
Mother of vinegar is a biofilm composed of a form of cellulose, yeast, and bacteria that sometimes develops on fermenting alcoholic liquids during the process that turns alcohol into acetic acid with the help of oxygen from the air and acetic acid bacteria (AAB). It is similar to the symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) mostly known from production of kombucha, but develops to a much lesser extent due to lesser availability of yeast, which is often no longer present in wine/cider at this stage, and a different population of bacteria. Mother of vinegar is often added to wine, cider, or other alcoholic liquids to produce vinegar at home, although only the bacteria is required, but historically has also been used in large scale production.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.

Kombucha is a fermented, lightly effervescent, sweetened black tea drink. Sometimes the beverage is called kombucha tea to distinguish it from the culture of bacteria and yeast. Juice, spices, fruit or other flavorings are often added.

Traditional ginger beer is a sweetened and carbonated, usually non-alcoholic beverage. Historically it was produced by the natural fermentation of prepared ginger spice, yeast and sugar.

Malolactic conversion is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often performed as a secondary fermentation shortly after the end of the primary fermentation, but can sometimes run concurrently with it. The process is standard for most red wine production and common for some white grape varieties such as Chardonnay, where it can impart a "buttery" flavor from diacetyl, a byproduct of the reaction.
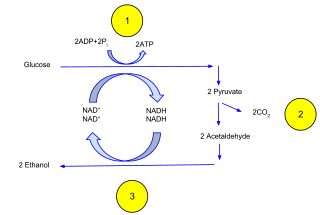
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. Because yeasts perform this conversion in the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation is considered an anaerobic process. It also takes place in some species of fish where it provides energy when oxygen is scarce.

Viili (Finnish) is a mesophilic fermented milk product found in the Nordic countries, particularly Finland. Viili is similar to yoghurt or kefir, but when left unmixed, its texture is malleable, or "long". The metabolism of the bacteria used in the fermentation also gives viili a slightly different taste.
Acidogenesis is the second stage in the four stages of anaerobic digestion:
A wine fault is a sensory-associated (organoleptic) characteristic of a wine that is unpleasant, and may include elements of taste, smell, or appearance, elements that may arise from a "chemical or a microbial origin", where particular sensory experiences might arise from more than one wine fault. Wine faults may result from poor winemaking practices or storage conditions that lead to wine spoilage.
Leuconostoc is a genus of gram-positive bacteria, placed within the family of Lactobacillaceae. They are generally ovoid cocci often forming chains. Leuconostoc spp. are intrinsically resistant to vancomycin and are catalase-negative. All species within this genus are heterofermentative and are able to produce dextran from sucrose. They are generally slime-forming.

Tibicos, or water kefir, is a traditional fermented drink made with water and a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeasts (SCOBY) held in a polysaccharide biofilm matrix created by the bacteria. It is sometimes consumed as an alternative to milk-based probiotic drinks or tea-cultured products such as kombucha. Water kefir is typically made as a probiotic homebrew beverage. The finished product, if bottled, will produce a carbonated beverage.

Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substances through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is broadly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology.

In food processing, fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms—yeasts or bacteria—under anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions. Fermentation usually implies that the action of microorganisms is desired. The science of fermentation is known as zymology or zymurgy.

Food microbiology is the study of the microorganisms that inhabit, create, or contaminate food. This includes the study of microorganisms causing food spoilage; pathogens that may cause disease ; microbes used to produce fermented foods such as cheese, yogurt, bread, beer, and wine; and microbes with other useful roles, such as producing probiotics.

Symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) is a culinary symbiotic fermentation culture (starter) consisting of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeast which arises in the preparation of sour foods and beverages such as kombucha. Beer and wine also undergo fermentation with yeast, but the lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria components unique to SCOBY are usually viewed as a source of spoilage rather than a desired addition. Both LAB and AAB enter on the surface of barley and malt in beer fermentation and grapes in wine fermentation; LAB lowers the pH of the beer/wine while AAB takes the ethanol produced from the yeast and oxidizes it further into vinegar, resulting in a sour taste and smell. AAB are also responsible for the formation of the cellulose SCOBY.

Kefir is a fermented milk drink similar to a thin yogurt or ayran that is made from kefir grains, a specific type of mesophilic symbiotic culture. It is prepared by inoculating the milk of cows, goats, or sheep with kefir grains.

Biopreservation is the use of natural or controlled microbiota or antimicrobials as a way of preserving food and extending its shelf life. The biopreservation of food, especially utilizing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) that are inhibitory to food spoilage microbes, has been practiced since early ages, at first unconsciously but eventually with an increasingly robust scientific foundation. Beneficial bacteria or the fermentation products produced by these bacteria are used in biopreservation to control spoilage and render pathogens inactive in food. There are a various modes of action through which microorganisms can interfere with the growth of others such as organic acid production, resulting in a reduction of pH and the antimicrobial activity of the un-dissociated acid molecules, a wide variety of small inhibitory molecules including hydrogen peroxide, etc. It is a benign ecological approach which is gaining increasing attention.
Microbial food cultures are live bacteria, yeasts or moulds used in food production. Microbial food cultures carry out the fermentation process in foodstuffs. Used by humans since the Neolithic period fermentation helps to preserve perishable foods and to improve their nutritional and organoleptic qualities. As of 1995, fermented food represented between one quarter and one third of food consumed in Central Europe. More than 260 different species of microbial food culture are identified and described for their beneficial use in fermented food products globally, showing the importance of their use.
Jun, or Xun, is a fermented drink similar to kombucha, differing only in that its base ingredients are green tea and honey instead of black tea and cane sugar. Jun is brewed by fermenting green tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). Fruits, sweeteners, spices, and other flavor enhancers are also commonly added to make the taste of the beverage more appealing. Though Jun bears similarities to other fermented drinks like kombucha, water kefir, and kvass, it has enough differences to be considered a distinct drink.

Industrial microbiology is a branch of biotechnology that applies microbial sciences to create industrial products in mass quantities, often using microbial cell factories. There are multiple ways to manipulate a microorganism in order to increase maximum product yields. Introduction of mutations into an organism may be accomplished by introducing them to mutagens. Another way to increase production is by gene amplification, this is done by the use of plasmids, and vectors. The plasmids and/ or vectors are used to incorporate multiple copies of a specific gene that would allow more enzymes to be produced that eventually cause more product yield. The manipulation of organisms in order to yield a specific product has many applications to the real world like the production of some antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, solvents, alcohol and daily products. Microorganisms play a big role in the industry, with multiple ways to be used. Medicinally, microbes can be used for creating antibiotics in order to treat infection. Microbes can also be used for the food industry as well. Microbes are very useful in creating some of the mass produced products that are consumed by people. The chemical industry also uses microorganisms in order to synthesize amino acids and organic solvents. Microbes can also be used in an agricultural application for use as a biopesticide instead of using dangerous chemicals and or inoculants to help plant proliferation.















