Argentinosaurus is a genus of giant sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Argentina. Although it is only known from fragmentary remains, Argentinosaurus is one of the largest known land animals of all time, perhaps the largest, measuring 30–35 metres (98–115 ft) long and weighing 65–80 tonnes. It was a member of Titanosauria, the dominant group of sauropods during the Cretaceous. It is widely regarded by many paleontologists as the biggest dinosaur ever, and perhaps lengthwise the longest animal ever, though both claims have no concrete evidence yet.

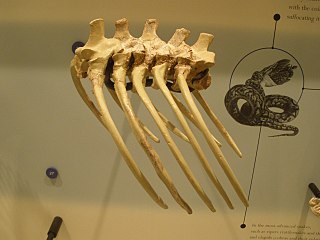
Sarcosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform and distant relative of living crocodilians that lived during the Early Cretaceous, from the late Hauterivian to the early Albian, 133 to 112 million years ago of what is now Africa and South America. The genus name comes from the Greek σάρξ (sarx) meaning flesh and σοῦχος (souchus) meaning crocodile. It was one of the largest pseudosuchians, with the largest specimen of S. imperator reaching approximately 9–9.5 metres (29.5–31.2 ft) long and weighing up to 3.45–4.3 metric tons. It is known from two species; S. imperator from the early Albian Elrhaz Formation of Niger, and S. hartti from the Late Hauterivian of northeastern Brazil. Other material is known from Morocco and Tunisia and possibly Libya and Mali.

Deinosuchus is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian, related to modern alligators and caimans, that lived 82 to 73 million years ago (Ma), during the late Cretaceous period. The name translates as "terrible crocodile" and is derived from the Greek deinos (δεινός), "terrible", and soukhos (σοῦχος), "crocodile". The first remains were discovered in North Carolina in the 1850s; the genus was named and described in 1909. Additional fragments were discovered in the 1940s and were later incorporated into an influential, though inaccurate, skull reconstruction at the American Museum of Natural History. Knowledge of Deinosuchus remains incomplete, but better cranial material found in recent years has expanded scientific understanding of this massive predator.
Gigantophis is an extinct genus represented by its sole member Gigantophis garstini, a giant snake. Before the Paleocene constrictor genus Titanoboa was described from Colombia in 2009, Gigantophis garstini was regarded as the largest snake ever recorded. It lived about 40 million years ago during the Eocene epoch of the Paleogene Period, in the Paratethys Sea, within the northern Sahara, where Egypt and Algeria are now located.

Stupendemys is an extinct genus of freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. It is the largest freshwater turtle known to have existed, with a carapace over 2 meters long. Its fossils have been found in northern South America, in rocks dating from the Middle Miocene to the very start of the Pliocene, about 13 to 5 million years ago. Male specimens are known to have possessed bony horns growing from the front edges of the shell and the discovery of the fossil of a young adult shows that the carapace of these turtles flattens with age. A fossil skull described in 2021 indicates that Stupendemys was a generalist feeder.

Palaeophis is an extinct genus of marine snake that is the type genus of the extinct snake family Palaeophiidae.
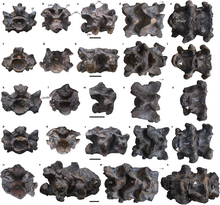
Madtsoiidae is an extinct family of mostly Gondwanan snakes with a fossil record extending from early Cenomanian to late Pleistocene strata located in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Southern Europe. Madtsoiidae include very primitive snakes, which like extant boas and pythons would likely dispatch their prey by constriction. Genera include some of the longest snakes known such as Vasuki, measuring at least 11–15 metres (36–49 ft) long, and the Australian Wonambi and Yurlunggur. As a grouping of basal forms the composition and even the validity of Madtsoiidae is in a state of flux as new pertinent finds are described, with more recent evidence suggesting that it is paraphyletic as previously defined.
Goronyosaurus is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. Fossils of Goronyosaurus are exclusively known from the Late Maastrichtian of the Iullemmeden Basin in West Africa, specifically the Dukamaje Formation of Niger and Nigeria and Farin Doutchi Formation of Niger. The type specimen was first described in 1930 as Mosasaurus nigeriensis, but subsequent remains revealed a highly unique set of adaptations that prompted the species to be reclassified as the only species of the new genus Goronyosaurus in 1972. These unique adaptations have made Goronyosaurus notoriously difficult to classify within the Mosasauridae and it is often left out of phylogenetic analyses, although most authors agree that Goronyosaurus belonged to Mosasauridae.
Pachycheilosuchus is an extinct genus of neosuchian from the Early Cretaceous of Texas, United States. Previously known, in part, as the "Glen Rose form", this crocodylomorph is notable for its procoelous vertebrae, otherwise found only in derived eusuchian crocodilians, a thick margin on the maxillae, and a shield of armor on the neck formed by the fusion of six individual scutes.

Taniwhasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasaurs that lived during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. It is a member of the subfamily Tylosaurinae, a lineage of mosasaurs characterized by a long toothless conical rostrum. Two valid species are attached to the genus, T. oweni and T. antarcticus, known respectively from the fossil record of present-day New Zealand and Antarctica. Two other species have been nominally classified within the genus, T. 'capensis' and T. 'mikasaensis', recorded in present-day South Africa and Japan, but their attribution remains problematic due to the fragmentary state of their fossils. The generic name literally means "taniwha lizard", referring to a supernatural aquatic creature from Māori mythology.
The Bluff Downs giant python is an extinct species of snake from Queensland, Australia, that lived during the Early Pliocene. Named in 2002, Liasis dubudingala was likely the biggest snake found in Australia, with a total length of up to 9 m (30 ft). This length rivals the largest extant snake species, the reticulated python from Asia and the green anaconda from South America. It may have fed on larger prey such as juvenile diprotodontids, but it is also possible that it was a skilled climber capable of catching birds and arboreal marsupials.

Titanoboa is an extinct genus of giant boid snake that lived during the middle and late Paleocene. Titanoboa was first discovered in the early 2000s by the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute who, along with students from the University of Florida, recovered 186 fossils of Titanoboa from La Guajira in northeastern Colombia. It was named and described in 2009 as Titanoboa cerrejonensis, the largest snake ever found at that time. It was originally known only from thoracic vertebrae and ribs, but later expeditions collected parts of the skull and teeth. Titanoboa is in the subfamily Boinae, being most closely related to other extant boines from Madagascar and the Pacific.
Cerrejonisuchus is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph. It is known from a complete skull and mandible from the Cerrejón Formation in northeastern Colombia, which is Paleocene in age. Specimens belonging to Cerrejonisuchus and to several other dyrosaurids have been found from the Cerrejón open-pit coal mine in La Guajira. The length of the rostrum is only 54-59% of the total length of the skull, making the snout of Cerrejonisuchus the shortest of all dyrosaurids.

Sanajeh is a genus of late Cretaceous madtsoiid snake from western India. A fossil described in 2010 from the Lameta Formation was found coiled around an egg and an adjacent skeleton of a 50 cm (19 in) long sauropod dinosaur hatchling. This suggests that the snake preyed on hatchling sauropods at nesting sites.

Astorgosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of crocodilian, closely related to true crocodiles, that lived in Pakistan during the late Oligocene period. This crocodile may have reached lengths of up to 8 m (26 ft) and is known to have preyed on many of the large mammals found in its environment. Bite marks of a large crocodile have been found on the bones of juvenile Paraceratherium, however if these were left by Astorgosuchus cannot be said with certainty. The genus contains a single species, Astorgosuchus bugtiensis, which was originally named as a species of Crocodylus in 1908 and was moved to its own genus in 2019.
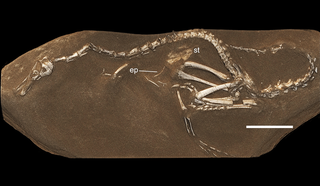
Halszkaraptor is a genus of waterfowl-like dromaeosaurid dinosaurs from Mongolia that lived during the Late Cretaceous period. It contains only one known species, Halszkaraptor escuilliei.

Pterosphenus is an extinct genus of marine snake of the Eocene period.

Maip is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, M. macrothorax, known from an incomplete, disarticulated skeleton. Maip may represent the largest megaraptorid known from South America, and possibly the world.
Powellophis is a genus of extinct Madtsoiid snake from the Mealla Formation of Argentina, dating back to the Paleocene. It is a monospecific genus, with the only species being P. andina. The genus name means "Jaime Powell's Snake". The name is constructed from the words Powell and ophis, the first in honor of the scientist who recovered the specimen, the late Dr. Jaime Powell, and the second meaning snake in Greek. The species name andina is named for the Andes region of Northwestern Argentina, where the fossil remains of the animal were discovered.
The Naredi Formation is a Cenozoic geologic formation in India. Remains of large snakes such as Vasuki are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, as well as other flora and fauna.