Related Research Articles

Andrew Stuart Tanenbaum, sometimes referred to by the handle ast, is an American-Dutch Physicist and Professor emeritus of Computer Science at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam in Netherlands. He is best known as the author of MINIX, a free Unix-like operating system for teaching purposes, and for his computer science textbooks, regarded as standard texts in the field. He regards his teaching job as his most important work. Since 2004 he has operated Electoral-vote.com, a website dedicated to analysis of polling data in federal elections in the United States.
grep is a command-line utility for searching plain-text data sets for lines that match a regular expression. Its name comes from the ed command g/re/p, which has the same effect. grep was originally developed for the Unix operating system, but later available for all Unix-like systems and some others such as OS-9.

Dial-up Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an Internet service provider (ISP) by dialing a telephone number on a conventional telephone line. Dial-up connections use modems to decode audio signals into data to send to a router or computer, and to encode signals from the latter two devices to send to another modem.

Computer chess includes both hardware and software capable of playing chess. Computer chess provides opportunities for players to practice even in the absence of human opponents, and also provides opportunities for analysis, entertainment and training.
The term netizen is a portmanteau of the English words internet and citizen, as in a "citizen of the net" or "net citizen". It describes a person actively involved in online communities or the Internet in general.

Henry Spencer is a Canadian computer programmer and space enthusiast. He wrote "regex", a widely used software library for regular expressions, and co-wrote C News, a Usenet server program. He also wrote The Ten Commandments for C Programmers. He is coauthor, with David Lawrence, of the book Managing Usenet. While working at the University of Toronto he ran the first active Usenet site outside the U.S., starting in 1981. His records from that period were eventually acquired by Google to provide an archive of Usenet in the 1980s.

USENIX is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit membership organization based in Berkeley, California and founded in 1975 that supports advanced computing systems and operating system (OS) research. Its stated mission is to foster technical excellence and innovation, support and disseminate research with a practical bias, provide a neutral forum for discussion of technical issues, and encourage computing outreach into the community at large.

A News, or Netnews Version A, originally known simply as news, was the first widely distributed program for serving and reading Usenet newsgroups. The program, written at Duke University by Steve Daniel and Tom Truscott, was released on a tape given out at the June 1980 USENIX conference held at the University of Delaware. Steve Daniel from Duke offered a presentation on the then-new Usenet network and invited attendees to join.
John R. Mashey is an American computer scientist, director and entrepreneur.

Mary Ann Horton, is a Usenet and Internet pioneer. Horton contributed to Berkeley UNIX (BSD), including the vi editor and terminfo database, created the first email attachment tool uuencode, and led the growth of Usenet in the 1980s.

In computer chess, a chess engine is a computer program that analyzes chess or chess variant positions, and generates a move or list of moves that it regards as strongest. A chess engine is usually a back end with a command-line interface with no graphics or windowing. Engines are usually used with a front end, a windowed graphical user interface such as Chessbase or WinBoard that the user can interact with via a keyboard, mouse or touchscreen. This allows the user to play against multiple engines without learning a new user interface for each, and allows different engines to play against each other. Many chess engines are now available for mobile phones and tablets, making them even more accessible.
World Computer Chess Championship (WCCC) is an event held periodically since 1974 where computer chess engines compete against each other. The event is organized by the International Computer Games Association. It is often held in conjunction with the Computer Olympiad, a collection of computer tournaments for other board games.

Barbara Liskov is an American computer scientist who is an Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Ford Professor of Engineering in its School of Engineering's electrical engineering and computer science department.
James Tice Ellis was an American computer scientist best known as the co-creator of Usenet, along with Tom Truscott.
This article documents the progress of significant human–computer chess matches.
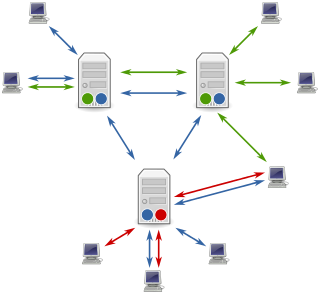
Usenet is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980. Users read and post messages to one or more categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to Internet forums that became widely used. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSs, though posts are stored on the server sequentially.

Thomas S. "Tom" Christiansen, nicknamed tchrist or occasionally thoth, is a Unix developer and user known for his work with the Perl programming language.

Michael Frederick Hauben was an American Internet theorist and author. He pioneered the study of the social impact of the Internet. Based on his interactive online research, in 1993 he coined the term and developed the concept of Netizen to describe an Internet user who actively contributes towards the development of the Net and acts as a citizen of the Net and of the world. Along with Ronda Hauben, he co-authored the 1997 book Netizens: On the History and Impact of Usenet and the Internet. Hauben's work is widely referenced in many scholarly articles and publications about the social impact of the Internet.
References
- ↑ Bonnett, Cara (May 17, 2010). "Duke to shut Usenet server, home to the first electronic newsgroups". Duke University.