The Battle of Adrianople, in which Gothic rebels defeated the Eastern Roman Empire, was the main battle of the Gothic War (376–382).

Valens was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half of the Roman Empire to rule. In 378, Valens was defeated and killed at the Battle of Adrianople against the invading Goths, which astonished contemporaries and marked the beginning of barbarian encroachment into Roman territory.

Year 376 (CCCLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valens and Augustus. The denomination 376 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 378 (CCCLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valens and Augustus. The denomination 378 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 370s decade ran from January 1, 370, to December 31, 379.
Fritigern was a Thervingian Gothic chieftain whose decisive victory at Adrianople during the Gothic War (376–382) led to favourable terms for the Goths when peace was made with Gratian and Theodosius I in 382.

The Battle of Adrianople, sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels led by Fritigern. The battle took place in the vicinity of Adrianople, in the Roman province of Thracia. It ended with an overwhelming victory for the Goths and the death of Emperor Valens.
Foederati were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as foedus, with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the socii, but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire.

The Russo-Turkish War of 1828–1829 was sparked by the Greek War of Independence of 1821–1829. War broke out after the Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II closed the Dardanelles to Russian ships and revoked the 1826 Akkerman Convention in retaliation for Russian participation in the Battle of Navarino.

This is a chronology of warfare between the Romans and various Germanic peoples. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings, later Germanic invasions of the Western Roman Empire that started in the late second century BC, and more. The series of conflicts was one factor which led to the ultimate downfall of the Western Roman Empire in particular and ancient Rome in general in 476.

Ciudad Rodrigo is a small cathedral city in the province of Salamanca, in western Spain, with a population in 2016 of 12,896. It is also the seat of a judicial district.
Alatheus and Saphrax were Greuthungi chieftains who served as co-regents for Vithericus, son and heir of the Gothic king Vithimiris.

Between 376 and 382 the Goths fought against the Eastern Roman Empire, one of several Gothic Wars in Roman history. This conflict included a catastrophic Roman defeat at the Battle of Adrianople, and is commonly seen as a part— albeit a part of disputed significance— of the century of events leading to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire.
Flavius Richomeres or Ricomer was a Frank who lived in the late 4th century. He took service in the Roman army and made a career as comes, magister militum, and consul. He was an uncle of the general Arbogastes. He is possibly to be identified with the Richomeres who married Ascyla, whose son Theodemer later became king of the Franks.
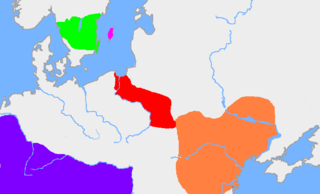
The Greuthungi were a Gothic people who lived on the Pontic steppe between the Dniester and Don rivers in what is now Ukraine, in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Tervingi, another Gothic people, who lived west of the Dniester River. To the east of the Greuthungi, living near the Don river, were the Alans.
Traianus was a Roman general under Emperor Valens, with whom he died in the battle of Adrianople.
Victor was a Roman military officer and politician, who served the emperors Constantius II, Julian, Jovian and Valens. He was appointed consul in AD 369, alongside Valentinianus Galates.
The Battle of Constantinople was a Gothic attack on Constantinople in 378 following the Gothic victory at the Battle of Adrianople. The emperor Valens's widow prepared the defence, and also reinforced the city with Arab warriors, who performed excellently in combat. It is said that the Goths were impressed when one of the Arab warriors stormed out of the city naked, slaughtered enemies, and drank blood from the neck of a decapitated Goth. Other sources maintain that the Goths actually abandoned the attack because they were greatly outnumbered.
Alavivus was a Gothic co-king of a group of Thervingi together with Fritigern. Along with the latter he led the migration of the Thervingi from Dacia across the Danube into the Roman Empire in the late 4th century AD. Upon arrival in the Roman Empire, the Goths suffered from widespread famine, with some Gothic parents reportedly being forced to sell their children into slavery in return for rotten dog meat in order to avoid starvation. In 376, Valens' lieutenant Lupicinus invited Alavivus and Fritigern to a banquet to discuss provisions for their people, where Alavivus was assassinated. Fritigern on the other hand managed to escape, inciting a revolt which culminated with a decisive Gothic victory at the Battle of Adrianople.
Sebastianus was a Roman general who died at the Battle of Adrianople alongside the Emperor Valens during the Gothic War.







