| Look up Synapse or synapse in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A synapse is a neural junction used for communication between neurons
Contents
Synapse may also refer to:
| Look up Synapse or synapse in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A synapse is a neural junction used for communication between neurons
Synapse may also refer to:

Software is a collection of instructions and data that tell a computer how to work. This is in contrast to physical hardware, from which the system is built and actually performs the work. In computer science and software engineering, computer software is all information processed by computer systems, including programs and data. Computer software includes computer programs, libraries and related non-executable data, such as online documentation or digital media. Computer hardware and software require each other and neither can be realistically used on its own.
Spring(s) may refer to:
Network and networking may refer to:
Social software, also known as social apps, include communication and interactive tools often based on the Internet. Communication tools typically handle the capturing, storing and presentation of communication, usually written but increasingly including audio and video as well. Interactive tools handle mediated interactions between a pair or group of users. They focus on establishing and maintaining a connection among users, facilitating the mechanics of conversation and talk. Social software generally refers to software that makes collaborative behaviour, the organisation and moulding of communities, self-expression, social interaction and feedback possible for individuals. Another element of the existing definition of social software is that it allows for the structured mediation of opinion between people, in a centralized or self-regulating manner. The most improved area for social software is that Web 2.0 applications can all promote cooperation between people and the creation of online communities more than ever before.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to software engineering:
Neuromorphic engineering, also known as neuromorphic computing, is a concept developed by Carver Mead, in the late 1980s, describing the use of very-large-scale integration (VLSI) systems containing electronic analog circuits to mimic neuro-biological architectures present in the nervous system. In recent times, the term neuromorphic has been used to describe analog, digital, mixed-mode analog/digital VLSI, and software systems that implement models of neural systems. The implementation of neuromorphic computing on the hardware level can be realized by oxide-based memristors, spintronic memories, threshold switches, and transistors.

Application software is computing software designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Examples of an application include a word processor, a spreadsheet program, an accounting application, a web browser, an email client, a media player, a console game, or a photo editor. The collective noun application software refers to all applications collectively. The other principal classifications of software are system software, relating to the operation of the computer, and utility software ("utilities").
Apex may refer to:
AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture (AUTOSAR) is a global development partnership of automotive interested parties founded in 2003. It pursues the objective to create and establish an open and standardized software architecture for automotive electronic control units (ECUs). Goals include the scalability to different vehicle and platform variants, transferability of software, the consideration of availability and safety requirements, a collaboration between various partners, sustainable use of natural resources, and maintainability during the whole product lifecycle.
Neuroinformatics is the field that combines informatics and neuroscience. Neuroinformatics is related with neuroscience data and information processing by artificial neural networks. There are three main directions where neuroinformatics has to be applied:
Neural network software is used to simulate, research, develop, and apply artificial neural networks, software concepts adapted from biological neural networks, and in some cases, a wider array of adaptive systems such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
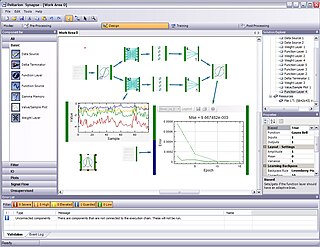
Synapse is a component-based development environment for neural networks and adaptive systems. Created by Peltarion, Synapse allows data mining, statistical analysis, visualization, preprocessing, design and training of neural networks and adaptive systems and the deployment of them. It utilizes a plug-in based architecture making it a general platform for signal processing. The first version of the product was released in May 2006.
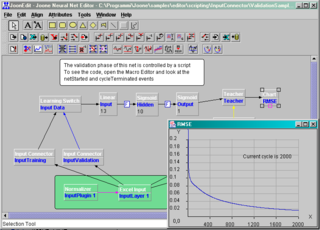
JOONE is a component based neural network framework built in Java.

Roger D. Jones is an American physicist and entrepreneur. He currently is a Research Fellow at the Center for Complex Systems and Enterprises at the Stevens Institute of Technology and a scientist with the X-Center Network.

TIBCO Software Inc. is an enterprise data company founded in 1997 in Palo Alto, California.
GENESIS is a simulation environment for constructing realistic models of neurobiological systems at many levels of scale including: sub-cellular processes, individual neurons, networks of neurons, and neuronal systems. These simulations are “computer-based implementations of models whose primary objective is to capture what is known of the anatomical structure and physiological characteristics of the neural system of interest”. GENESIS is intended to quantify the physical framework of the nervous system in a way that allows for easy understanding of the physical structure of the nerves in question. “At present only GENESIS allows parallelized modeling of single neurons and networks on multiple-instruction-multiple-data parallel computers.” Development of GENESIS software spread from its home at Caltech to labs at the University of Texas at San Antonio, the University of Antwerp, the National Centre for Biological Sciences in Bangalore, the University of Colorado, the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center, the San Diego Supercomputer Center, and Emory University.
Robotics middleware is middleware to be used in complex robot control software systems.
Brain simulation is the concept of creating a functioning computer model of a brain or part of a brain. Brain simulation projects intend to contribute to a complete understanding of the brain, and eventually also assist the process of treating and diagnosing brain diseases.
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. It most commonly refers to the open-source model, in which open-source software or other products are released under an open-source license as part of the open-source-software movement. Use of the term originated with software, but has expanded beyond the software sector to cover other open content and forms of open collaboration.