
Sternal foramen (or perforated sternum) is an oval foramen present at lower one-third of the sternum. It is a relatively common anatomical variation found in 2.5% to 13.8% of individuals. [1]

Sternal foramen (or perforated sternum) is an oval foramen present at lower one-third of the sternum. It is a relatively common anatomical variation found in 2.5% to 13.8% of individuals. [1]
This variation is usually present at the lower one-third of the sternal body. It has an oval shape and a unique "bow tie" appearance when seen on axial computed tomography. The diameter of the sternal foramen ranges from 6 to 16 mm with an average diameter of 6.5 mm. [2] Sometimes, the foramen can be present at the xiphod process. In extremely rare cases, the foramen is found at the manubrium. [3]
Developmentally, sternal foramen results from the incomplete fusion of the sternal bars while they are still cartilaginous. [4]
Although sternal foramen is asymptomatic, it may entail a risk of serious complications from blinded sternal interventions. The foramen may be misdiagnosed as sternal fracture or a gunshot wound. Awareness of sternal foramen is also crucial in acupuncture to avoid cardiac tamponade. [5]

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The xiphoid process, also referred to as the ensiform process, xiphisternum, or metasternum, constitutes a small cartilaginous process (extension) located in the inferior segment of the sternum, typically ossified in adult humans. Both the Greek-derived term xiphoid and its Latin equivalent, ensiform, connote a "swordlike" or "sword-shaped" morphology.

The foramen magnum is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull.

The foramen ovale is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.

The foramen spinosum is a small open hole in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone that gives passage to the middle meningeal artery and vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

In the base of the skull, in the great wings of the sphenoid bone, medial to the foramen ovale, a small aperture, the sphenoidal emissary foramen, may occasionally be seen opposite the root of the pterygoid process. When present, it opens below near the scaphoid fossa. Vesalius was the first to describe and illustrate this foramen, and is also called the foramen Vesalius. Other names include foramen venosum and canaliculus sphenoidalis.

The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater.
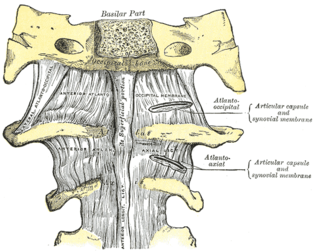
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit. It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.

The sternalismuscle is an anatomical variation that lies in front of the sternal end of the pectoralis major parallel to the margin of the sternum. The sternalis muscle may be a variation of the pectoralis major or of the rectus abdominis.

The clivus, or Blumenbach clivus, is a bony part of the cranium at the base of the skull. It is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. It slopes gradually to the anterior part of the basilar occipital bone at its junction with the sphenoid bone. It extends to the foramen magnum. It is related to the pons and the abducens nerve.
The caroticotympanic artery is a small, sometimes doubled artery which arises from the internal carotid artery. It leaves the carotid canal through a foramen to reach the tympanic cavity. It contributes arterial supply to the osseous part of the pharyngotympanic tube.
The incisive papilla is an oval midline mucosal prominence of the anterior hard palate overlying the incisive fossa. It is situated posteriorly to the central incisors, and represents the anterior extremity of the palatine raphe.

The cruciate ligament of the atlas is a cross-shaped ligament in the neck forming part of the atlanto-axial joint. It consists of the transverse ligament of atlas, a superior longitudinal band, and an inferior longitudinal band.
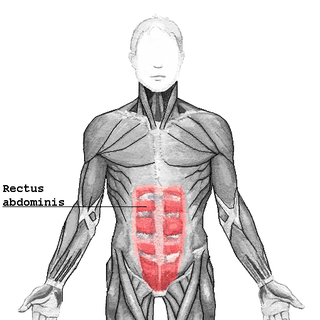
A rectus sheath hematoma is an accumulation of blood in the sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle. It causes abdominal pain with or without a mass.

The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word sternum originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon) 'chest'.

Fossa navicularis magna is a variant bony depression found at the midline of the occipital part of clivus. This fossa was first described by Tourtual. Its prevalence ranges from 0.9 to 5.3%.
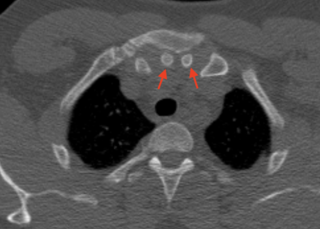
Episternal ossicles are small bones that are sometimes present at the upper end of the chest bone. The prevalence of these ossicles is around 1.5%.