
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents, and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and was patented in 1867. It rapidly gained wide-scale use as a more robust alternative to the traditional black powder explosives. It allows the use of nitroglycerine's favorable explosive properties while greatly reducing its risk of accidental detonation.

An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.
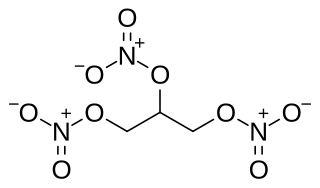
Nitroglycerin (NG), also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is an organic nitrate compound rather than a nitro compound, but the traditional name is retained. Discovered in 1847 by Ascanio Sobrero, nitroglycerin has been used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, namely dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. It is combined with nitrocellulose to form double-based smokeless powder, which has been used as a propellant in artillery and firearms since the 1880s.

Trinitrotoluene, more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.

Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN), also known as PENT, pentyl, PENTA, TEN, corpent, or penthrite, is an explosive material. It is the nitrate ester of pentaerythritol, and is structurally very similar to nitroglycerin. Penta refers to the five carbon atoms of the neopentane skeleton. PETN is a very powerful explosive material with a relative effectiveness factor of 1.66. When mixed with a plasticizer, PETN forms a plastic explosive. Along with RDX it is the main ingredient of Semtex and C4.

2,4,6-Trinitrophenylmethylnitramine or tetryl (C7H5N5O8) is an explosive compound used to make detonators and explosive booster charges.

A detonator, sometimes called a blasting cap in the US, is a small sensitive device used to provoke a larger, more powerful but relatively insensitive secondary explosive of an explosive device used in commercial mining, excavation, demolition, etc.
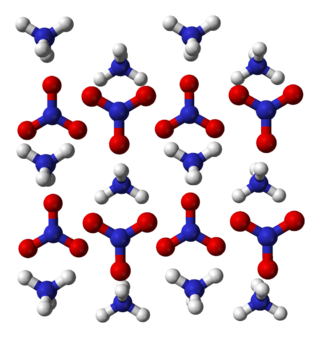
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.

ANFO ( AN-foh) (or AN/FO, for ammonium nitrate/fuel oil) is a widely used bulk industrial explosive. It consists of 94% porous prilled ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) (AN), which acts as the oxidizing agent and absorbent for the fuel, and 6% number 2 fuel oil (FO). The use of ANFO originated in the 1950s.
A triggering sequence, also called an explosive train or a firing train, is a sequence of events that culminates in the detonation of explosives. For safety reasons, most widely used high explosives are difficult to detonate. A primary explosive of higher sensitivity is used to trigger a uniform and predictable detonation of the main body of the explosive. Although the primary explosive itself is generally a more sensitive and expensive compound, it is only used in small quantities and in relatively safely packaged forms. By design there are low explosives and high explosives made such that the low explosives are highly sensitive and high explosives are comparatively insensitive. This not only affords inherent safety to the usage of explosives during handling and transport, but also necessitates an explosive triggering sequence or explosive train. The explosive triggering sequence or the explosive train essentially consists of an 'initiator', an 'intermediary' and the 'high explosive'.

Detonating cord is a thin, flexible plastic tube usually filled with pentaerythritol tetranitrate. With the PETN exploding at a rate of approximately 6,400 m/s (21,000 ft/s), any common length of detonation cord appears to explode instantaneously. It is a high-speed fuse which explodes, rather than burns, and is suitable for detonating high explosives. The detonation velocity is sufficient to use it for synchronizing multiple charges to detonate almost simultaneously even if the charges are placed at different distances from the point of initiation. It is used to reliably and inexpensively chain together multiple explosive charges. Typical uses include mining, drilling, demolitions, and warfare.

Smokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to black powder. Because of their similar use, both the original black powder formulation and the smokeless propellant which replaced it are commonly described as gunpowder. The combustion products of smokeless powder are mainly gaseous, compared to around 55% solid products for black powder. In addition, smokeless powder does not leave the thick, heavy fouling of hygroscopic material associated with black powder that causes rusting of the barrel.

Ammonal is an explosive made up of ammonium nitrate and aluminium powder, not to be confused with T-ammonal which contains trinitrotoluene as well to increase properties such as brisance. The mixture is often referred to as Tannerite, which is a brand of ammonal.

Methyl nitrate is the methyl ester of nitric acid and has the chemical formula CH3NO3. It is a colourless explosive volatile liquid.
Shock sensitivity is a comparative measure of the sensitivity to sudden compression of an explosive chemical compound. Determination of the shock sensitivity of a material intended for practical use is one important aspect of safety testing of explosives. A variety of tests and indices are in use, of which one of the more common is the Rotter Impact Test with results expressed as FoI At least four other impact tests are in common use, while various "gap tests" are used to measure sensitivity to blast shock.
Astrolite is the trade name of a family of explosives, invented by chemist Gerald Hurst in the 1960s during his employment with the Atlas Powder Company. The Astrolite family consists of two compounds, Astrolite G and Astrolite A. Both are two-part liquid-state high explosive mixtures, composed of ammonium nitrate oxidizer and hydrazine rocket fuel. The explosives were extensively studied, manufactured, and used in many countries because of their advantages of high energy, excellent performance, and wide application. They still find some use in commercial and civil blasting applications, but have mostly been superseded by cheaper and safer compounds, largely due to the expense and exceptionally poisonous nature of the hydrazine component.

Methylammonium nitrate is an explosive chemical with the molecular formula CH6N2O3, alternately CH3NH3+NO3−. It is the salt formed by the neutralization of methylamine with nitric acid. This substance is also known as methylamine nitrate and monomethylamine nitrate, not to be confused with methyl nitramine or monomethyl nitramine.
Explosive materials are produced in numerous physical forms for their use in mining, engineering, or military applications. The different physical forms and fabrication methods are grouped together in several use forms of explosives.

A water-gel explosive is a fuel sensitized explosive mixture consisting of an aqueous ammonium nitrate solution that acts as the oxidizer. Water gels that are cap-insensitive are referred to under United States safety regulations as blasting agents. Water gel explosives have a jelly-like consistency and come in sausage-like packing stapled shut on both sides.

Apache Nitrogen Products began in 1920 as an American manufacturer of nitroglycerin-based explosives (dynamite) for the mining industry and other regional users of dynamite. It occupies a historic location in Cochise County, Arizona and is one of its largest employers. The company changed its name to Apache Nitrogen Products in 1990.

















