
The Klamath people are a Native American tribe of the Plateau culture area in Southern Oregon and Northern California. Today Klamath people are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes:

The Nez Perce are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who still live on a fraction of the lands on the southeastern Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest. This region has been occupied for at least 11,500 years.
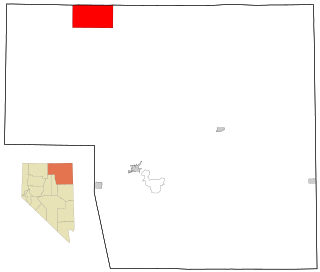
Owyhee is a census-designated place (CDP) in Elko County, Nevada, United States, along the banks of the Owyhee River. The population was 953 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Elko Micropolitan Statistical Area. It is the primary town of the federally recognized Shoshone-Paiute tribe's Duck Valley Indian Reservation, which covers portions of northern Nevada and southern Idaho, and the majority of its population are Native American.

The Northern Paiute people are a Numic tribe that has traditionally lived in the Great Basin region of the United States in what is now eastern California, western Nevada, and southeast Oregon. The Northern Paiutes' pre-contact lifestyle was well adapted to the harsh desert environment in which they lived. Each tribe or band occupied a specific territory, generally centered on a lake or wetland that supplied fish and waterfowl. Communal hunt drives, which often involved neighboring bands, would take rabbits and pronghorn from surrounding areas. Individuals and families appear to have moved freely among the bands.
The Shoshone or Shoshoni are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:

The Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin are Native Americans of the northern Great Basin, Snake River Plain, and upper Colorado River basin. The "Great Basin" is a cultural classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas and a cultural region located between the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada, in what is now Nevada, and parts of Oregon, California, Idaho, Wyoming, and Utah. The Great Basin region at the time of European contact was ~400,000 sq mi (1,000,000 km2). There is very little precipitation in the Great Basin area which affects the lifestyles and cultures of the inhabitants.
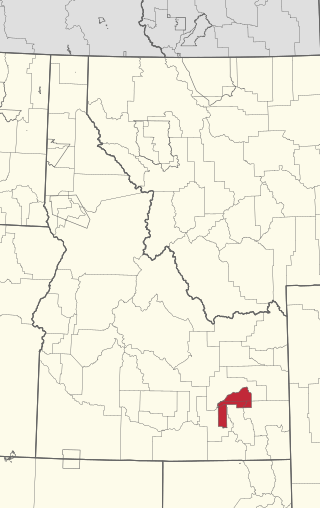
The Fort Hall Reservation is a Native American reservation of the federally recognized Shoshone-Bannock Tribes in the U.S. state of Idaho. This is one of five federally recognized tribes in the state. The reservation is located in southeastern Idaho on the Snake River Plain about 20 miles (32 km) north and west of Pocatello. It comprises 814.874 sq mi (2,110.51 km2) of land area in four counties: Bingham, Power, Bannock, and Caribou. To the east is the 60-mile-long (97 km) Portneuf Range; both Mount Putnam and South Putnam Mountain are located on the Fort Hall Reservation.
The Bannock War of 1878 was an armed conflict between the U.S. military and Bannock and Paiute warriors in Idaho and northeastern Oregon from June to August 1878. The Bannock totaled about 600 to 800 in 1870 because of other Shoshone peoples being included with Bannock numbers. they were led by Chief Buffalo Horn, who was killed in action on June 8, 1878. After his death, Chief Egan led the Bannocks. He and some of his warriors were killed in July by a Umatilla party that entered his camp in subterfuge.
The Snake War (1864–1868) was an irregular war fought by the United States of America against the "Snake Indians," the settlers' term for Northern Paiute, Bannock and Western Shoshone bands who lived along the Snake River. Fighting took place in the states of Oregon, Nevada, and California, and in Idaho Territory. Total casualties from both sides of the conflict numbered 1,762 dead, wounded, or captured.

Numic is the northernmost branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. It includes seven languages spoken by Native American peoples traditionally living in the Great Basin, Colorado River basin, Snake River basin, and southern Great Plains. The word Numic comes from the cognate word in all Numic languages for “person”, which reconstructs to Proto-Numic as. For example, in the three Central Numic languages and the two Western Numic languages it is. In Kawaiisu it is and in Colorado River, and.

The Bannock tribe were originally Northern Paiute but are more culturally affiliated with the Northern Shoshone. They are in the Great Basin classification of Indigenous People. Their traditional lands include northern Nevada, southeastern Oregon, southern Idaho, and western Wyoming. Today they are enrolled in the federally recognized Shoshone-Bannock Tribes of the Fort Hall Reservation of Idaho, located on the Fort Hall Indian Reservation.

Western Shoshone comprise several Shoshone tribes that are indigenous to the Great Basin and have lands identified in the Treaty of Ruby Valley 1863. They resided in Idaho, Nevada, California, and Utah. The tribes are very closely related culturally to the Paiute, Goshute, Bannock, Ute, and Timbisha tribes.

The Mono are a Native American people who traditionally live in the central Sierra Nevada, the Eastern Sierra, the Mono Basin, and adjacent areas of the Great Basin. They are often grouped under the historical label "Paiute" together with the Northern Paiute and Southern Paiute – but these three groups, although related within the Numic group of Uto-Aztecan languages, do not form a single, unique, unified group of Great Basin tribes.

Ute are the indigenous, or Native American people, of the Ute tribe and culture among the Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin. They had lived in sovereignty in the regions of present-day Utah and Colorado.

Winnemucca was a Northern Paiute war chief. He was born a Shoshone around 1820 in what would later become the Oregon Territory.

The Duck Valley Indian Reservation was established in the 19th century for the federally recognized Shoshone-Paiute Tribe. It is isolated in the high desert of the western United States, and lies on the state line, the 42nd parallel, between Idaho and Nevada.
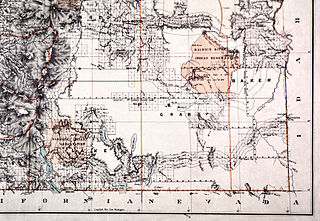
The Malheur Indian Reservation was an American Indian reservation established for the Northern Paiute in eastern Oregon and northern Nevada from 1872 to 1879. The federal government discontinued the reservation after the Bannock War of 1878, under pressure from European-American settlers who wanted the land. This negative recommendation against continuing by its agent William V. Rinehart, led to the internment of more than 500 Paiute on the Yakama Indian Reservation, as well as the reluctance of the Bannock and Paiute to return to the lands after the war.

Eastern Shoshone are Shoshone who primarily live in Wyoming and in the northeast corner of the Great Basin where Utah, Idaho and Wyoming meet and are in the Great Basin classification of Indigenous People. They lived in the Rocky Mountains during the 1805 Lewis and Clark Expedition and adopted Plains horse culture in contrast to Western Shoshone that maintained a Great Basin culture.

Northern Shoshone are Shoshone of the Snake River Plain of southern Idaho and the northeast of the Great Basin where Idaho, Wyoming and Utah meet. They are culturally affiliated with the Bannock people and are in the Great Basin classification of Indigenous People.

The Fort McDermitt Paiute and Shoshone Tribe is a federally recognized tribe of Northern Paiute and Western Shoshone peoples, whose reservation Fort McDermitt Paiute and Shoshone Tribes of the Fort McDermitt Indian Reservation spans the Nevada and Oregon border next to Idaho. The reservation has 16,354 acres (6,618 ha) in Nevada and 19,000 acres (7,700 ha) in Oregon.


















