Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3, is the name for what has now become a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Formerly named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy, based on the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) algorithm. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints; today, it is now also used for applications such as TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles.

Home cinema, also called home theaters or theater rooms, are home entertainment audio-visual systems that seek to reproduce a movie theater experience and mood using consumer electronics-grade video and audio equipment that is set up in a room or backyard of a private home. Some studies show films are rated better and generate more intense emotions when watched in a movie theater, however, convenience is a major appeal for home cinemas. In the 1980s, home cinemas typically consisted of a movie pre-recorded on a LaserDisc or VHS tape; a LaserDisc Player or VCR ; and a heavy, bulky large-screen cathode ray tube TV set, although sometimes CRT projectors were used instead. In the 2000s, technological innovations in sound systems, video player equipment and TV screens and video projectors have changed the equipment used in home cinema set-ups and enabled home users to experience a higher-resolution screen image, improved sound quality and components that offer users more options. The development of Internet-based subscription services means that 2016-era home theatre users do not have to commute to a video rental store as was common in the 1980s and 1990s

Quadraphonic sound – equivalent to what is now called 4.0 surround sound – uses four audio channels in which speakers are positioned at the four corners of a listening space. The system allows for the reproduction of sound signals that are independent of one another.

Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener. Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to surround sound, theater sound systems commonly had three screen channels of sound that played from three loudspeakers located in front of the audience. Surround sound adds one or more channels from loudspeakers to the side or behind the listener that are able to create the sensation of sound coming from any horizontal direction around the listener.
The low-frequency effects (LFE) channel is a band-limited audio track that is used for reproducing deep and intense low-frequency sounds in the 3–120 Hz frequency range.
Dolby Pro Logic is a surround sound processing technology developed by Dolby Laboratories, designed to decode soundtracks encoded with Dolby Surround.

Dolby Laboratories, Inc. is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers.
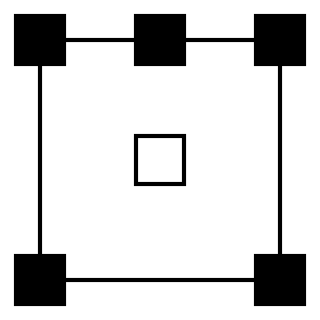
5.1 surround sound is the common name for surround sound audio systems. 5.1 is the most commonly used layout in home theatres. It uses five full bandwidth channels and one low-frequency effects channel. Dolby Digital, Dolby Pro Logic II, DTS, SDDS, and THX are all common 5.1 systems. 5.1 is also the standard surround sound audio component of digital broadcast and music.
Matrix decoding is an audio technology where a small number of discrete audio channels are decoded into a larger number of channels on play back. The channels are generally, but not always, arranged for transmission or recording by an encoder, and decoded for playback by a decoder. The function is to allow multichannel audio, such as quadraphonic sound or surround sound to be encoded in a stereo signal, and thus played back as stereo on stereo equipment, and as surround on surround equipment – this is "compatible" multichannel audio.
10.2 is the surround sound format developed by THX creator Tomlinson Holman of TMH Labs and the University of Southern California. Developed along with Chris Kyriakakis of the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, 10.2 refers to the format's slogan: "Twice as good as 5.1". However, there actually may be 14 discrete channels if the left and right point surround channels are included. He states that 5.1, a name which he himself came up with in 1987 was chosen as it was "the minimum number of channels necessary to give a sense of spaciousness". Holman and others state that higher sampling rates, which is a recent trend in digital recording, does not have a significant perceivable effect and that the next frontier in sound engineering is to increase the number of discrete channels to meet human spatial sound perception. As of 2015, several decoding, UHD, or virtual expansion processors have approached numbers as great or greater than 10.2.

DTS, Inc. is an American company that makes multichannel audio technologies for film and video. Based in Calabasas, California, the company introduced its DTS technology in 1993 as a competitor to Dolby Laboratories, incorporating DTS in the film Jurassic Park (1993). The DTS product is used in surround sound formats for both commercial/theatrical and consumer-grade applications. It was known as The Digital Experience until 1995. DTS licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers.
Dolby Stereo is a sound format made by Dolby Laboratories. It is a unified brand for two completely different basic systems: the Dolby SVA 1976 system used with optical sound tracks on 35mm film, and Dolby Stereo 70mm noise reduction on 6-channel magnetic soundtracks on 70mm prints.
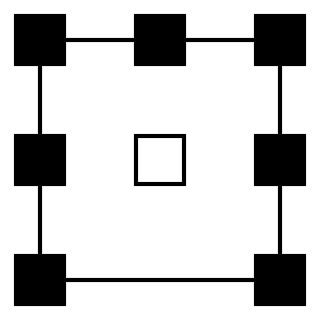
7.1 surround sound is the common name for an eight-channel surround audio system commonly used in home theatre configurations. It adds two additional speakers to the more conventional six-channel (5.1) audio configuration. As with 5.1 surround sound, 7.1 surround sound positional audio uses the standard front left and right, center, and LFE (subwoofer) speaker configuration. However, whereas a 5.1 surround sound system combines both surround and rear channel effects into two channels, a 7.1 surround system splits the surround and rear channel information into four distinct channels, in which sound effects are directed to left and right surround channels, plus two rear surround channels.

A dipole speaker enclosure in its simplest form is constructed by mounting a loudspeaker driver on a flat panel. The panel may be folded to conserve space.

An audio/video receiver (AVR) is a consumer electronics component used in a home theater. Its purpose is to receive audio and video signals from a number of sources, and to process them and provide power amplifiers to drive loudspeakers and route the video to displays such as a television, monitor or video projector. Inputs may come from a satellite receiver, radio, DVD players, Blu-ray Disc players, VCRs or video game consoles, among others. The AVR source selection and settings such as volume, are typically set by a remote controller.
SQ Quadraphonic was a matrix 4-channel quadraphonic sound system for vinyl LP records. It was introduced by CBS Records in 1971. Many recordings using this technology were released on LP during the 1970s.
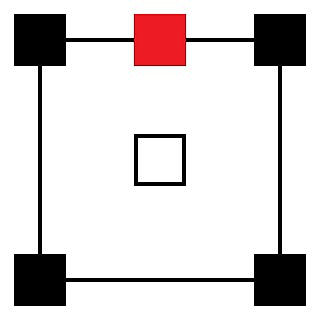
Center channel refers to an audio channel common to many surround sound formats. It is the channel that is mostly, or fully, dedicated to the reproduction of the dialogue of an audiovisual program. The speaker(s) connected to the center channel are placed in the center of and behind the perforated projection screen, to give the effect that sounds from the center channel are coming from the screen. In many home surround sound units, the center channel is positioned above or below the video screen.

Home audio systems are audio electronics intended for home entertainment use, such as shelf stereos, music centres and surround sound receivers. Home audio generally does not include standard equipment such as built-in television speakers, but rather accessory equipment, which may be intended to enhance or replace standard equipment, such as standard TV speakers. Since surround sound receivers, which are primarily intended to enhance the reproduction of a movie, are the most popular home audio device, the primary field of home audio is home cinema.
Height channels are audio channels in surround sound multichannel audio. Height channels are located above the listening area and increase the sound field beyond the horizontal plane.

Dolby Atmos is a surround sound technology developed by Dolby Laboratories. It expands on existing surround sound systems by adding height channels, allowing sounds to be interpreted as three-dimensional objects. Following the release of Atmos for the cinema market, a variety of consumer technologies have been released under the Atmos brand, using in-ceiling and up-firing speakers.















