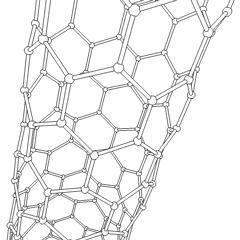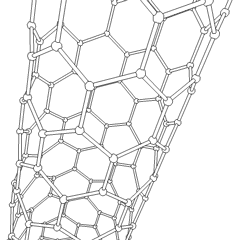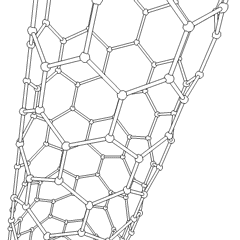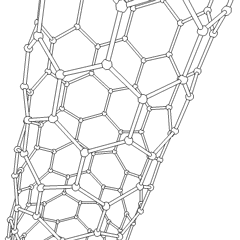
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers.

Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers is their processability, mainly by dispersion. Conductive polymers are generally not thermoplastics, i.e., they are not thermoformable. But, like insulating polymers, they are organic materials. They can offer high electrical conductivity but do not show similar mechanical properties to other commercially available polymers. The electrical properties can be fine-tuned using the methods of organic synthesis and by advanced dispersion techniques.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polyacetylene</span> Organic polymer made of the repeating unit [C2H2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png/320px-Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png)
Polyacetylene usually refers to an organic polymer with the repeating unit [C2H2]n. The name refers to its conceptual construction from polymerization of acetylene to give a chain with repeating olefin groups. This compound is conceptually important, as the discovery of polyacetylene and its high conductivity upon doping helped to launch the field of organic conductive polymers. The high electrical conductivity discovered by Hideki Shirakawa, Alan Heeger, and Alan MacDiarmid for this polymer led to intense interest in the use of organic compounds in microelectronics. This discovery was recognized by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2000. Early work in the field of polyacetylene research was aimed at using doped polymers as easily processable and lightweight "plastic metals". Despite the promise of this polymer in the field of conductive polymers, many of its properties such as instability to air and difficulty with processing have led to avoidance in commercial applications.

Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents at the 3- or 4-position(s). They are also colored solids, but tend to be soluble in organic solvents.

Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.

Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of the most studied conducting polymers.
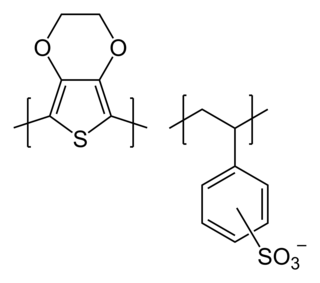
poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) is a polymer mixture of two ionomers. One component in this mixture is made up of polystyrene sulfonate which is a sulfonated polystyrene. Part of the sulfonyl groups are deprotonated and carry a negative charge. The other component poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) is a conjugated polymer and carries positive charges and is based on polythiophene. Together the charged macromolecules form a macromolecular salt.

Aggregated diamond nanorods, or ADNRs, are a nanocrystalline form of diamond, also known as nanodiamond or hyperdiamond.
A non-carbon nanotube is a cylindrical molecule often composed of metal oxides, or group III-Nitrides and morphologically similar to a carbon nanotube. Non-carbon nanotubes have been observed to occur naturally in some mineral deposits.

Nanocomposite is a multiphase solid material where one of the phases has one, two or three dimensions of less than 100 nanometers (nm) or structures having nano-scale repeat distances between the different phases that make up the material.

Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylinders of one or more layers of graphene (lattice). Diameters of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) are typically 0.8 to 2 nm and 5 to 20 nm, respectively, although MWNT diameters can exceed 100 nm. CNT lengths range from less than 100 nm to 0.5 m.

