The 1360s BC is a decade which lasted from 1369 BC to 1360 BC.

Akhenaten, also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning c. 1353–1336 or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV.

Nefertiti was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. Some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as Neferneferuaten after her husband's death and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as Pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes.

Tiye was the Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III, mother of pharaoh Akhenaten and grandmother of pharaoh Tutankhamun; her parents were Yuya and Thuya. In 2010, DNA analysis confirmed her as the mummy known as "The Elder Lady" found in the tomb of Amenhotep II (KV35) in 1898.

Amenhotep III, also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great and Hellenized as Amenophis III, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors, he ruled Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya.

Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's ‘Great royal wife’, Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess. Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him. She disappears from history a few years before her royal husband's death. In previous years, she was thought to be mother of Tutankhamun, but recent DNA evidence suggests this is unlikely.
Thutmose, also known as "The King's Favourite and Master of Works, the Sculptor Thutmose", was an Ancient Egyptian sculptor. He flourished around 1350 BC, and is thought to have been the official court sculptor of the Egyptian pharaoh Akhenaten in the latter part of his reign. A German archaeological expedition digging in Akhenaten's deserted city of Akhetaten, known today as Amarna, found a ruined house and studio complex in early December 1912; the building was identified as that of Thutmose based on an ivory horse blinker found in a rubbish pit in the courtyard inscribed with his name and job title. Since it gave his occupation as "sculptor" and the building was clearly a sculpture workshop, the determination seemed logical and has proven to be accurate.

Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten, was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.
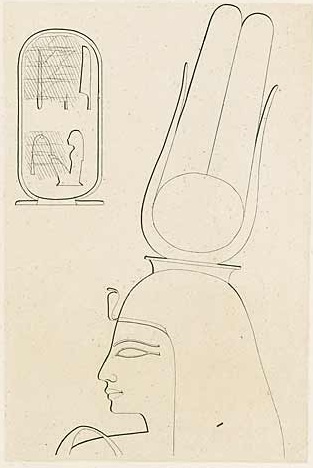
Tey was the Great Royal Wife of Kheperkheprure Ay, who was the penultimate pharaoh of Ancient Egypt's Eighteenth Dynasty. She also had been the wet nurse of Nefertiti.

Tushratta was a king of Mitanni, c. 1358–1335 BCE, at the end of the reign of Amenhotep III and throughout the reign of Akhenaten. He was the son of Shuttarna II. Tushratta stated that he was the grandson of Artatama I. His sister Gilukhipa and his daughter Tadukhipa were married to the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III; Tadukhipa later married Akhenaten who took over his father's royal harem.
Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit and another princess, Meritaten Tasherit are two princesses who appear in scenes dating to the later part of the reign of Akhenaten. The titles of at least one of the princess is of the form "[...-ta]sherit, born of [...], born of the King's Great Wife [...]. The inscription is damaged and the name of the mother and grandmother of the princesses has not been preserved. Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit has been known to archaeologists since 1938, when a talatat block with her picture and name was found in Hermopolis.
The Amarna Period was an era of Egyptian history during the later half of the Eighteenth Dynasty when the royal residence of the pharaoh and his queen was shifted to Akhetaten in what is now Amarna. It was marked by the reign of Amenhotep IV, who changed his name to Akhenaten in order to reflect the dramatic change of Egypt's polytheistic religion into one where the sun disc Aten was worshipped over all other gods. The Egyptian pantheon was restored under Akhenaten's successor, Tutankhamun.

Meketaten was the second daughter of six born to the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti. She likely lived between Year 4 and Year 14 of Akhenaten's reign. Although little is known about her, she is frequently depicted with her sisters accompanying her royal parents in the first two-thirds of the Amarna Period.
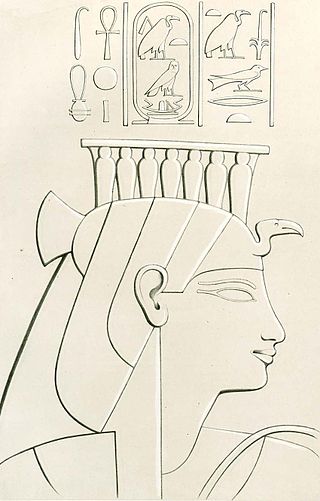
Mutemwiya was a minor wife of the Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Thutmose IV, and the mother of Pharaoh Amenhotep III. Mutemwiya's name means "Mut in the divine barque". While unconfirmed, it has been suggested that she acted as regent during the minority of her son Amenhotep III.

Neferneferuaten Tasherit or Neferneferuaten the younger was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty and the fourth daughter of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti.

Beketaten (14th century BCE) was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. Beketaten is considered to be the youngest daughter of Pharaoh Amenhotep III and his Great Royal Wife Tiye, thus the sister of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Her name means "Handmaid of Aten".
Pirissi and Tulubri are a pair of messengers of the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Pirissi and Tulubri are the messengers of King Tushratta of Mitanni, and are referenced in Amarna letters EA 27, 28, and EA 29,.
Dakhamunzu is the name of an Egyptian queen known from the Hittite annals The Deeds of Suppiluliuma, which were composed by Suppiluliuma I's son Mursili II. The identity of this queen has not yet been established with any degree of certainty and Dakhamunzu has variously been identified as either Nefertiti, Meritaten or Ankhesenamen. The identification of this queen is of importance both for Egyptian chronology and for the reconstruction of events during the late Eighteenth Dynasty.

Bek or Bak was the first chief royal sculptor during the reign of Pharaoh Akhenaten. His father Men held the same position under Akhenaten's father Amenhotep III; his mother Roi was a woman from Heliopolis.

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmosid Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.














