
There are 38 subspecies of Canis lupus listed in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World. These subspecies were named over the past 250 years, and since their naming, a number of them have gone extinct. The nominate subspecies is the Eurasian wolf.

The Arctic wolf, also known as the white wolf, polar wolf, and the Arctic grey wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to the High Arctic tundra of Canada's Queen Elizabeth Islands, from Melville Island to Ellesmere Island. Unlike some populations that move between tundra and forest regions, Arctic wolves spend their entire lives north of the northern treeline. Their distribution to south is limited to the northern fringes of the Middle Arctic tundra on the southern half of Prince of Wales and Somerset Islands. It is a medium-sized subspecies, distinguished from the northwestern wolf by its smaller size, its whiter colouration, its narrower braincase, and larger carnassials. Since 1930, there has been a progressive reduction in size in Arctic wolf skulls, which is likely the result of wolf-dog hybridization.

The Italian wolf, also known as the Apennine wolf, is a subspecies of the grey wolf native to the Italian Peninsula. It inhabits the Apennine Mountains and the Western Alps, though it is undergoing expansion towards the north and east. As of 2022 the wolf population within Italy is estimated to be 3,307 individuals. Although not universally recognised as a distinct subspecies, it nonetheless possesses a unique mtDNA haplotype and a distinct skull morphology.

The Great Plains wolf, also known as the buffalo wolf or loafer, is a subspecies of gray wolf that once extended throughout the Great Plains, from southern Manitoba and Saskatchewan in Canada southward to northern Texas in the United States. The subspecies was thought to be extinct in 1926, until studies declared that its descendants were found in Minnesota, Wisconsin and Michigan. They were described as a large, light-colored wolf but with black and white varying between individual wolves, with some all white or all black. The Native Americans of North Dakota told of how only three Great Plains wolves could bring down any sized bison.

The domestication of the dog was the process which led to the domestic dog. This included the dog's genetic divergence from the wolf, its domestication, and the emergence of the first dogs. Genetic studies suggest that all ancient and modern dogs share a common ancestry and descended from an ancient, now-extinct wolf population – or closely related wolf populations – which was distinct from the modern wolf lineage. The dog's similarity to the grey wolf is the result of substantial dog-into-wolf gene flow, with the modern grey wolf being the dog's nearest living relative. An extinct Late Pleistocene wolf may have been the ancestor of the dog.

The Iberian wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf. It inhabits the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, which includes northwestern Spain and northern Portugal. It is home to 2,200-2,700 wolves which have been isolated from mixing with other wolf populations for over a century. They form the largest wolf population in Western Europe.

Palaeoloxodon falconeri is an extinct species of dwarf elephant from the Middle Pleistocene of Sicily and Malta. It is amongst the smallest of all dwarf elephants at only 1 metre (3.3 ft) in height. A member of the genus Palaeoloxodon, it derived from a population of the mainland European straight-tusked elephant.

The Japanese wolf, also known as the Honshū wolf, is an extinct subspecies of the gray wolf that was once endemic to the islands of Honshū, Shikoku and Kyūshū in the Japanese archipelago.

The Himalayan wolf is a canine of debated taxonomy. It is distinguished by its genetic markers, with mitochondrial DNA indicating that it is genetically basal to the Holarctic grey wolf, genetically the same wolf as the Tibetan and Mongolian wolf, and has an association with the African wolf. No striking morphological differences are seen between the wolves from the Himalayas and those from Tibet. The Himalayan wolf lineage can be found living in Ladakh in the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the mountains of Central Asia predominantly above 4,000 m (13,000 ft) in elevation because it has adapted to a low-oxygen environment, compared with other wolves that are found only at lower elevations.

In the taxonomic treatment presented in the third (2005) edition of Mammal Species of the World, Canis lupus dingo is a taxonomic rank that includes both the dingo that is native to Australia and the New Guinea singing dog that is native to the New Guinea Highlands. It also includes some extinct dogs that were once found in coastal Papua New Guinea and the island of Java in the Indonesian Archipelago. In this treatment it is a subspecies of Canis lupus, the wolf, although other treatments consider the dog as a full species, with the dingo and its relatives either as a subspecies of the dog, a species in its own right, or simply as an unnamed variant or genetic clade within the larger population of dogs. The genetic evidence indicates that the dingo clade originated from East Asian domestic dogs and was introduced through the Malay Archipelago into Australia, with a common ancestry between the Australian dingo and the New Guinea singing dog. The New Guinea singing dog is genetically closer to those dingoes that live in southeastern Australia than to those that live in the northwest.
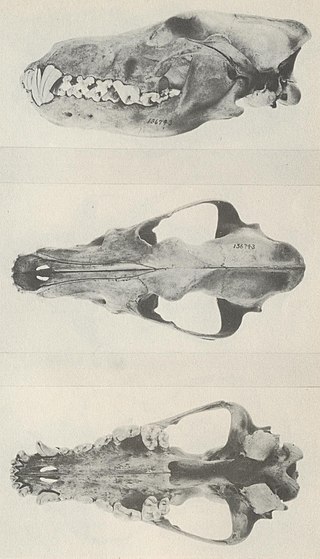
The Kenai Peninsula wolf, also known as the Kenai Peninsula grey wolf, is an extinct subspecies of the gray wolf that lived on the Kenai Peninsula in southern Alaska.

