
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells.

Demosponges (Demospongiae) are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include greater than 90% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide. They are sponges with a soft body that covers a hard, often massive skeleton made of calcium carbonate, either aragonite or calcite. They are predominantly leuconoid in structure. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges. Some species, in particular from the Antarctic, obtain the silica for spicule building from the ingestion of siliceous diatoms.

Anheteromeyenia argyrosperma is a freshwater sponge found across North America.

Xestospongia testudinaria is a species of barrel sponge in the family Petrosiidae. More commonly known as Giant Barrel Sponges, they have the basic structure of a typical sponge. Their body is made of a reticulation of cells aggregate on a siliceous scaffold composed of small spikes called spicules. Water is taken into the inner chamber of the sponge through ostia. Flagellated choanocytes line the inner chamber and help generate water currents through the sponge.
Arturia canariensis, commonly known as the yellow calcareous sponge, is a species of sponge in the family Clathrinidae. It is found in shallow seas in the Canary Islands, Cape Verde, the Adriatic Sea and the Caribbean Sea. The specific epithet "canariensis" was given to this species because it was first described from Lanzarote in the Canary Islands.

Spongilla lacustris is a species of freshwater sponge from the family Spongillidae. It inhabits freshwater rivers and lakes, often growing under logs or rocks. Lacustris is a Latin word meaning "related to or associated with lakes". The species ranges from North America to Europe and Asia. It is the most common freshwater sponge in central Europe. It is the most widespread sponge in Northern Britain, and is one of the most common species of sponges in lakes and canals. Spongilla lacustris have the ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. They become dormant during winter. The growth form ranges from encrusting, to digitate, to branched, depending upon the quality of the habitat.

Callyspongia (Cladochalina) aculeata, commonly known as the branching vase sponge is a species of sea sponge in the family Callyspongiidae. Poriferans are typically characterized by ostia, pores that filter out plankton, with an osculum as the opening which water leaves through, and choanocytes trap food particles.

Spongilidae is a family of sponges that live in freshwater lakes and rivers. The following genera are recognized in the family:
Radiospongilla sceptroides is a species of freshwater sponge in the family Spongillidae. It was described as Spongilla sceptroides by Scottish-born Australian zoologist William A. Haswell in 1883, who discovered it growing on submerged wood in a pond in the vicinity of Brisbane. He described it as "Sponge green, encrusting, smooth, moderately elastic, not crumbling." He noted the spicules were fusiform and pointed. It was found growing next to a yellowish freshwater sponge that he described as Spongilla botryoides. A 1968 review of freshwater sponges failed to locate Haswell's original type specimen, so a new one was selected from the Merrika River near Womboyn in New South Wales.
Suberites ficus is a species of sponge in the family Suberitidae. It is sometimes known as the fig sponge or orange sponge.

Tectitethya crypta is a species of demosponge belonging to the family Tethyidae. Its classified family is characterized by fourteen different known genera, one of them being Tectitethya. It is a massive, shallow-water sponge found in the Caribbean Sea. This sponge was first discovered by Werner Bergmann in 1945 and later classified by de Laubenfels in 1949. It is located in reef areas situated on softer substrates such as sand or mud. Oftentimes, it is covered in sand and algae. This results in an appearance that is cream colored/ gray colored; however, when the animal is washed free of its sediment coverings, its body plan appears more green and gray. It's characterized with ostia peaking out of its body cavity, with the ability to abruptly open or close, changing its desired water flow rate through its mesohyl.
Agelas schmidti, commonly known as the brown tubular sponge, is a species of demosponge. It occurs at moderate depths in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea and often has a colonial coral growing over the surface. The type locality is Puerto Rico.
Neofibularia nolitangere, commonly known as the touch-me-not sponge, is a species of sea sponge in the family Biemnidae. It is found in shallow waters in the Western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.

Callyspongia truncata is a species of marine sea sponge. Like all marine sponges, C. truncata is a member of phylum Porifera and is defined by its filter-feeding lifestyle and flagellated choanocytes, or collar cells, that allow for water movement and feeding. It is a species of demosponge and a member of Demospongiae, the largest class of sponges as well as the family Callyspongiidae. C. truncata is most well known for being the organism from which the polyketide Callystatin A was identified. Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of antibiotics. It was first isolated in 1997 from this organism, which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Recent studies have revealed numerous other bioactive compounds that have been found in this species.

Arturia is a genus of calcareous sponge in the family Clathrinidae which contains 14 species. It is named after Arthur Dendy, a prominent researcher of calcareous sponges. It was renamed Arturia in 2017 because the name Arthuria was already assigned to a genus of molluscs.
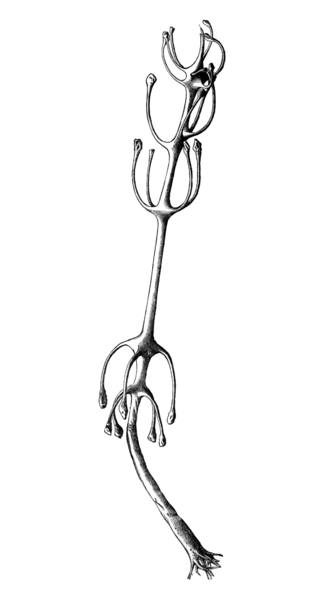
Chondrocladia concrescens is a species of deep-sea carnivorous sponge in the family Cladorhizidae. It is commonly known as the "ping pong tree sponge" due to its distinctive tree-like shape with multiple branches. The species is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean and can grow up to one meter in height.

Pachydictyum is a genus of freshwater sponge in the family Malawispongiidae. It is monotypic and represented by a single species, Pachydictyum globosum. It lives in Sulawesi, Indonesia.

Lubomirskiidae is a family of freshwater sponges from Lake Baikal in Russia.
Calcifibrospongiidae is a family of sponges belonging to the order Haplosclerida. The order Haplosclerida is distinguished by isodictyal skeleton. In general, Porifera are basal animals with bodies full of pores and channels. Calcifibrospongiidae includes the species Calcifibrospongia actinostromarioides. There have only been ten recorded occurrences of this species: in Hogsty Reef and San Salvador, as well as in the subtropics of the Bahamas.













