
William Jefferson Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again from 1983 to 1992, and as attorney general of Arkansas from 1977 to 1979. A member of the Democratic Party, Clinton became known as a New Democrat, as many of his policies reflected a centrist "Third Way" political philosophy. He is the husband of Hillary Clinton, who was a U.S. senator from New York from 2001 to 2009, secretary of state from 2009 to 2013 and the Democratic nominee for president in the 2016 presidential election.
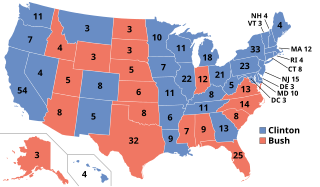
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush, independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas, and a number of minor candidates. The election marked the end of a period of Republican dominance in American presidential politics that began in 1968, and also marked the end of 12 years of Republican rule of the White House, as well as the end of the Greatest Generation's 32-year American rule and the beginning of the Baby boomers 28-year dominance until 2020. It was the last time the incumbent president failed to win a second term until 2020, when Donald Trump lost the election to Joe Biden; it was the first such occurrence since 1980.

The Bush Doctrine refers to multiple interrelated foreign policy principles of the 43rd President of the United States, George W. Bush. These principles include unilateralism, preemptive war, and regime change.

The Reagan Doctrine was stated by United States President Ronald Reagan in his State of the Union address on February 6, 1985: "We must not break faith with those who are risking their lives—on every continent from Afghanistan to Nicaragua—to defy Soviet-supported aggression and secure rights which have been ours from birth." It was a strategy implemented by the Reagan Administration to overwhelm the global influence of the Soviet Union in the late Cold War. The doctrine was a centerpiece of United States foreign policy from the early 1980s until the end of the Cold War in 1991.

The 2008 United States presidential election was the 56th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 2008. The Democratic ticket of Barack Obama, the junior senator from Illinois, and Joe Biden, the senior senator from Delaware, defeated the Republican ticket of John McCain, the senior senator from Arizona, and Sarah Palin, the governor of Alaska. Obama became the first African American to be elected to the presidency, as well as being only the third sitting United States senator elected president, joining Warren G. Harding and John F. Kennedy. Meanwhile, Biden became the first senator running mate of a senator elected president since Lyndon B. Johnson in the 1960 election. This is the only election where both major party nominees were sitting Senators.
Steven E. Schier is a professor of political science at Carleton College who specializes in American politics. He earned a BA at Simpson College and his MA and PhD degrees from the University of Wisconsin.

In political studies, surveys have been conducted in order to construct historical rankings of the success of the presidents of the United States. Ranking systems are usually based on surveys of academic historians and political scientists or popular opinion. The scholarly rankings focus on presidential achievements, leadership qualities, failures and faults. Popular-opinion polls typically focus on recent or well-known presidents.

In politics, triangulation is a strategy associated with U.S. president Bill Clinton in the 1990s. The politician presents a position as being above or between the left and right sides of a democratic political spectrum. It involves adopting for oneself some of the ideas of one's political opponent. The logic behind it is that it both takes credit for the opponent's ideas, and insulates the triangulator from attacks on that particular issue.
This bibliography of George W. Bush is a list of published works, both books and films, about George W. Bush, the 43rd president of the United States.
This is a list of books and scholarly articles by and about Hillary Clinton, as well as columns by her.
Nancy Kassop is a professor at the State University of New York at New Paltz, and former chair of the Political Science Department at the school. Some of the courses she teaches are American Government and Politics and Constitutional Law.
The Department of Social Relations for Interdisciplinary Social Science Studies, more commonly known as the "Department of Social Relations", was an interdisciplinary collaboration among three of the social science departments at Harvard University beginning in 1946. Originally, the program was headquartered in Emerson Hall at Harvard before moving to William James Hall in 1965. While the name "Social Relations" is often associated with the program's long-time chair and guiding spirit, sociologist Talcott Parsons, many major figures of mid-20th-century social science also numbered among the program's faculty, including psychologists Gordon Allport, Jerome Bruner, Roger Brown, and Henry Murray (personality); anthropologists Clyde and Florence Kluckhohn, John and Beatrice Whiting, Evon Z. Vogt ; and sociologist Alex Inkeles. Other prominent scholars, such as Jerome Kagan and Ezra Vogel belonged to the department early in their careers before it split. Many of the department's graduate students also went on to be major figures in US social sciences during the latter part of the twentieth century; their work tends towards strong interdisciplinary and cross-disciplinary approaches.

George H. W. Bush's tenure as the 41st president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 1989, and ended on January 20, 1993. Bush was a Republican from Texas and the incumbent vice president for two terms under president Ronald Reagan. Bush took office following a victory over Democrat nominee Michael Dukakis in the 1988 presidential election. His presidency ended following his defeat in the 1992 presidential election by Democrat Bill Clinton. Bush was the father of the 43rd president, George W. Bush.

The 2008 United States elections were held on November 4. It was a Democratic wave, Democratic Senator Barack Obama of Illinois won the presidential election, by defeating his challenger, Senator John McCain, by a wide margin, and the Democrats bolstered their majorities in both chambers of Congress.
The post-presidency of Bill Clinton began on January 20, 2001 following the end of Bill Clinton's second term as president. Clinton was the 42nd president of the United States, serving from 1993 to 2001. After he left office, he continued to be active in the public sphere, touring the world, writing books, and campaigning for Democrats, including his wife, Hillary Clinton, who served as the junior U.S. senator from New York between 2001 and 2009 and the 67th United States Secretary of State between 2009 and 2013, on her presidential campaigns in 2008, in which she was runner-up for the Democratic nomination, and in 2016, when she lost the election to Donald Trump.
The Obama Doctrine is a catch-all term frequently used to describe one or several principles of the foreign policy of U.S. President Barack Obama. It is still not agreed whether there was an actual Obama Doctrine. Nevertheless, in 2015, during an interview with The New York Times, Obama briefly commented about the doctrine saying: "You asked about an Obama doctrine, the doctrine is we will engage, but we preserve all our capabilities".
This bibliography of Barack Obama is a list of written and published works, both books and films, about Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States.

The Reagan era or Age of Reagan is a periodization of recent American history used by historians and political observers to emphasize that the conservative "Reagan Revolution" led by President Ronald Reagan in domestic and foreign policy had a lasting impact. It overlaps with what political scientists call the Sixth Party System. Definitions of the Reagan era universally include the 1980s, while more extensive definitions may also include the late 1970s, the 1990s, the 2000s, the 2010s, and even the 2020s. In his 2008 book, The Age of Reagan: A History, 1974–2008, historian and journalist Sean Wilentz argues that Reagan dominated this stretch of American history in the same way that Franklin D. Roosevelt and his New Deal legacy dominated the four decades that preceded it.
This bibliography of Bill Clinton is a selected list of generally available published works about Bill Clinton, the 42nd president of the United States. Further reading is available on Bill Clinton, his presidency and his foreign policy, as well as in the footnotes in those articles.
Helen Block Lewis was an American psychiatrist and psychoanalyst. Her work pioneered the study of the differences between guilt and shame. She founded the journal Psychoanalytic Psychology, taught at universities, was the psychoanalysis division president of the American Psychological Association, and wrote several books. Her books include Shame and Guilt in Neurosis, Psychic War in Men and Women, Freud and Modern Psychology volume 1 and 2, Sex and the Superego, and The Role of Shame in Symptom Formation.








