Related Research Articles

Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases, and the affix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.
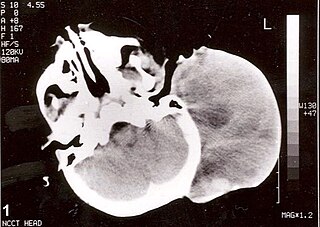
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts.

Liposarcomas are the most common subtype of soft tissue sarcomas, accounting for at least 20% of all sarcomas in adults. Soft tissue sarcomas are rare neoplasms with over 150 different histological subtypes or forms. Liposarcomas arise from the precursor lipoblasts of the adipocytes in adipose tissues. Adipose tissues are distributed throughout the body, including such sites as the deep and more superficial layers of subcutaneous tissues as well as in less surgically accessible sites like the retroperitoneum and visceral fat inside the abdominal cavity.

A synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma.

Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue, causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells.

Nodular fasciitis (NF) is a benign, soft tissue tumor composed of myofibroblasts that typically occurs in subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and/or muscles. The literature sometimes titles rare NF variants according to their tissue locations. The most frequently used and important of these are: cranial fasciitis and intravascular fasciitis. In 2020, the World Health Organization classified nodular fasciitis as in the category of benign fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumors. NF is the most common of the benign fibroblastic proliferative tumors of soft tissue and exceeds in frequency any other tumor or tumor-like lesion in this group of tumors.
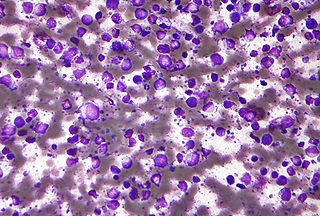
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a cancer of B cells, a type of lymphocyte that is responsible for producing antibodies. It is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among adults, with an annual incidence of 7–8 cases per 100,000 people per year in the US and UK. This cancer occurs primarily in older individuals, with a median age of diagnosis at ~70 years, although it can occur in young adults and, in rare cases, children. DLBCL can arise in virtually any part of the body and, depending on various factors, is often a very aggressive malignancy. The first sign of this illness is typically the observation of a rapidly growing mass or tissue infiltration that is sometimes associated with systemic B symptoms, e.g. fever, weight loss, and night sweats.
An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous. In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word fibroma for benign tumors and assigns the word fibrosarcoma to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved.
In medicine, histiocytosis is an excessive number of histiocytes, and the term is also often used to refer to a group of rare diseases which share this sign as a characteristic. Occasionally and confusingly, the term "histiocytosis" is sometimes used to refer to individual diseases.

Digital pathology is a sub-field of pathology that focuses on data management based on information generated from digitized specimen slides. Through the use of computer-based technology, digital pathology utilizes virtual microscopy. Glass slides are converted into digital slides that can be viewed, managed, shared and analyzed on a computer monitor. With the practice of Whole-Slide Imaging (WSI), which is another name for virtual microscopy, the field of digital pathology is growing and has applications in diagnostic medicine, with the goal of achieving efficient and cheaper diagnoses, prognosis, and prediction of diseases due to the success in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
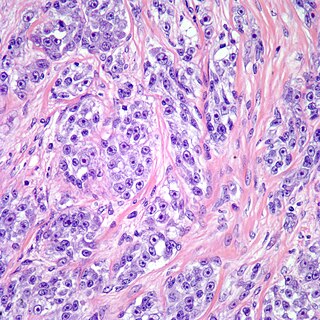
Clear cell sarcoma is a rare form of cancer called a sarcoma. It is known to occur mainly in the soft tissues and dermis. Rare forms were thought to occur in the gastrointestinal tract before they were discovered to be different and redesignated as GNET.
A mixed tumor is a tumor that derives from multiple tissue types. A biplastic tumor or biphasic tumor has two tissue types.
Sharon Ann Whelan Weiss is an American pathologist who is best known for her contribution to the subspecialty of soft tissue pathology. She is the main author of Soft Tissue Tumors, one of the most widely used textbooks in the field of sarcoma and soft tissue pathology. She is also well known for her seminal descriptions of multiple soft tissue tumors, such as epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor of soft parts among others. She has also mentored and trained other well-known soft tissue pathologists.

Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) is a rare type of low-grade sarcoma first described by H. L. Evans in 1987. LGFMS are soft tissue tumors of the mesenchyme-derived connective tissues; on microscopic examination, they are found to be composed of spindle-shaped cells that resemble fibroblasts. These fibroblastic, spindle-shaped cells are neoplastic cells that in most cases of LGFMS express fusion genes, i.e. genes composed of parts of two different genes that form as a result of mutations. The World Health Organization (2020) classified LGFMS as a specific type of tumor in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.

Mammary-type myofibroblastoma (MFB), also named mammary and extramammary myofibroblastoma, was first termed myofibrolastoma of the breast, or, more simply, either mammary myofibroblastoma (MMFB) or just myofibroblastoma. The change in this terminology occurred because the initial 1987 study and many subsequent studies found this tumor only in breast tissue. However, a 2001 study followed by numerous reports found tumors with the microscopic histopathology and other key features of mammary MFB in a wide range of organs and tissues. Further complicating the issue, early studies on MFB classified it as one of various types of spindle cell tumors that, except for MFB, were ill-defined. These other tumors, which have often been named interchangeably in different reports, are: myelofibroblastoma, benign spindle cell tumor, fibroma, spindle cell lipoma, myogenic stromal tumor, and solitary stromal tumor. Finally, studies suggest that spindle cell lipoma and cellular angiofibroma are variants of MFB. Here, the latter two tumors are tentatively classified as MFB variants but otherwise MFB is described as it is more strictly defined in most recent publications. The World Health Organization, 2020, classified mammary type myofibroblastoma tumors and myofibroblastoma tumors as separate tumor forms within the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.

The histopathology of colorectal cancer of the adenocarcinoma type involves analysis of tissue taken from a biopsy or surgery. A pathology report contains a description of the microscopical characteristics of the tumor tissue, including both tumor cells and how the tumor invades into healthy tissues and finally if the tumor appears to be completely removed. The most common form of colon cancer is adenocarcinoma, constituting between 95% to 98% of all cases of colorectal cancer. Other, rarer types include lymphoma, adenosquamous and squamous cell carcinoma. Some subtypes have been found to be more aggressive.
Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma (AMSF), also termed myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma (MSF), is a rare, low-grade, soft tissue tumor that the World Health Organization (2020) classified as in the category of rarely metastasizing fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. It is a locally aggressive neoplasm that often recurs at the site of its surgical removal. However, it usually grows slowly and in only 1-2% of cases spreads to distant tissues.
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.
The FET protein family the EWSR1 protein encoded by the EWSR1 gene located at band 12.2 of the long arm of chromosome 22; 2) the FUS protein encoded by the FUS gene located at band 16 on the short arm of chromosome 16; and 3) the TAF15 protein encoded by the TAF15 gene located at band 12 on the long arm of chromosome 7 The FET in this protein family's name derives form the first letters of FUS, EWSR1, and TAF15.
Cellular angiofibroma (CAF) is a rare, benign tumor of superficial soft tissues that was first described by M. R. Nucci et al. in 1997. These tumors occur predominantly in the distal parts of the female and male reproductive systems, i.e. in the vulva-vaginal and inguinal-scrotal areas, respectively, or, less commonly, in various other superficial soft tissue areas throughout the body. CAF tumors develop exclusively in adults who typically are more than 30 years old.
References
- ↑ Kuhn, Karin J.; Cloutier, Jeffrey M.; Boutin, Robert D.; Steffner, Robert; Riley, Geoffrey (2021-01-01). "Soft tissue pathology for the radiologist: a tumor board primer with 2020 WHO classification update". Skeletal Radiology. 50 (1): 29–42. doi:10.1007/s00256-020-03567-w. ISSN 1432-2161.
- ↑ Folpe, Andrew L. (2020-01-01). ""Hey! Whatever happened to hemangiopericytoma and fibrosarcoma?" An update on selected conceptual advances in soft tissue pathology which have occurred over the past 50 years". Human Pathology. 95: 113–136. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2019.10.001. ISSN 0046-8177.
- ↑ Folpe, Andrew L. (January 2022). "'I Can't Keep Up!': an update on advances in soft tissue pathology occurring after the publication of the 2020 World Health Organization classification of soft tissue and bone tumours". Histopathology. 80 (1): 54–75. doi:10.1111/his.14460. ISSN 1365-2559. PMID 34958510.