
Southern Iran consists of the southern mountain ranges of Zagros and Central Iranian Range, Khuzestan Plain and the northern coasts of Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz.

Southern Iran consists of the southern mountain ranges of Zagros and Central Iranian Range, Khuzestan Plain and the northern coasts of Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz.
It includes the provinces of Fars, Kohgiluyeh and Buyer Ahmad, Hormozgan and Bushehr. Sometimes Khuzestan and Kerman are also included in this region. The major cities in the region are Shiraz, Bandarabbas, Bushehr, Marvdasht, Jahrom, Yasuj, Fasa and Borazjan. [1]
Southern Iran is ethnically diverse, including Persians, Lurs, Bakhtiaris, Qashqais, Achomians, Basseries, Baloch, Arabs, Armenians, and Jews. Southern Iran is the homeland of the Persian people. Most people in southern Iran are ethnically Persian (including Persian subgroups like Lurs and Bakhtiaris).
Most people in Southern Iran are part of the Iranian ethno-linguistic group and speak an Iranian language. [2]

Geographically, the country of Iran is located in West Asia and borders the Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf, and Gulf of Oman. Topographically, it is predominantly located on the Persian Plateau. Its mountains have impacted both the political and the economic history of the country for several centuries. The mountains enclose several broad basins, on which major agricultural and urban settlements are located. Until the 20th century, when major highways and railroads were constructed through the mountains to connect the population centers, these basins tended to be relatively isolated from one another.
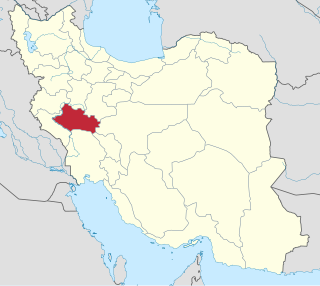
Lorestan province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the western part of the country in the Zagros Mountains and covers an area of 28,392 km2. Its capital is the city of Khorramabad. At the time of the National Census in 2006, the province had a population of 1,689,650 in 382,805 households. The 2011 national census counted 1,754,243 residents in 462,260 households. In 2014 it was placed in Region 4. At the most recent census in 2016, the population of Lorestan province had risen to 1,760,649 inhabitants in 509,025 households.

Khuzestan province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Located in the southwest of the country, the province borders Iraq and the Persian Gulf. Its capital is Ahvaz and it covers an area of 63,238 square kilometres (24,416 sq mi). Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's Region 4.

The Zagros Mountains are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of 1,600 km (990 mi). The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues southeast under also the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highlands, the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at 4,409 metres (14,465 ft).
This article focuses on the status of ethnic minorities in contemporary Iran.

The Bakhtiari are a Lur tribe from Iran. They speak the Bakhtiari dialect of the Luri language.

Luri is a Southwestern Iranian language continuum spoken by the Lurs, an Iranian people native to Western Asia. The Luri dialects are descended from Middle Persian and are Central Luri, Bakhtiari, and Southern Luri. This language is spoken mainly by the Bakhtiari and Southern Lurs in Iran.
Iran has been divided into regions in a number of different ways historically. It has been divided into five administrative regions since 2014.

Borujerd, also Romanized as Borūjerd, is a city in the Central District of Borujerd County, Lorestan province in western Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.

Khuzestan province is located in southwestern Iran. Its history extends from the pre-Aryan ancient Elamite civilization to the modern-day Islamic Republic.
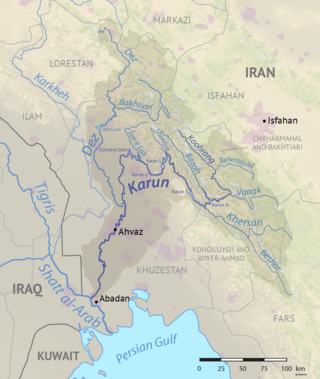
The Karun is the Iranian river with the highest water flow, and the country's only navigable river. It is 950 km (590 mi) long. The Karun rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tributaries, such as the Dez and the Kuhrang. It passes through the capital of the Khuzestan Province of Iran, the city of Ahvaz, before emptying to its mouth into Arvand Rud.

Bakhtiari dialect is a distinct dialect of Southern Luri spoken by Bakhtiari people in Chaharmahal-o-Bakhtiari, Bushehr, eastern Khuzestan and parts of Isfahan and Lorestan provinces. It is closely related to the Boir-Ahamadi, Kohgiluyeh, and Mamasani dialects in northwestern Fars. These dialects, together with the Lori dialects of Lorestan, are referred to as the “Perside” southern Zagros group, or Lori dialects. Luri and Bakhtiari are much more closely related to Persian than Lurish." Dialects of Farsi spoken in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province are mutually intelligible with Bakhtiari.

The Lurs are an Iranian people living in western Iran. The four Luri branches are the Bakhtiari, Mamasani, Kohgiluyeh and Lur proper, who are principally linked by the Luri language.
Dasht, Dasht-e, Dashhti (دشتی), or Dasht-i, are Persian words for "plain" or "plain of", and may refer to:
The majority of the population of Iran consists of Iranic peoples. The largest groups in this category include Persians and Kurds, with smaller communities including Gilakis, Mazandaranis, Lurs, Tats, Talysh, and Baloch.

Sheikh Khazal rebellion refers to the 1924 Arab separatist uprising by Khazal al-Kabi, the Sheikh of Muhammara, in Iranian Khuzestan. The rebellion was quickly and efficiently suppressed by Reza Shah with minimal casualties, subduing the Bakhtiari tribes allied with Sheikh Khazal and resulting in his surrender and the end of Arab autonomy in Khuzestan.

Southern Lurs are a large part of Lurs who natively speak the Southern Luri language a branch of Western Iranian languages, and are an Iranian people. They occupy some regions in Southwest of Iran including Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad (fully), Sotheastern parts of Khuzestan Northwestern parts of Fars, and Western parts of Bushehr Province.
Lurs are an Iranian people living mainly in western and southwestern Iran. There is also a significant population of Lurs in eastern and central parts of Iraq The word Luristan or Lorestan, is attributed to the areas inhabited by the Lurs. The boundaries of Luristan stretch from the eastern Iraqi plains to the west and southwest of Iran. Today, Lorestan is the name of one of the western provinces of Iran.

Fars territory or Ancient Persia in the southern part of Iran leading to the Persian Gulf, which has historical, continental, cultural and especially dialectal commonalities and includes the provinces of Khuzestan, Fars, Esfahan, Bushehr, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, Hormozgan and Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari and the western part of Kerman Province, which is known as the origin of Persian language and inherited from Middle Persian. Which is still culturally and linguistically distinct to this day.
The 2021 Iranian water protests were a series of protests by Iranians against water shortages in Khuzestan province during the summer. Protests broke out on 15 July 2021 due to the ongoing water crisis in Iran but spread across the country to other provinces and cities where people organised rallies in solidarity with Khuzestan, including Tehran, Kermanshah, Isfahan, Bushehr, Lorestan, Kurdistan, East Azerbaijan, North Khorasan and Alborz. Protests were soon dubbed 'The Uprising of the Thirsty" and turned violent as police forces attempted to suppress them due to demands for the end of the current regime. Casualties were recorded both amongst police forces and civilian demonstrators. Protests in Khuzestan lasted for around 10 days and were predominantly urban. The last large-scale demonstration in solidarity with Khuzestan took place on 31 July in Tehran. The violent nature of the protests received a lot media-attention and various government officials made statements promising extended and specific support to the region. This included releasing more water from Karkheh Dam in northern Khuzestan and sending emergency water tanks to most affected regions.