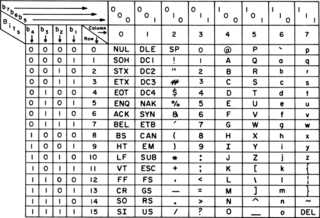
ASCII, an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are printable characters, which severely limited its scope. Modern computer systems have evolved to use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set.
UTF-8 is a variable-length character encoding standard used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from Unicode Transformation Format – 8-bit.

The Universal Product Code is a barcode symbology that is used worldwide for tracking trade items in stores.

Code 39 is a variable length, discrete barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 16388:2007.
Extended Unix Code (EUC) is a multibyte character encoding system used primarily for Japanese, Korean, and simplified Chinese (characters).
128 is the natural number following 127 and preceding 129.

PDF417 is a stacked linear barcode format used in a variety of applications such as transport, identification cards, and inventory management. "PDF" stands for Portable Data File. The "417" signifies that each pattern in the code consists of 4 bars and spaces in a pattern that is 17 units (modules) long. The PDF417 symbology was invented by Dr. Ynjiun P. Wang at Symbol Technologies in 1991. It is defined in ISO 15438.

Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 15417:2007. It is used for alphanumeric or numeric-only barcodes. It can encode all 128 characters of ASCII and, by use of an extension symbol (FNC4), the Latin-1 characters defined in ISO/IEC 8859-1. It generally results in more compact barcodes compared to other methods like Code 39, especially when the texts contain mostly digits. Code 128 was developed by the Computer Identics Corporation in 1981.

Code 93 is a barcode symbology designed in 1982 by Intermec to provide a higher density and data security enhancement to Code 39. It is an alphanumeric, variable length symbology. Code 93 is used primarily by Canada Post to encode supplementary delivery information. Every symbol includes two check characters.

Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) is a continuous two-width barcode symbology encoding digits. It is used commercially on 135 film, for ITF-14 barcodes, and on cartons of some products, while the products inside are labeled with UPC or EAN.
CPC Binary Barcode is Canada Post's proprietary symbology used in its automated mail sortation operations. This barcode is used on regular-size pieces of mail, especially mail sent using Canada Post's Lettermail service. This barcode is printed on the lower-right-hand corner of each faced envelope, using a unique ultraviolet-fluorescent ink.

The International Article Number is a standard describing a barcode symbology and numbering system used in global trade to identify a specific retail product type, in a specific packaging configuration, from a specific manufacturer. The standard has been subsumed in the Global Trade Item Number standard from the GS1 organization; the same numbers can be referred to as GTINs and can be encoded in other barcode symbologies defined by GS1. EAN barcodes are used worldwide for lookup at retail point of sale, but can also be used as numbers for other purposes such as wholesale ordering or accounting. These barcodes only represent the digits 0–9, unlike some other barcode symbologies which can represent additional characters.
Codabar is a linear barcode symbology developed in 1972 by Pitney Bowes Corp. It and its variants are also known as Codeabar, Ames Code, NW-7, Monarch, Code 2 of 7, Rationalized Codabar, ANSI/AIM BC3-1995 or USD-4. Although Codabar has not been registered for US federal trademark status, its hyphenated variant Code-a-bar is a registered trademark.

Code 11 is a barcode symbology developed by Intermec in 1977, and it is used primarily in telecommunications. The symbol can encode any length string consisting of the digits 0–9 and the dash character (-). A twelfth code represents the start/stop character, commonly printed as "*". One or two modulo-11 check digit(s) can be included.
Plessey Code is a 1D linear barcode symbology based on pulse-width modulation, developed in 1971 by The Plessey Company plc, a British-based company. It is one of the first barcode symbology, and is still used rarely in some libraries and for shelf tags in retail stores, in part as a solution to their internal requirement for stock control. The system was first used in the early 1970s by J.Sainsbury to identify all of its products on supermarket shelves for its product restocking system.

Industrial 2 of 5. is a variable length, discrete, two width symbology. Industrial 2 of 5 is a subset of two-out-of-five codes.

Codablock is a family of stacked 1D barcodes which was invented in Identcode Systeme GmbH in Germany in 1989 by Heinrich Oehlmann. Codablock barcodes are based on stacked Code 39 and Code 128 symbologies and have some advantages of 2D barcodes.

Matrix 2 of 5 is a variable length, discrete, two width symbology. Matrix 2 of 5 is a subset of two-out-of-five codes. Unlike Industrial 2 of 5 code, Matrix 2 of 5 can encode data not only with black bars but with white spaces.

DotCode is two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode invented in 2008 by Hand Held Products company to replace outdated Code 128. At this time, it is issued by Association for Automatic Identification and Mobility (AIM) as “ISS DotCode Symbology Specification 4.0”. DotCode consists of sparse black round dots and white spaces on white background. In case of black background round dots, creating barcode, can be white. DotCode was developed to use with high-speed industrial printers where printing accuracy can be low. Because DotCode by the standard does not require complicated elements like continuous lines or special shapes it can be applied with laser engraving or industrial drills.

Rectangular Micro QR Code is two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode invented and standardized in 2022 by Denso Wave as ISO/IEC 23941. rMQR Code is designed as a rectangular variation of QR code and has the same parameters and applications as original QR code. But rMQR Code is more suitable for the rectangular areas and has difference between width and height up to 19 in R7x139 version. In this way it can be used in places where 1D barcodes are used. rMQR Code can replace Code 128 and Code 39 barcodes with more effective data encoding.
















