
A bulletproof vest, also known as a ballistic vest or a bullet-resistant vest, is an item of body armour that helps absorb the impact and reduce or stop penetration to the torso by firearm-fired projectiles and fragmentation from explosions. The vest may come in a soft form, as worn by many police officers, prison officers, security guards, and some private citizens, used to protect against stabbing attacks or light projectiles, or hard form, using metallic or para-aramid components. Soldiers and police tactical units wear hard armour, either in conjunction with soft armour or alone, to protect against rifle ammunition or fragmentation.
The Interceptor Multi-Threat Body Armor System (IBA) is a bullet-resistant body armor system that was used by the United States Armed Forces during the 2000s, with some limited usage into the mid-2010s. IBA and its design replaced the older standardized fragmentation protective Personnel Armor System for Ground Troops (PASGT) body armor system that was designed in the late 1970s and introduced in the early 1980s.

Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment, or MOLLE, is the current generation of load-bearing equipment and backpacks used by a number of NATO armed forces, especially the British Army and the United States Army.

Personal Load Carrying Equipment (PLCE) is one of several tactical webbing systems of the British Armed Forces. Dependent upon the year of design, and the decade of introduction, the webbing system was named and is commonly referred to as the 85 Pattern, the 90 Pattern or the 95 Pattern webbing.

The Small Arms Protective Insert (SAPI) is a ceramic ballistic plate used by the United States Armed Forces. It was first used in the Ranger Body Armor and Interceptor Body Armor, both are ballistic vests. It is now also used in the Improved Outer Tactical Vest as well as the Modular Tactical Vest, in addition to commercially available "plate carriers". The Kevlar Interceptor vest itself is designed to stop projectiles up to and including 9×19mm Parabellum submachine gun rounds, in addition to fragmentation. To protect against higher-velocity rifle rounds, SAPI plates are needed.
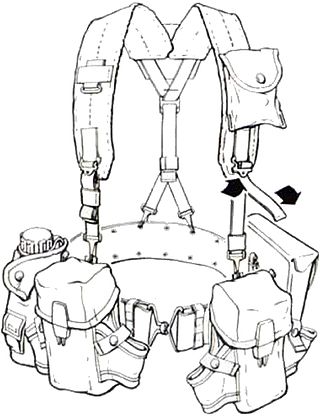
The All-Purpose Lightweight Individual Carrying Equipment (ALICE) is a set of load-carrying equipment adopted as United States Army Standard A on 17 January 1973 to replace the M-1956 Individual Load-Carrying Equipment (ILCE) and M-1967 Modernized Load-Carrying Equipment (MLCE). Although since superseded by MOLLE, ALICE gear is still in some limited use with the U.S. Army National Guard, State Guard, also some ground units of the Navy and Air Force.

The IIFS was introduced in 1988, to serve as a fighting and existence carrying system—a possible replacement for the All-purpose Lightweight Individual Carrying Equipment employed and fielded by United States Armed Forces since 1973.

The Modular Tactical Vest is a ballistic vest originally adopted by the United States Marine Corps in 2006. The MTV was designed as a solution to shortcomings in the Interceptor Body Armor (IBA) and was selected after a rigorous proposal and examination process by the Marine Corps. The MTV provides better protection levels than the IBA, although it uses the same Small Arms Protective Insert (SAPI) plates. The MTV weighs 30 pounds (14 kg), three pounds more than the IBA, but is designed to more effectively distribute its weight throughout the wearer's torso.

CIRAS is a modular protective vest designed for US Special Operations Forces by Eagle Industries. The vest is currently the new FSBE II system and has replaced the FSBE AAVs. It features PALS webbing, making it MOLLE-compatible and allowing the attachment of various pouches or accessories. Two versions of the vest are available, known as the "land" and "maritime" versions. The vest consists of front and rear panels with pockets for BALCS or SPEAR-cut soft armor panels and standard-issue SAPI plates. This gives the wearer up to NIJ Level IV protection on the front and back and Level IIIA protection on the sides. On the lower rear side of the front of the vest, there are two quick-releasable buckles for attaching groin protection. The wearer's sides are covered by an external cummerbund, which is also covered with PALS webbing. The vest body is constructed of 1000-denier Cordura Nylon, and the interior is lined with heavy-duty mesh to aid in cooling the wearer.

