
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (trigeminal, from Latin tri- 'three', and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. It is a chronic condition which is often resistant to treatment. When the cut ends of sensory fibres are stimulated during thigh movements, the patient feels as if the sensation is arising from the non-existent limb. Sometimes the patient might feel pain in the non-existent limb. Approximately 80–100% of individuals with an amputation experience sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painful phantom limb sensation. These sensations are relatively common in amputees and usually resolve within two to three years without treatment. Research continues to explore the underlying mechanisms of phantom limb pain (PLP) and effective treatment options.

Vilayanur Subramanian Ramachandran is an Indian-American neuroscientist. He is known for his wide-ranging experiments and theories in behavioral neurology, including the invention of the mirror box. Ramachandran is a distinguished professor in UCSD's Department of Psychology, where he is the director of the Center for Brain and Cognition.

The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal column of the spinal cord to the medulla, where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.
Phantom pain is a painful perception that an individual experiences relating to a limb or an organ that is not physically part of the body, either because it was removed or was never there in the first place.

Monoplegia is paralysis of a single limb, usually an arm. Common symptoms associated with monoplegic patients are weakness, numbness, and pain in the affected limb. Monoplegia is a type of paralysis that falls under hemiplegia. While hemiplegia is paralysis of half of the body, monoplegia is localized to a single limb or to a specific region of the body. Monoplegia of the upper limb is sometimes referred to as brachial monoplegia, and that of the lower limb is called crural monoplegia. Monoplegia in the lower extremities is not as common of an occurrence as in the upper extremities. Monoparesis is a similar, but less severe, condition because one limb is very weak, not paralyzed. For more information, see paresis.
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.
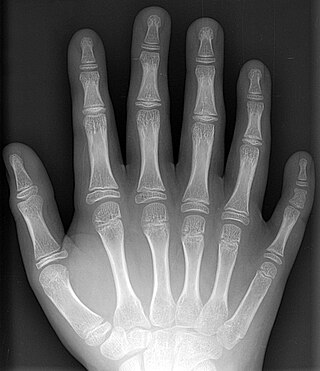
Supernumerary body parts are most commonly a congenital disorder involving the growth of an additional part of the body and a deviation from the body plan. Body parts may be easily visible or hidden away, such as internal organs.
Pallesthesia, or vibratory sensation, is the ability to perceive vibration. This sensation, often conducted through skin and bone, is usually generated by mechanoreceptors such as Pacinian corpuscles, Merkel disk receptors, and tactile corpuscles. All of these receptors stimulate an action potential in afferent nerves found in various layers of the skin and body. The afferent neuron travels to the spinal column and then to the brain where the information is processed. Damage to the peripheral nervous system or central nervous system can result in a decline or loss of pallesthesia.
Body schema is an organism's internal model of its own body, including the position of its limbs. The neurologist Sir Henry Head originally defined it as a postural model of the body that actively organizes and modifies 'the impressions produced by incoming sensory impulses in such a way that the final sensation of body position, or of locality, rises into consciousness charged with a relation to something that has happened before'. As a postural model that keeps track of limb position, it plays an important role in control of action.
Tactile discrimination is the ability to differentiate information through the sense of touch. The somatosensory system is the nervous system pathway that is responsible for this essential survival ability used in adaptation. There are various types of tactile discrimination. One of the most well known and most researched is two-point discrimination, the ability to differentiate between two different tactile stimuli which are relatively close together. Other types of discrimination like graphesthesia and spatial discrimination also exist but are not as extensively researched. Tactile discrimination is something that can be stronger or weaker in different people and two major conditions, chronic pain and blindness, can affect it greatly. Blindness increases tactile discrimination abilities which is extremely helpful for tasks like reading braille. In contrast, chronic pain conditions, like arthritis, decrease a person's tactile discrimination. One other major application of tactile discrimination is in new prosthetics and robotics which attempt to mimic the abilities of the human hand. In this case tactile sensors function similarly to mechanoreceptors in a human hand to differentiate tactile stimuli.

