sikh nobility during the period of the Sikh Empire in the mid-19th century in Punjab, and later served under the British during the Revolt of 1857.

Raja Sher Singh Attariwala, OBI was a royal military commander and a member of the Sikh nobility during the period of the Sikh Empire in the mid-19th century in Punjab, and later served under the British during the Revolt of 1857.

He commanded the Sikh Khalsa army in the Second Anglo-Sikh War against the British East India Company. His father was General Chattar Singh Attariwalla. General Sher Singh and the army, under his command, gave a devastating blow to the British Army at Chillianwala. Under his command the Sikh Khalsa Army managed to successfully defend its position against a British army at the Battle of Chillianwala. Both armies retreated after the battle, with both sides claiming victory, although it became clear after the rains subsided that the Sikhs had defeated the British.. It was one of the hardest fought battles in the British Army's history. The loss of British prestige at Chillianwala was one of the factors that contributed to the Indian Rebellion of 1857 some nine years later. Within the British Army, such was the consternation over the events in the battle that, after the disastrous Charge of the Light Brigade, when Lord Lucan remarked "This is a most serious matter", General Airey replied, "It is nothing to Chillianwalah."
With the establishment of British control, Sher Singh Attariwalla was forced into exile from Punjab. The British feared that such a powerful leader could reignite a full-scale war with them. Sher Singh was in exile, at Benares, away from his Punjabi homeland. [1] He was then called to serve with the British to put down the Revolt of 1857 in Delhi against the Mughals. [1] He was given the title of Sardar Bahadur, a diamond encrusted tapestry from Bahadur Shah Zafar's treasury and the Order of British India. [1] He also visited England and a received letter from Queen Victoria I stating that his descendants would get preferential treatment from British authorities. [1]

The first Anglo-Sikh war was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company in 1845 and 1846 around the Ferozepur district of Punjab. It resulted in defeat and partial subjugation of the Sikh empire and cession of Jammu & Kashmir as a separate princely state under British suzerainty.
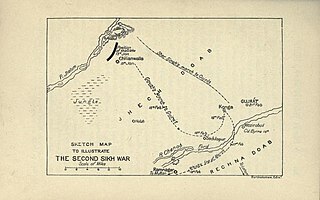
The second Anglo-Sikh war was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the East India Company which took place from 1848 to 1849. It resulted in the fall of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently became the North-West Frontier Province, by the East India Company.

The Battle of Chillianwala was fought in January 1849 during the Second Anglo-Sikh War in the Chillianwala region of Punjab, now part of modern-day Pakistan. The battle was one of the bloodiest fought by the British East India Company. Both armies held their positions at the end of the battle and both sides claimed victory. The battle was a strategic check to immediate British ambitions in India and a shock to British military prestige.

The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the British East India Company in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It was forged on the foundations of the Khalsa from a collection of autonomous misls. At its peak in the 19th century, the empire extended from Gilgit and Tibet in the north to the deserts of Sindh in the south and from the Khyber Pass in the west to the Sutlej in the east as far as Oudh. It was divided into four provinces: Lahore, which became the Sikh capital; Multan; Peshawar; and Kashmir from 1799 to 1849. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 4.5 million in 1831, it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Empire.

Maharani Jind Kaur was regent of the Sikh Empire from 1843 until 29 March 1847. After the Sikh Empire was dissolved on 29 March 1847 the Sikhs claimed her as the Maharani and successor of Maharaja Duleep Singh. However, on the same day the British took full control and refused to accept the claims.

Dal Khalsa was the name of the combined military forces of 11 Sikh misls that operated in the 18th century (1748–1799) in the Punjab region. It was established by Nawab Kapur Singh in late 1740s.

The Battle of Sobraon was fought on 10 February 1846, between the forces of the East India Company and the Sikh Khalsa Army, the army of the Sikh Empire of the Punjab. The Sikhs were completely defeated, making this the decisive battle of the First Anglo-Sikh War.

The Battle of Mudki was fought on 18 December 1845, between the forces of the East India Company and part of the Sikh Khalsa Army, the army of the Sikh Empire of the Punjab. The British army won an untidy encounter battle, sustaining heavy casualties.

