Related Research Articles

Nanoarchaeota is a proposed phylum in the domain Archaea that currently has only one representative, Nanoarchaeum equitans, which was discovered in a submarine hydrothermal vent and first described in 2002.
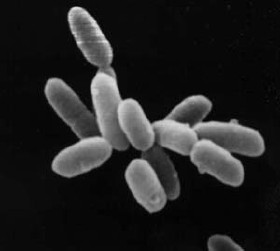
Euryarchaeota is a phylum of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, halobacteria, which survive extreme concentrations of salt, and some extremely thermophilic aerobes and anaerobes, which generally live at temperatures between 41 and 122 °C. They are separated from the other archaeans based mainly on rRNA sequences and their unique DNA polymerase.
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the domain Archaea, although some bacteria are also able to tolerate extreme temperatures. Some of these bacteria are able to live at temperatures greater than 100 °C, deep in the ocean where high pressures increase the boiling point of water. Many hyperthermophiles are also able to withstand other environmental extremes, such as high acidity or high radiation levels. Hyperthermophiles are a subset of extremophiles. Their existence may support the possibility of extraterrestrial life, showing that life can thrive in environmental extremes.

The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones.
Archaeoglobus is a genus of the phylum Euryarchaeota. Archaeoglobus can be found in high-temperature oil fields where they may contribute to oil field souring.

Sulfolobus is a genus of microorganism in the family Sulfolobaceae. It belongs to the archaea domain.

A thermoacidophile is an extremophilic microorganism that is both thermophilic and acidophilic; i.e., it can grow under conditions of high temperature and low pH. The large majority of thermoacidophiles are archaea or bacteria, though occasional eukaryotic examples have been reported. Thermoacidophiles can be found in hot springs and solfataric environments, within deep sea vents, or in other environments of geothermal activity. They also occur in polluted environments, such as in acid mine drainage.
Halobacteriaceae is a family in the order Halobacteriales and the domain Archaea. Halobacteriaceae represent a large part of halophilic Archaea, along with members in two other methanogenic families, Methanosarcinaceae and Methanocalculaceae. The family consists of many diverse genera that can survive extreme environmental niches. Most commonly, Halobacteriaceae are found in hypersaline lakes and can even tolerate sites polluted by heavy metals. They include neutrophiles, acidophiles, alkaliphiles, and there have even been psychrotolerant species discovered. Some members have been known to live aerobically, as well as anaerobically, and they come in many different morphologies. These diverse morphologies include rods in genus Halobacterium, cocci in Halococcus, flattened discs or cups in Haloferax, and other shapes ranging from flattened triangles in Haloarcula to squares in Haloquadratum, and Natronorubrum. Most species of Halobacteriaceae are best known for their high salt tolerance and red-pink pigmented members, but there are also non-pigmented species and those that require moderate salt conditions. Some species of Halobacteriaceae have been shown to exhibit phosphorus solubilizing activities that contribute to phosphorus cycling in hypersaline environments. Techniques such as 16S rRNA analysis and DNA-DNA hybridization have been major contributors to taxonomic classification in Halobacteriaceae, partly due to the difficulty in culturing halophilic Archaea.

In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmataceae are a family of the Thermoplasmatales. It contains only one genus, Thermoplasma. All species within Thermoplasmataceae are thermoacidophiles, and they grow at a temperature of 60 °C and pH 2. They were isolated from hydrothermal vents, fumaroles and similar environments.

In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmatales are an order of the Thermoplasmata. All are acidophiles, growing optimally at pH below 2. Picrophilus is currently the most acidophilic of all known organisms, being capable of growing at a pH of -0.06. Many of these organisms do not contain a cell wall, although this is not true in the case of Picrophilus. Most members of the Thermotoplasmata are thermophilic.
In taxonomy, Picrophilus is an archaean genus of the family Picrophilaceae.
Methanococcus is a genus of coccoid methanogens of the family Methanococcaceae. They are all mesophiles, except the thermophilic M. thermolithotrophicus and the hyperthermophilic M. jannaschii. The latter was discovered at the base of a “white smoker” chimney at 21°N on the East Pacific Rise and it was the first archaeal genome to be completely sequenced, revealing many novel and eukaryote-like elements.

Acidilobales are an order of archaea in the class Thermoprotei.

Acidilobus is a genus of archaea in the family Acidilobaceae.

Archaea is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this term has fallen out of use.

The outflow of acidic liquids and other pollutants from mines is often catalysed by acid-loving microorganisms; these are the acidophiles in acid mine drainage.
Thermoplasma acidophilum is an archaeon, the type species of its genus. T. acidophilum was originally isolated from a self-heating coal refuse pile, at pH 2 and 59 °C. Its genome has been sequenced.
Thermoplasma volcanium is a moderate thermoacidophilic archaea isolated from acidic hydrothermal vents and solfatara fields. It contains no cell wall and is motile. It is a facultative anaerobic chemoorganoheterotroph. No previous phylogenetic classifications have been made for this organism. Thermoplasma volcanium reproduces asexually via binary fission and is nonpathogenic.
Acidilobus saccharovorans is a thermoacidophilic species of anaerobic archaea. The species was originally described in 2009 after being isolated from hot springs in Kamchatka.

"Candidatus Aciduliprofundum boonei" is an obligate thermoacidophilic candidate species of archaea belonging to the phylum "Euryarchaeota". Isolated from acidic hydrothermal vent environments, "Ca. A. boonei" is the first cultured representative of a biogeochemically significant clade of thermoacidophilic archaea known as the "Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Euryarchaeota 2 (DHVE2)".
References
- ↑ See the NCBI webpage on Thermoplasma. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information . Retrieved 2014-06-25.