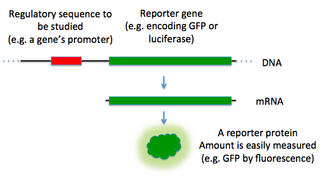
In molecular biology, a reporter gene is a gene that researchers attach to a regulatory sequence of another gene of interest in bacteria, cell culture, animals or plants. Such genes are called reporters because the characteristics they confer on organisms expressing them are easily identified and measured, or because they are selectable markers. Reporter genes are often used as an indication of whether a certain gene has been taken up by or expressed in the cell or organism population.
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach to biological research.
Cheminformatics refers to use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "in silico" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such in silico techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied.
Systems Science, also referred to as Systems Research, or, simply, Systems, is an interdisciplinary field concerned with understanding systems—from simple to complex—in nature, society, cognition, engineering, technology and science itself. The field is diverse, spanning the formal, natural, social, and applied sciences.

Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature.
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are only two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric.

Andrew (Drew) David Endy is a synthetic biologist and tenured associate professor of bioengineering at Stanford University, California.
In September 2021, Synthetic Genomics Inc. (SGI), a private company located in La Jolla, California, changed its name to Viridos. The company is focused on the field of synthetic biology, especially harnessing photosynthesis with micro algae to create alternatives to fossil fuels. Viridos designs and builds biological systems to address global sustainability problems.
Steven Albert Benner has been a professor at Harvard University, ETH Zurich, and the University of Florida where he was the V.T. & Louise Jackson Distinguished Professor of Chemistry. In 2005, he founded The Westheimer Institute of Science and Technology (TWIST) and the Foundation For Applied Molecular Evolution. Benner has also founded the companies EraGen Biosciences and Firebird BioMolecular Sciences LLC.

Eduardo Daniel Sontag is an American mathematician, and distinguished university professor at Northeastern University, who works in the fields control theory, dynamical systems, systems molecular biology, cancer and immunology, theoretical computer science, neural networks, and computational biology.

ChemSpider is a database of chemicals. ChemSpider is owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Mihajlo D. Mesarovic is a Serbian scientist, who is a professor of Systems Engineering and Mathematics at Case Western Reserve University. Mesarovic has been a pioneer in the field of systems theory, he was UNESCO Scientific Advisor on Global change and also a member of the Club of Rome.
BMC Systems Biology was an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal that covered research in systems biology. Filling a gap in what was a new research field, the journal was established in 2007 and is published by BioMed Central. Part of the BMC Series of journals, it had a broad scope covering the engineering of biological systems, network modelling, quantitative analyses, integration of different levels of information and synthetic biology. In January 2019 the Editorial Board was informed that the journal was closing and no more submissions would be accepted after March 1. The last articles were published on 5 April 2019, but content is still archived in perpetuity from the homepage and PubMed Central.

The Journal of Liposome Research is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes original research on the topics of liposomes and related systems, lipid-based delivery systems, lipid biology, and both synthetic and physical lipid chemistry. The journal also publishes special issues focusing on particular topics and themes within the general scope of the journal and abstracts and conference proceedings including those from the International Liposome Society. The journal is owned by Informa plc
Natural computing, also called natural computation, is a terminology introduced to encompass three classes of methods: 1) those that take inspiration from nature for the development of novel problem-solving techniques; 2) those that are based on the use of computers to synthesize natural phenomena; and 3) those that employ natural materials to compute. The main fields of research that compose these three branches are artificial neural networks, evolutionary algorithms, swarm intelligence, artificial immune systems, fractal geometry, artificial life, DNA computing, and quantum computing, among others.
ACS Synthetic Biology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society. It began publishing accepted articles in the Fall of 2011, with the first full monthly issue published in January 2012. It covers all aspects of synthetic biology, including molecular, systems, and synthetic research. The founding editor-in-chief is Christopher Voigt.

Artificial life is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American theoretical biologist, in 1986. In 1987 Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: soft, from software; hard, from hardware; and wet, from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena.
Jamie A. Davies is a British scientist, Professor of Experimental Anatomy at the University of Edinburgh, and leader of a laboratory in its Centre for Integrative Physiology. He works in the fields of Developmental biology, Synthetic biology, and Tissue engineering. He is also Principal Investigator for the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology database.

bioRxiv is an open access preprint repository for the biological sciences co-founded by John Inglis and Richard Sever in November 2013. It is hosted by the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL). As preprints, papers hosted on bioRxiv are not peer-reviewed, but undergo basic screening and checked against plagiarism. Readers may offer comments on the preprint. It was inspired by and intends to complement the arXiv repository, which mostly focuses on mathematics, physics and connected disciplines, launched in 1991 by Paul Ginsparg. It received support from both the CSHL and the Lourie Foundation. Additional funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative was confirmed in April 2017.









