
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) is a standard for data transmission in a local area network. It uses optical fiber as its standard underlying physical medium, although it was also later specified to use copper cable, in which case it may be called CDDI, standardized as TP-PMD, also referred to as TP-DDI.

A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high bandwidth of a HFC and RFoG network. They are commonly deployed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Europe.

In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common.

In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards.
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.

IEEE 802.16 is a series of wireless broadband standards written by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The IEEE Standards Board established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband for wireless metropolitan area networks. The Workgroup is a unit of the IEEE 802 local area network and metropolitan area network standards committee.
The Storage Management Initiative Specification, commonly called SMI-S, is a computer data storage management standard developed and maintained by the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA). It has also been ratified as an ISO standard. SMI-S is based upon the Common Information Model and the Web-Based Enterprise Management standards defined by the Distributed Management Task Force, which define management functionality via HTTP. The most recent approved version of SMI-S is available on the SNIA website.

Netnod AB is a private limited company based in Stockholm, Sweden, that operates Internet exchange points and manages one of the thirteen root name servers for the Domain Name System (DNS). It also distributes the official Swedish time through the Network Time Protocol (NTP). It is fully owned by the nonprofit foundation TU-stiftelsen / TU-foundation.
In computer networking, jumbo frames are Ethernet frames with more than 1500 bytes of payload, the limit set by the IEEE 802.3 standard. Commonly, jumbo frames can carry up to 9000 bytes of payload, but smaller and larger variations exist and some care must be taken using the term. Many Gigabit Ethernet switches and Gigabit Ethernet network interface controllers and some Fast Ethernet switches and Fast Ethernet network interface cards can support jumbo frames.

The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer.

The Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 or ERS 8600, previously known as the Passport 8600 or the Accelar 8000, is a modular chassis combination hardware router and switch used in computer networking. The system, originally designed and manufactured by Nortel, was manufactured by Avaya from 2009 until 2017. The system provided the 10G Ethernet equipment backbone for the 2010 Winter Olympics games, providing service for 15,000 VoIP Phones, 40,000 Ethernet connections and supporting 1.8 million live spectators. The system is configurable as a 1.440 Terabit Switch cluster using SMLT and R-SMLT protocols, to provide high reliability cluster failover.
IEEE 802.11 – or more correctly IEEE 802.11-1997 or IEEE 802.11-1999 – refer to the original version of the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard released in 1997 and clarified in 1999. Most of the protocols described by this early version are rarely used today.

The OpenFabrics Alliance is a non-profit organization that promotes remote direct memory access (RDMA) switched fabric technologies for server and storage connectivity. These high-speed data-transport technologies are used in high-performance computing facilities, in research and various industries.

The Ethernet Alliance was incorporated in the US state of California in August 2005 and officially launched in January 2006 as a non-profit industry consortium to promote and support Ethernet. The objectives were to provide an unbiased, industry-based source of educational information; to ensure interoperability among disparate, standards-based components and systems; to support the development of standards that support Ethernet technology; and to bring together the Ethernet industry to collaborate on the future of the technology.
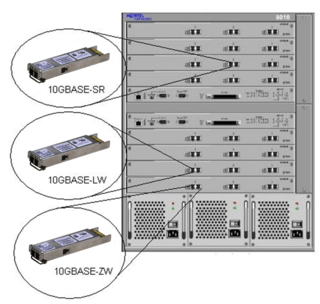
10 Gigabit Ethernet is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10 Gigabit Ethernet defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE.
iSCSI conformance testing is testing to determine whether an iSCSI Initiator/Target meets the iSCSI standard.

The OPEN Alliance is a non-profit, special interest group (SIG) of mainly automotive industry and technology providers collaborating to encourage wide scale adoption of Ethernet-based communication as the standard in automotive networking applications.
Avnu Alliance is a consortium of member companies working together to create an interoperable ecosystem of low-latency, time-synchronized, highly reliable networking devices using the IEEE open standard, Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and its Pro AV networking protocol, Milan. Avnu Alliance creates comprehensive certification programs to ensure interoperability of network devices. In the Professional Audio Video (AV) industry, Alliance member companies worked together to develop Milan: a standards-based, user-driven deterministic network protocol for professional media, that through certification, assures devices will work together at new levels of convenience, reliability, and functionality. Milan™ is a standards-based deterministic network protocol for real time media. Avnu Members may use the Avnu-certified or Milan-certified logo on devices that pass the conformance tests from Avnu. Not every device based on AVB or TSN is submitted for certification to the Avnu Alliance. The lack of the Avnu logo does not necessarily imply a device is incompatible with other Avnu-certified devices. The Alliance, in conjunction with other complimentary standards bodies and alliances, provides a united network foundation for use in professional AV, automotive, industrial control and consumer segments.
AES67 is a technical standard for audio over IP and audio over Ethernet (AoE) interoperability. The standard was developed by the Audio Engineering Society and first published in September 2013. It is a layer 3 protocol suite based on existing standards and is designed to allow interoperability between various IP-based audio networking systems such as RAVENNA, Livewire, Q-LAN and Dante.
25 Gigabit Ethernet and 50 Gigabit Ethernet are standards for Ethernet connectivity in a datacenter environment, developed by IEEE 802.3 task forces 802.3by and 802.3cd and are available from multiple vendors.