Touch is perceiving the environment using skin. Specialized receptors in the skin send signals to the brain indicating light and soft pressure, hot and cold, body position and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also includes the visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory and vestibular senses.
Somatosensory evoked potential is the electrical activity of the brain that results from the stimulation of touch. SEP tests measure that activity and are a useful, noninvasive means of assessing somatosensory system functioning. By combining SEP recordings at different levels of the somatosensory pathways, it is possible to assess the transmission of the afferent volley from the periphery up to the cortex. SEP components include a series of positive and negative deflections that can be elicited by virtually any sensory stimuli. For example, SEPs can be obtained in response to a brief mechanical impact on the fingertip or to air puffs. However, SEPs are most commonly elicited by bipolar transcutaneous electrical stimulation applied on the skin over the trajectory of peripheral nerves of the upper limb or lower limb, and then recorded from the scalp. In general, somatosensory stimuli evoke early cortical components, generated in the contralateral primary somatosensory cortex (S1), related to the processing of the physical stimulus attributes. About 100 ms after stimulus application, additional cortical regions are activated, such as the secondary somatosensory cortex (S2), and the posterior parietal and frontal cortices, marked by a parietal P100 and bilateral frontal N140. SEPs are routinely used in neurology today to confirm and localize sensory abnormalities, to identify silent lesions and to monitor changes during surgical procedures.
Many types of sense loss occur due to a dysfunctional sensation process, whether it be ineffective receptors, nerve damage, or cerebral impairment. Unlike agnosia, these impairments are due to damages prior to the perception process.
Sensory stimulation therapy (SST) is an experimental therapy that aims to use neural plasticity mechanisms to aid in the recovery of somatosensory function after stroke or cognitive ageing. Stroke and cognitive ageing are well known sources of cognitive loss, the former by neuronal death, the latter by weakening of neural connections. SST stimulates a specific sense at a specific frequency. Research suggests that this technique may reverse cognitive ageing by up to 30 years, and may selectively improve or impair two point discrimination thresholds.
Mirror-touch synesthesia is a rare condition which causes individuals to experience a similar sensation in the same part or opposite part of the body that another person feels. For example, if someone with this condition were to observe someone touching their cheek, they would feel the same sensation on their own cheek. Synesthesia, in general, is described as a condition in which a concept or sensation causes an individual to experience an additional sensation or concept. Synesthesia is usually a developmental condition; however, recent research has shown that mirror touch synesthesia can be acquired after sensory loss following amputation.
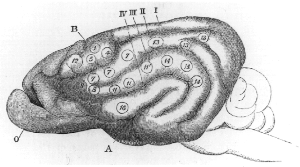
Cortical remapping, also referred to as cortical reorganization, is the process by which an existing cortical map is affected by a stimulus resulting in the creating of a 'new' cortical map. Every part of the body is connected to a corresponding area in the brain which creates a cortical map. When something happens to disrupt the cortical maps such as an amputation or a change in neuronal characteristics, the map is no longer relevant. The part of the brain that is in charge of the amputated limb or neuronal change will be dominated by adjacent cortical regions that are still receiving input, thus creating a remapped area. Remapping can occur in the sensory or motor system. The mechanism for each system may be quite different. Cortical remapping in the somatosensory system happens when there has been a decrease in sensory input to the brain due to deafferentation or amputation, as well as a sensory input increase to an area of the brain. Motor system remapping receives more limited feedback that can be difficult to interpret.

Tactile hallucination is the false perception of tactile sensory input that creates a hallucinatory sensation of physical contact with an imaginary object. It is caused by the faulty integration of the tactile sensory neural signals generated in the spinal cord and the thalamus and sent to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) and secondary somatosensory cortex (SII). Tactile hallucinations are recurrent symptoms of neurological diseases such as schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Ekbom's syndrome and delirium tremens. Patients who experience phantom limb pains also experience a type of tactile hallucination. Tactile hallucinations are also caused by drugs such as cocaine and alcohol.
Dyschiria, also known as dyschiric syndrome, is a neurological disorder where one-half of an individual's body or space cannot be recognized or respond to sensations. The term dyschiria is rarely used in modern scientific research and literature. Dyschiria has been often referred to as unilateral neglect, visuo-spatial neglect, or hemispatial neglect from the 20th century onwards. Psychologists formerly characterized dyschiric patients to be unable to discriminate or report external stimuli. This left the patients incapable of orienting sensory responses in their extrapersonal and personal space. Patients with dyschiria are unable to distinguish one side of their body in general, or specific segments of the body. There are three stages to dyschiria: achiria, allochiria, and synchiria, in which manifestations of dyschiria evolve in varying degrees.
McGeoch, P.D. et al. (2009). Apotemnophilia – the neurological basis of a ‘psychological’ disorder. Nature Precedings DOI: 10101/npre.2009.2954.1.