Ranger Body Armor (RBA) is a US military-issue ballistic vest that was designed for, and used chiefly by, US Army 75th Ranger Regiment operators ("Rangers") in the 1990s and 2000s. The RBA system has since been replaced by other specialized body armor systems adopted by the United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM).
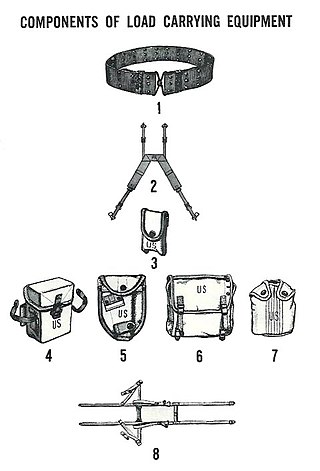
The M-1956 Load-Carrying Equipment (LCE), also known as the Individual Load-Carrying Equipment (ILCE), was developed by the U.S. Army and first issued in the early 1960s. The M-1956 LCE was designed to replace the M-1945 Combat Pack, the M-1923 cartridge belt, the M-1936 pistol belt and the M-1937 BAR magazine belt. The M-1956 LCE was designed to be quickly configured, using no tools, to accommodate various mission and ammunition loads. The M-1956 LCE remained in service through the 1980s and set the standard for future United States military load-carrying equipment.

Osprey body armour is a system of body armour used by the British Armed Forces. The system is in its fourth iteration following extensive development and engagement with front line users.

The Improved Outer Tactical Vest (IOTV) is an enhanced version of, and a replacement for, the older Outer Tactical Vest (OTV) component of the Interceptor Multi-Threat Body Armor System, as fielded by the United States Army beginning in the mid-2000s. The IOTV is compatible with the Deltoid and Axillary Protector System (DAPS) components, ESAPI, Enhanced Side Ballistic Inserts (ESBI), as well as the OTV's groin protector. It has a flame-resistant standalone shirt, the Army Combat Shirt (ACS), designed specifically for use with the IOTV.

The Pouch Attachment Ladder System or PALS is a grid of webbing invented and patented by United States Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center used to attach smaller equipment onto load-bearing platforms, such as vests and backpacks. It was first used on MOLLE rucksacks, but is now found on a variety of tactical equipment, such as the U.S. Improved Outer Tactical Vest, Interceptor body armor, USMC Improved Load Bearing Equipment backpack and Modular Tactical Vest. It is used to attach items such as holsters, magazine pouches, radio pouches, knife sheathes, and other gear. A wide variety of pouches are commercially available, allowing soldiers to customize their kit. There is also a variety of attachment methods including the Alice Clip, the Natick snap, and soft, interwoven straps. The PALS system has begun to be adopted by other forces, such as the British Army, who use it on their Osprey body armor.
The Amphibious Assault Vest, Quick-Release, or FSBE AAV QR, is a light-weight assault vest system that incorporates both protection and cargo retention. Protection includes soft armor coupled with hard ballistic inserts. Cargo retention capabilities include various pouches and pockets attached via standard PALS webbing. The entire FSBE kit includes the vest body, a throat protector, a groin protector and an assortment of load bearing pouches. A fully loaded vest with armor plates can prove quite heavy, and is typically used only in high-risk direct action (DA) missions.

The Scalable Plate Carrier (SPC) is a plate carrier used by the United States Marine Corps as an alternative to the heavier Modular Tactical Vest (MTV).
Family of Improved Load Bearing Equipment (FILBE) is a series of equipment used by the United States Marine Corps for personal load carrying. It comprises the backpack and various attachments carried by an individual Marine in the field. The FILBE was designed as an improvement over the prior ILBE system that was not compatible with the newest body armor systems.

The Modular Scalable Vest (MSV) is a bullet-resistant vest that has been introduced by the United States Armed Forces in 2018.

6B45 is a standard ballistic vest of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. It is a part of Ratnik infantry combat system. It was adopted in 2014 as a replacement for the 6B23 vest. 6B45 vest has been developed by Techinkom company located in Saint Petersburg.
















