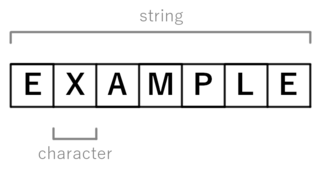
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed. A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. String may also denote more general arrays or other sequence data types and structures.
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learning Research Group (LRG) scientists, including Alan Kay, Dan Ingalls, Adele Goldberg, Ted Kaehler, Diana Merry, and Scott Wallace.

A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. Such programs are sometimes known as "notepad" software. Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to change files such as configuration files, documentation files and programming language source code.

In computer and machine-based telecommunications terminology, a character is a unit of information that roughly corresponds to a grapheme, grapheme-like unit, or symbol, such as in an alphabet or syllabary in the written form of a natural language.

The C shell is a Unix shell created by Bill Joy while he was a graduate student at University of California, Berkeley in the late 1970s. It has been widely distributed, beginning with the 2BSD release of the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) which Joy first distributed in 1978. Other early contributors to the ideas or the code were Michael Ubell, Eric Allman, Mike O'Brien and Jim Kulp.
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer.

In computing, PEEK and POKE are commands used in some high-level programming languages for accessing the contents of a specific memory cell referenced by its memory address. PEEK gets the byte located at the specified memory address. POKE sets the memory byte at the specified address. These commands originated with machine code monitors such as the DECsystem-10 monitor; these commands are particularly associated with the BASIC programming language, though some other languages such as Pascal and COMAL also have these commands. These commands are comparable in their roles to pointers in the C language and some other programming languages.

Adobe Authorware was an elearning authoring tool with its own interpreted, flowchart-based, graphical programming language. Authorware was used for creating interactive elearning programs that could integrate a range of multimedia content, particularly electronic educational technology applications. The flowchart model differentiated Authorware from other authoring tools, such as Adobe Flash and Adobe Director, which rely on a visual stage, time-line and script structure.
The Burroughs Large Systems Group produced a family of large 48-bit mainframes using stack machine instruction sets with dense syllables. The first machine in the family was the B5000 in 1961, which was optimized for compiling ALGOL 60 programs extremely well, using single-pass compilers. The B5000 evolved into the B5500 and the B5700. Subsequent major redesigns include the B6500/B6700 line and its successors, as well as the separate B8500 line.
Dartmouth BASIC is the original version of the BASIC programming language. It was designed by two professors at Dartmouth College, John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz. With the underlying Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), it offered an interactive programming environment to all undergraduates as well as the larger university community.

The IBM System/3 was an IBM midrange computer introduced in 1969, and marketed until 1985. It was produced by IBM Rochester in Minnesota as a low-end business computer aimed at smaller organizations that still used IBM 1400 series computers or unit record equipment. The first member of what IBM refers to as their "midrange" line, it also introduced the RPG II programming language. It is the first ancestor in the product line whose current version is the IBM i series and includes the highly successful AS/400.

PLATO, also known as Project Plato and Project PLATO, was the first generalized computer-assisted instruction system. Starting in 1960, it ran on the University of Illinois's ILLIAC I computer. By the late 1970s, it supported several thousand graphics terminals distributed worldwide, running on nearly a dozen different networked mainframe computers. Many modern concepts in multi-user computing were first developed on PLATO, including forums, message boards, online testing, email, chat rooms, picture languages, instant messaging, remote screen sharing, and multiplayer video games.

Commodore DOS, also known as CBM DOS, is the disk operating system used with Commodore's 8-bit computers. Unlike most other DOSes, which are loaded from disk into the computer's own RAM and executed there, CBM DOS is executed internally in the drive: the DOS resides in ROM chips inside the drive, and is run there by one or more dedicated MOS 6502 family CPUs. Thus, data transfer between Commodore 8-bit computers and their disk drives more closely resembles a local area network connection than typical disk/host transfers.
FOCAL is an interactive interpreted programming language based on JOSS and mostly used on Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series machines.
MBASIC is the Microsoft BASIC implementation of BASIC for the CP/M operating system. MBASIC is a descendant of the original Altair BASIC interpreters that were among Microsoft's first products. MBASIC was one of the two versions of BASIC bundled with the Osborne 1 computer. The name "MBASIC" is derived from the disk file name MBASIC.COM of the BASIC interpreter.

The Machine Operating System (MOS) or OS is a discontinued computer operating system (OS) used in Acorn Computers' BBC computer range. It included support for four-channel sound, graphics, file system abstraction, and digital and analogue input/output (I/O) including a daisy-chained expansion bus. The system was single-tasking, monolithic and non-reentrant.

BASICODE was a computer project intended to create a unified standard for the BASIC programming language. BASIC was available on many popular home computers, but there were countless variants that were mostly incompatible with each other. The project was initiated in 1980 by Hobbyscoop, a radio program of the Dutch broadcasting organisation Nederlandse Omroep Stichting (NOS).
Systems Programming Language, often shortened to SPL but sometimes known as SPL/3000, was a procedurally-oriented programming language written by Hewlett-Packard for the HP 3000 minicomputer line and first introduced in 1972. SPL was used to write the HP 3000's primary operating system, Multi-Programming Executive (MPE). Similar languages on other platforms were generically referred to as system programming languages, confusing matters.

The ZX Spectrum character set is the variant of ASCII used in the ZX Spectrum family computers. It is based on ASCII-1967 but the characters ^, ` and DEL are replaced with ↑, £ and ©. It also differs in its use of the C0 control codes other than the common BS and CR, and it makes use of the 128 high-bit characters beyond the ASCII range. The ZX Spectrum's main set of printable characters and system font are also used by the Jupiter Ace computer.
The Hack Computer is a theoretical computer design created by Noam Nisan and Shimon Schocken and described in their book, The Elements of Computing Systems: Building a Modern Computer from First Principles. In using the term “modern”, the authors refer to a digital, binary machine that is patterned according to the von Neumann architecture model.