The Battle of Ramnagar was fought on 22 November 1848 between British East India Company and Sikh Empire forces during the Second Anglo-Sikh War. The British were led by Sir Hugh Gough, while the Sikhs were led by Raja Sher Singh Attariwalla. The Sikhs repelled an attempted British surprise attack.

The Battle of Gujrat was a decisive battle in the Second Anglo-Sikh War, fought on 21 February 1849, between the forces of the East India Company, and a Sikh army in rebellion against the company's control of the Sikh Empire, represented by the child Maharaja Duleep Singh who was in British custody in Lahore. The Sikh army was defeated by the British regular and Bengal Army forces of the British East India Company. After it capitulated a few days later, the Punjab was annexed to the East India Company's territories and Duleep Singh was deposed.

The siege of Multan began on 19 April 1848 and lasted until 22 January 1849, and saw fighting around Multan between the British East India Company and the Sikh Empire. It began with a rebellion against a ruler imposed by the East India Company, which precipitated the Second Anglo-Sikh War, and ended when the last defenders of the city surrendered to British forces.
Guru Nanak founded the Sikh religion in the Punjab region of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the 15th century and opposed many traditional practices like fasting, janeu, idolatry, caste system, ascetism, azan, economic materialism, and gender discrimination.

Chattar Singh Attariwalla, also spelt Chatar Singh Aṭārīvālā, was Governor of Hazara province and a military commander in the army of the Sikh Empire during the reign of Maharaja Duleep Singh in the Punjab. He fought in the Second Anglo-Sikh War against the British.

The Sikh Khalsa Army, also known as Khalsaji or simply Sikh Army, was the military force of the Sikh Empire. With its roots in the Khalsa founded by Guru Gobind Singh, the army was later modernised on Franco-British principles by Maharaja Ranjit Singh. It was divided in three wings: the Fauj-i-Khas (elites), Fauj-i-Ain and Fauj-i-Be Qawaid (irregulars). Due to the lifelong efforts of the Maharaja and his European officers, it gradually became a prominent fighting force of Asia. Ranjit Singh changed and improved the training and organisation of his army. He reorganized responsibility and set performance standards in logistical efficiency in troop deployment, manoeuvre, and marksmanship. He reformed the staffing to emphasize steady fire over cavalry and guerrilla warfare, improved the equipment and methods of war. The military system of Ranjit Singh combined the best of both old and new ideas. He strengthened the infantry and the artillery. He paid the members of the standing army from treasury, instead of the Mughal method of paying an army with local feudal levies.

Mulraj Chopra was the Diwan (governor) of Multan and leader of a Sikh rebellion against the British which led to the Second Anglo-Sikh War.

Sir Frederick Currie, 1st Baronet was a British diplomat, who had a distinguished career in the British East India Company and the Indian Civil Service. His posts included Foreign Secretary to the Government of India, Member of the Supreme Council of India, Resident at Lahore and Chairman of the East India Company.

Banda Singh Bahadur, was a Sikh warrior and a general of the Khalsa Army. At age 15, he left home to become an ascetic, and was given the name Madho Das Bairagi. He established a monastery at Nānded, on the bank of the river Godāvarī. In 1707, Guru Gobind Singh accepted an invitation to meet Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah I in southern India, he visited Banda Singh Bahadur in 1708. Banda became disciple of Guru Gobind Singh and was given a new name, Gurbaksh Singh(as written in Mahan Kosh), after the baptism ceremony. He is popularly known as Banda Singh Bahadur. He was given five arrows by the Guru as a blessing for the battles ahead. He came to Khanda, Sonipat and assembled a fighting force and led the struggle against the Mughal Empire.

Tej Singh was a Sikh commander in the Sikh Empire. He was appointed as Commander in chief of the Sikh Khalsa Army during the First Anglo-Sikh War.
Ilahi Bakhsh was a Muslim Punjabi Arain general who served in the Sikh Khalsa Fauj for over forty years and was regarded as one of the best artillery officers.