Related Research Articles
Microsoft Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.

Liberty BASIC (LB) is a commercial computer programming language and integrated development environment (IDE). It has an interpreter, developed in Smalltalk, which recognizes its own dialect of the BASIC programming language. It runs on 16- and 32-bit Windows and OS/2.
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer.
An environment variable is a user-definable value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. Environment variables are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location to store temporary files, or the HOME or USERPROFILE variable to find the directory structure owned by the user running the process.

Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies.

Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a series of Microsoft Windows computer operating systems produced from 1995 to 2000, which were based on the Windows 95 kernel and its underlying foundation of MS-DOS, both of which were updated in subsequent versions. The first version in the 9x series was Windows 95, which was succeeded by Windows 98 and then Windows Me, which was the third and last version of Windows on the 9x line, until the series was superseded by Windows XP.

A COM file is a type of simple executable file. On the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) VAX operating systems of the 1970s, .COM was used as a filename extension for text files containing commands to be issued to the operating system. With the introduction of Digital Research's CP/M, the type of files commonly associated with COM extension changed to that of executable files. This convention was later carried over to DOS. Even when complemented by the more general EXE file format for executables, the compact COM files remained viable and frequently used under DOS.
JAWS is a computer screen reader program for Microsoft Windows that allows blind and visually impaired users to read the screen either with a text-to-speech output or by a refreshable Braille display. JAWS is produced by the Blind and Low Vision Group of Freedom Scientific.
DOSBox is a free and open-source emulator which runs software for MS-DOS compatible disk operating systems—primarily video games. It was first released in 2002, when DOS technology was becoming obsolete. Its adoption for running DOS games is widespread, with it being used in commercial re-releases of those games as well.
Virtual DOS machines (VDM) refer to a technology that allows running 16-bit/32-bit DOS and 16-bit Windows programs when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware.
MOPAC is a popular computer program used in computational chemistry. It is designed to implement semi-empirical quantum chemistry algorithms, and it runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
VisSim is a visual block diagram program for simulation of dynamical systems and model-based design of embedded systems, with its own visual language. It is developed by Visual Solutions of Westford, Massachusetts. Visual Solutions was acquired by Altair in August 2014 and its products have been rebranded as Altair Embed as a part of Altair's Model Based Development Suite. With Embed, you can develop virtual prototypes of dynamic systems. Models are built by sliding blocks into the work area and wiring them together with the mouse. Embed automatically converts the control diagrams into C-code ready to be downloaded to the target hardware.

International Futures (IFs) is a global integrated assessment model designed to help with thinking strategically and systematically about key global systems. It is housed at the Frederick S. Pardee Center for International Futures. Initially created by Barry B. Hughes of the Josef Korbel School of International Studies at the University of Denver in Colorado, the model is free for public use in both its online and downloadable forms.
Caliper Corporation was founded in 1983 as a developer of mapping software and is headquartered in Newton, Massachusetts.

Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE) is a free and open source ecosystem modelling software suite, initially started at NOAA by Jeffrey Polovina, but has since primarily been developed at the formerly UBC Fisheries Centre of the University of British Columbia. In 2007, it was named as one of the ten biggest scientific breakthroughs in NOAA's 200-year history. The NOAA citation states that Ecopath "revolutionized scientists' ability worldwide to understand complex marine ecosystems". Behind this lie more than three decades of development work in association with a thriving network of fisheries scientists such as Villy Christensen, Carl Walters and Daniel Pauly, and software engineers around the world. EwE is funded through projects, user contributions, user support, training courses and co-development collaborations. Per November 2021 there are an estimated 8000+ users across academia, non-government organizations, industry and governments in 150+ countries.
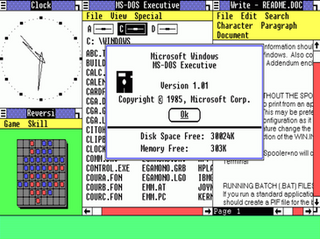
Windows 1.0 is the first major release of Microsoft Windows, a family of graphical operating systems for personal computers developed by Microsoft. It was first released to manufacturing in the United States on November 20, 1985, while the European version was released as Windows 1.02 in May 1986.

Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched in 1990. It features a new graphical user interface (GUI) where applications are represented as clickable icons, as opposed to the list of file names seen in its predecessors. Later updates would expand the software's capabilities, one of which added multimedia support for sound recording and playback, as well as support for CD-ROMs.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of Microsoft's MS-DOS and a rebranded version, IBM PC DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.
ProCite, a commercial reference management software program, was designed in the early 1980s by Victor Rosenberg, associate professor in the School of Library and Information Studies at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. ProCite was published in 1983 by Personal Bibliographic Software of Ann Arbor, Michigan. In 1996, ProCite was purchased by the Institute for Scientific Information, a division of Thomson Reuters. Thomson Reuters discontinued sales and support of Procite in May 2013.