
A chessboard is a gameboard used to play chess. It consists of 64 squares, 8 rows by 8 columns, on which the chess pieces are placed. It is square in shape and uses two colours of squares, one light and one dark, in a chequered pattern. During play, the board is oriented such that each player's near-right corner square is a light square.

Algebraic notation is the standard method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is based on a system of coordinates to uniquely identify each square on the board. It is used by most books, magazines, and newspapers.

Three-dimensional chess is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practice, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional chess has often appeared in science fiction—the Star Trek franchise in particular—contributing to the game's familiarity.
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like fork and pin. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants; for a list of terms general to board games, see Glossary of board games.
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts as it can be noted in the list of fairy chess pieces.
Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a standard plain text format for recording chess games, which can be read by humans and is also supported by most chess software.
Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position.
Chess notation systems are used to record either the moves made or the position of the pieces in a game of chess. Chess notation is used in chess literature, and by players keeping a record of an ongoing game. The earliest systems of notation used lengthy narratives to describe each move; these gradually evolved into more compact notation systems. Algebraic notation is now the accepted international standard, with several variants. Descriptive chess notation was used in English- and Spanish-language literature until the late 20th century, but is now obsolescent. Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a text file format based on English algebraic notation which can be processed by most chess software. Other notation systems include ICCF numeric notation, used for international correspondence chess, and systems for transmission using Morse code over telegraph or radio. The standard system for recording chess positions is Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN).
A Go game record is an archival record for a game of Go.
Fast Infoset is an international standard that specifies a binary encoding format for the XML Information Set as an alternative to the XML document format. It aims to provide more efficient serialization than the text-based XML format.
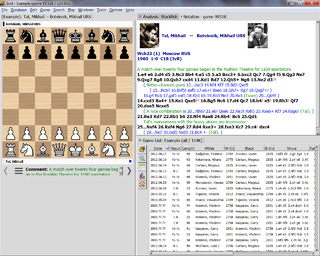
Shane's Chess Information Database (Scid) is a free and open source UNIX, Windows, Linux, and Mac application for viewing and maintaining large databases of chess games. It has features comparable to popular commercial chess software. Scid is written in Tcl/Tk and C++.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
Portable Draughts Notation (.PDN) is the standard computer-processable format for recording draughts games. This format is derived from Portable Game Notation, which is the standard chess format.
X-FEN is an extension of Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) introduced by Reinhard Scharnagl in 2003. It was designed to be able to represent all possible positions in Fischer random chess (FRC) and Capablanca random chess (CRC). It is fully backward compatible with FEN.
Sensei's Library is an Internet website and wiki, dedicated to articles about, and discussion of, the game of Go. It was started in September 2000, by the Go players Morten Pahle and Arno Hollosi. Hollosi is also known for designing version 4 of Anders Kierulf's popular SGF file format and for his work with the Austrian Citizen Card project.

There is an abundance of go software available to support players of the game of Go. This includes software programs that play Go themselves, programs that can be used to view and/or edit game records and diagrams, programs that allow the user to search for patterns in the games of strong players and programs that allow users to play against each other over the Internet.

Zillions of Games is a commercial general game playing system developed by Jeff Mallett and Mark Lefler in 1998. The game rules are specified with S-expressions, Zillions rule language. It was designed to handle mostly abstract strategy board games or puzzles. After parsing the rules of the game, the system's artificial intelligence can automatically play one or more players. It treats puzzles as solitaire games and its AI can be used to solve them.
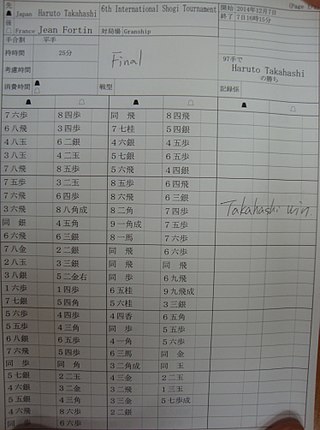
Shogi notation is the set of various abbreviatory notational systems used to describe the piece movements of a shogi game record or the positions of pieces on a shogi board.

A chess variant is a game related to, derived from, or inspired by chess. Such variants can differ from chess in many different ways.