The British Columbia wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf which lives in a narrow region that includes those parts of the mainland coast and near-shore islands that are covered with temperate rain-forest, which extends from Vancouver Island, British Columbia, to the Alexander Archipelago in south-east Alaska. This area is bounded by the Coast Mountains.

The southern Rocky Mountain wolf is an extinct subspecies of gray wolf which was once distributed over southeastern Idaho, southwestern Wyoming, northeastern Nevada, Utah, western and central Colorado, northwestern Arizona, and northwestern New Mexico. It was a light-colored, medium-sized subspecies closely resembling the Great Plains wolf, though larger, with more blackish-buff hairs on the back. This wolf went extinct by 1935. Wolves of the subspecies Canis lupus occidentalis have now been reestablished in Idaho and Wyoming.

The Beringian wolf is an extinct population of wolf that lived during the Ice Age. It inhabited what is now modern-day Alaska, Yukon, and northern British Columbia. Some of these wolves survived well into the Holocene. The Beringian wolf is an ecomorph of the gray wolf and has been comprehensively studied using a range of scientific techniques, yielding new information on their prey species and feeding behaviors. It has been determined that these wolves are morphologically distinct from modern North American wolves and genetically basal to most modern and extinct wolves. The Beringian wolf has not been assigned a subspecies classification and its relationship with the extinct European cave wolf is not clear.

The Pleistocene coyote, also known as the Ice Age coyote, is an extinct subspecies of coyote that lived in western North America during the Late Pleistocene era. Most remains of the subspecies were found in southern California, though at least one was discovered in Idaho. It was part of a North American carnivore guild that included other canids like foxes, gray wolves, and dire wolves. Some studies suggest that the Pleistocene "coyote" was not in fact a coyote, but rather an extinct western population of the red wolf.

The Pleistocene wolf, also referred to as the Late Pleistocene wolf, is an extinct lineage or ecomorph of the grey wolf. It was a Late Pleistocene 129 Ka – early Holocene 11 Ka hypercarnivore. While comparable in size to a large modern grey wolf, it possessed a shorter, broader palate with large carnassial teeth relative to its overall skull size, allowing it to prey and scavenge on Pleistocene megafauna. Such an adaptation is an example of phenotypic plasticity. It was once distributed across the northern Holarctic. Phylogenetic evidence indicates that despite being much smaller than this prehistoric wolf, the Japanese wolf, which went extinct in the early 20th century, was of a Pleistocene wolf lineage, thus extending its survival to several millennia after its previous estimated extinction around 7,500 years ago.

The cave wolf is an extinct glacial mammoth steppe-adapted white wolf that lived during the Middle Pleistocene to the Late Pleistocene. It inhabited Europe, where its remains have been found in many caves. Its habitat included the mammoth steppe grasslands and boreal needle forests. This large wolf was short-legged compared to its body size, yet its leg size is comparable with that of the Arctic wolf C. l. arctos. Mitochondrial DNA analysis shows it to be more closely related to the domestic dog than the modern wolf, indicating possible ancestry.

The Paleolithic dog was a Late Pleistocene canine. They were directly associated with human hunting camps in Europe over 30,000 years ago and it is proposed that these were domesticated. They are further proposed to be either a proto-dog and the ancestor of the domestic dog or an extinct, morphologically and genetically divergent wolf population.

The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of at least 300 thousand years. The grey wolf Canis lupus is a highly adaptable species that is able to exist in a range of environments and which possesses a wide distribution across the Holarctic. Studies of modern grey wolves have identified distinct sub-populations that live in close proximity to each other. This variation in sub-populations is closely linked to differences in habitat – precipitation, temperature, vegetation, and prey specialization – which affect cranio-dental plasticity.

Canis mosbachensis is an extinct wolf that once inhabited Europe 600,000—420,000 years ago. The Mosbach wolf was a short-legged carcass feeder adapted for scavenging megafauna on the mammoth steppe. The Mosbach wolf is proposed as the ancestor of the grey wolf Canis lupus but some mammalogists have assigned it as the subspecies Canis lupus mosbachensis.