Printed electronics is a set of printing methods used to create electrical devices on various substrates. Printing typically uses common printing equipment suitable for defining patterns on material, such as screen printing, flexography, gravure, offset lithography, and inkjet. By electronic-industry standards, these are low-cost processes. Electrically functional electronic or optical inks are deposited on the substrate, creating active or passive devices, such as thin film transistors; capacitors; coils; resistors. Some researchers expect printed electronics to facilitate widespread, very low-cost, low-performance electronics for applications such as flexible displays, smart labels, decorative and animated posters, and active clothing that do not require high performance.
An electrically conducting yarn is a yarn that conducts electricity. Conducting yarns are used to manufacture carpets and other items that dissipate static electricity, such as work clothes in highly flammable environments, e.g., in the petrochemistry industry.
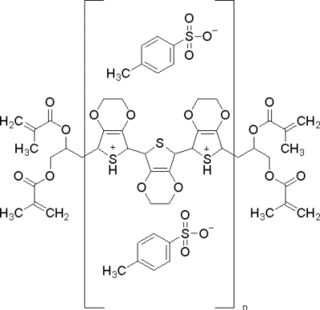
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-tetramethacrylate or PEDOT-TMA is a p-type conducting polymer based on 3,4-ethylenedioxylthiophene or the EDOT monomer. It is a modification of the PEDOT structure. Advantages of this polymer relative to PEDOT are that it is dispersible in organic solvents, and it is non-corrosive. PEDOT-TMA was developed under a contract with the National Science Foundation, and it was first announced publicly on April 12, 2004. The trade name for PEDOT-TMA is Oligotron. PEDOT-TMA was featured in an article entitled "Next Stretch for Plastic Electronics" that appeared in Scientific American in 2004. The U.S. Patent office issued a patent protecting PEDOT-TMA on April 22, 2008.

Hiromichi Kataura is a Japanese scientist known for his work on synthesis and characterization of single-wall and double-wall carbon nanotubes and on encapsulation of water, fullerenes and other organic molecules into carbon nanotubes.

The optical properties of carbon nanotubes are highly relevant for materials science. The way those materials interact with electromagnetic radiation is unique in many respects, as evidenced by their peculiar absorption, photoluminescence (fluorescence), and Raman spectra.

Transparent conducting films (TCFs) are thin films of optically transparent and electrically conductive material. They are an important component in a number of electronic devices including liquid-crystal displays, OLEDs, touchscreens and photovoltaics. While indium tin oxide (ITO) is the most widely used, alternatives include wider-spectrum transparent conductive oxides (TCOs), conductive polymers, metal grids and random metallic networks, carbon nanotubes (CNT), graphene, nanowire meshes and ultra thin metal films.
The exceptional electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes have made them alternatives to the traditional electrical actuators for both microscopic and macroscopic applications. Carbon nanotubes are very good conductors of both electricity and heat, and are also very strong and elastic molecules in certain directions. These properties are difficult to find in the same material and very needed for high performance actuators. For current carbon nanotube actuators, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) and bundles of MWNTs have been widely used mostly due to the easiness of handling and robustness. Solution dispersed thick films and highly ordered transparent films of carbon nanotubes have been used for the macroscopic applications.
Ester H. Segal is an Israeli nanotechnology researcher and professor in the Department of Biotechnology and Food Engineering at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, where she heads the Laboratory for Multifunctional Nanomaterials. She is also affiliated with the Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology. Segal is a specialist in porous silicon nanomaterials, as well as nanocomposite materials for active packaging technologies to extend the shelf life of food.

Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) is the combination of electrochemistry and quartz crystal microbalance, which was generated in the eighties. Typically, an EQCM device contains an electrochemical cells part and a QCM part. Two electrodes on both sides of the quartz crystal serve two purposes. Firstly, an alternating electric field is generated between the two electrodes for making up the oscillator. Secondly, the electrode contacting electrolyte is used as a working electrode (WE), together with a counter electrode (CE) and a reference electrode (RE), in the potentiostatic circuit constituting the electrochemistry cell. Thus, the working electrode of electrochemistry cell is the sensor of QCM.



![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polyacetylene</span> Organic polymer made of the repeating unit [C2H2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png/320px-Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png)











