The Seleucid Empire was a Hellenistic kingdom in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC.

This article concerns the 200 BC decade, that lasted from 209 BC to 200 BC.
Year 208 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcellus and Crispinus. The denomination 208 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Antiochus III the Great was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in April/June 223 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, the Great, reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title Basileus Megas, the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome.

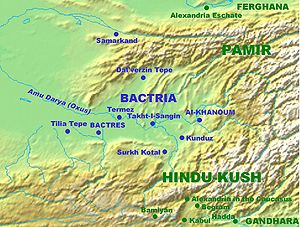
Euthydemus Ic. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a satrap of Sogdia, who usurped power from Diodotus II in 224 BC. Literary sources, notably Polybius, record how he and his son Demetrius resisted an invasion by the Seleucid king Antiochus III from 209 to 206 BC. Euthydemus expanded the Bactrian territory into Sogdia, constructed several fortresses, including the Derbent Wall in the Iron Gate, and issued a very substantial coinage.

Diodotus I Soter was the first Hellenistic king of Bactria. Diodotus was initially satrap of Bactria, but became independent of the Seleucid empire around 255 or 245 BCE, establishing the Diodotid Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, which endured in various forms until the beginning of the first century CE. In about 250 BCE, Diodotus repelled a Parthian invasion of Bactria by Arsaces. He also minted an extensive coinage and administered a powerful and prosperous new kingdom. He died around 235 BCE and was succeeded by his son Diodotus II.

Antiochus VII Euergetes, nicknamed Sidetes, also known as Antiochus the Pious, was ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire from July/August 138 to 129 BC. He was the last Seleucid king of any stature. After Antiochus was killed in battle, the Seleucid realm was restricted to Syria.

Demetrius I Anicetus, also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king, who ruled areas from Bactria to ancient northwestern India. He was the son of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom's ruler Euthydemus I and succeeded him around 200 BC, after which he conquered extensive areas in what is now southern Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan and India.

The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India. This kingdom was in existence from c. 200 BC to the beginning of the common era.

Diodotus II Theos was the son and successor of Diodotus I Soter, who rebelled against the Seleucid empire, establishing the Graeco-Bactrian Kingdom. Diodotus II probably ruled alongside his father as co-regent, before succeeding him as sole king around 235 BC. He prevented Seleucid efforts to reincorporate Bactria back into the empire, by allying with the Parthians against them. He was murdered around 225 BC by the usurper Euthydemus I, who succeeded him as king.

The Battle of Beth Zechariah was a battle around May 162 BC during the Maccabean revolt fought between Jewish rebels under the leadership of Judas Maccabeus against an army of the Seleucid Empire, the Greek successor state (diadochi) to the Macedonian conquests that controlled Syria and Babylonia. The battle was fought at Beth Zechariah and was a Seleucid victory, with the rebels driven from the field in retreat. Judas's brother Eleazar Avaran died in combat with a war elephant. The defeat allowed the Seleucids to continue their campaign and besiege the Jewish holy city of Jerusalem.

The Battle of the Arius was an engagement that was fought in 208 BC between the Seleucid Empire and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. The Seleucids were led by Antiochus III the Great, who launched an invasion of Bactria to recover his ancestor's past dominions. He would go on to be victorious in this battle, and would later go on to besiege the Bactrians at their capital of Bactra for three years.
Lysias was a 2nd-century BCE general and governor of Syria under the Seleucid Empire.

The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae, the Battle of Magnesia, and after Roman and Rhodian naval victories over the Seleucid navy.

The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of the few avenues into Egypt. These conflicts drained the material and manpower of both parties and led to their eventual destruction and conquest by Rome and Parthia. They are briefly mentioned in the biblical Books of the Maccabees.

The Roman–Seleucid war (192–188 BC), also called the Aetolian war, Antiochene war, Syrian war, and Syrian-Aetolian war was a military conflict between two coalitions, one led by the Roman Republic and the other led by the Seleucid king Antiochus III. The fighting took place in modern-day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea, and Asia Minor.

The Seleucid–Parthian wars were a series of conflicts between the Seleucid Empire and the Parthian Empire which resulted in the ultimate expulsion of the Seleucids from the Iranian Plateau and the surrounding regions. The wars were caused by the mass migration of the nomadic Iranian Parni tribe into Parthia and the establishment of the Parthian state, which challenged Seleucid hegemony.

The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Indian Subcontinent. It was founded in 256 BC by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter and lasted until its fall c. 120 BC with some cities still controlled by Greek kings as Hermaeus Soter in what is today Kabul. It was ruled by the Diodotid dynasty and the rival Euthydemid dynasty.

The Seleucid Dynastic Wars were a series of wars of succession that were fought between competing branches of the Seleucid royal household for control of the Seleucid Empire. Beginning as a by-product of several succession crises that arose from the reigns of Seleucus IV Philopator and his brother Antiochus IV Epiphanes in the 170s and 160s, the wars typified the final years of the empire and were an important cause of its decline as a major power in the Near East and Hellenistic world. The last war ended with the collapse of the kingdom and its annexation by the Roman Republic in 63 BC.

The Euthydemid dynasty was a Hellenistic dynasty founded by Euthydemus I in 230 BC which ruled the Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek kingdoms throughout the Hellenistic period from 230 BC to 10 AD, upon the death of its last ruler, Strato III in Gandhara.