
A space telescope is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid several problems caused by the atmosphere, including the absorption or scattering of certain wavelengths of light, obstruction by clouds, and distortions due to atmospheric refraction such as twinkling. Space telescopes can also observe dim objects during the daytime, and they avoid light pollution which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky, and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage, and other types of information gathering.

The Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF) was a proposed project by NASA to construct a system of space telescopes for detecting extrasolar terrestrial planets. TPF was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2011. There were two telescope systems under consideration, the TPF-I, which had several small telescopes, and TPF-C, which used one large telescope.

Subaru Telescope is the 8.2-metre (320 in) telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, located at the Mauna Kea Observatory on Hawaii. It is named after the open star cluster known in English as the Pleiades. It had the largest monolithic primary mirror in the world from its commissioning until the Large Binocular Telescope opened in 2005.

The W. M. Keck Observatory is an astronomical observatory with two telescopes at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have 10 m (33 ft) aperture primary mirrors, and, when completed in 1993 and 1996, they were the largest optical reflecting telescopes in the world. They are currently the third and fourth largest.

The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space telescope launched in 2003, that was deactivated when operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder.

The Hale Telescope is a 200-inch (5.1 m), f/3.3 reflecting telescope at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, US, named after astronomer George Ellery Hale. With funding from the Rockefeller Foundation in 1928, he orchestrated the planning, design, and construction of the observatory, but with the project ending up taking 20 years he did not live to see its commissioning. The Hale was groundbreaking for its time, with double the diameter of the second-largest telescope, and pioneered many new technologies in telescope mount design and in the design and fabrication of its large aluminum coated "honeycomb" low thermal expansion Pyrex mirror. It was completed in 1949 and is still in active use.

The Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) is a scientific instrument for infrared astronomy, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), operating from 1997 to 1999, and from 2002 to 2008. Images produced by NICMOS contain data from the near-infrared part of the light spectrum.

A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star or other bright object so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the object's bright glare – can be resolved. Most coronagraphs are intended to view the corona of the Sun, but a new class of conceptually similar instruments are being used to find extrasolar planets and circumstellar disks around nearby stars as well as host galaxies in quasars and other similar objects with active galactic nuclei (AGN).

The New Worlds Mission is a proposed project comprising a large occulter flying in formation with a space telescope designed to block the light of nearby stars in order to observe their orbiting exoplanets. The observations could be taken with an existing space telescope or a dedicated visible light optical telescope optimally designed for the task of finding exoplanets. A preliminary research project was funded from 2005 through 2008 by NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) and headed by Webster Cash of the University of Colorado at Boulder in conjunction with Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Northrop Grumman, Southwest Research Institute and others. Since 2010 the project has been looking for additional financing from NASA and other sources in the amount of roughly US$3 billion including its own four-meter telescope. If financed and launched, it would operate for five years.

Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported as of January 2024 have been observed directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star.

Heidi B. Hammel is a planetary astronomer who has extensively studied Neptune and Uranus. She was part of the team imaging Neptune from Voyager 2 in 1989. She led the team using the Hubble Space Telescope to view Shoemaker-Levy 9's impact with Jupiter in 1994. She has used the Hubble Space Telescope and the Keck Telescope to study Uranus and Neptune, discovering new information about dark spots, planetary storms and Uranus' rings. In 2002, she was selected as an interdisciplinary scientist for the James Webb Space Telescope.

HR 8799 is a roughly 30 million-year-old main-sequence star located 133.3 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus. It has roughly 1.5 times the Sun's mass and 4.9 times its luminosity. It is part of a system that also contains a debris disk and at least four massive planets. Those planets, along with Fomalhaut b, were the first exoplanets whose orbital motion was confirmed by direct imaging. The star is a Gamma Doradus variable: its luminosity changes because of non-radial pulsations of its surface. The star is also classified as a Lambda Boötis star, which means its surface layers are depleted in iron peak elements. It is the only known star which is simultaneously a Gamma Doradus variable, a Lambda Boötis type, and a Vega-like star.

Fomalhaut b, formally named Dagon, is a directly imaged extrasolar object and former candidate planet observed near the A-type main-sequence star Fomalhaut, approximately 25 light-years away in the constellation of Piscis Austrinus. The object's discovery was initially announced in 2008 and confirmed in 2012 via images taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) on the Hubble Space Telescope. Under the working hypothesis that the object was a planet, it was reported in January 2013 that it had a highly elliptical orbit with a period of 1,700 Earth years. The object was one of those selected by the International Astronomical Union as part of NameExoWorlds, their public process for giving proper names to exoplanets. The process involved public nomination and voting for the new name. In December 2015, the IAU announced the winning name was Dagon.

The 215th meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) took place in Washington, D.C., Jan. 3 to Jan. 7, 2010. It is one of the largest astronomy meetings ever to take place as 3,500 astronomers and researchers were expected to attend and give more than 2,200 scientific presentations. The meeting was actually billed as the "largest Astronomy meeting in the universe". An array of discoveries were announced, along with new views of the universe that we inhabit; such as quiet planets like Earth - where life could develop are probably plentiful, even though an abundance of cosmic hurdles exist - such as experienced by our own planet in the past.

The Gemini Planet Imager (GPI) is a high contrast imaging instrument that was built for the Gemini South Telescope in Chile. The instrument achieves high contrast at small angular separations, allowing for the direct imaging and integral field spectroscopy of extrasolar planets around nearby stars. The collaboration involved in planning and building the Gemini Planet imager includes the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH), Dunlap Institute, Gemini Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics (HIA), Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Lab (LLNL), Lowell Observatory, SETI Institute, The Space Telescope Science Institute (STSCI), the University of Montreal, University of California, Berkeley, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC), University of Georgia.

The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope, and formerly the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST) is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit by May 2027.

Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch (VLT-SPHERE) is an adaptive optics system and coronagraphic facility at the Very Large Telescope (VLT). It provides direct imaging as well as spectroscopic and polarimetric characterization of exoplanet systems. The instrument operates in the visible and near infrared, achieving exquisite image quality and contrast over a small field of view around bright targets.
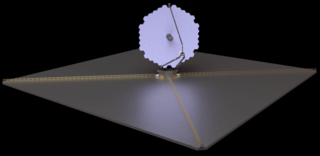
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR, is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astrophysics space mission concepts studied in preparation for the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey.

NIRCam is an instrument aboard the James Webb Space Telescope. It has two major tasks, as an imager from 0.6 to 5 μm wavelength, and as a wavefront sensor to keep the 18-section mirrors functioning as one. In other words, it is a camera and is also used to provide information to align the 18 segments of the primary mirror. It is an infrared camera with ten mercury-cadmium-telluride (HgCdTe) detector arrays, and each array has an array of 2048×2048 pixels. The camera has a field of view of 2.2×2.2 arcminutes with an angular resolution of 0.07 arcseconds at 2 μm. NIRCam is also equipped with coronagraphs, which helps to collect data on exoplanets near stars. It helps with imaging anything next to a much brighter object, because the coronagraph blocks that light.

The Habitable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx) is a space telescope concept that would be optimized to search for and image Earth-size habitable exoplanets in the habitable zones of their stars, where liquid water can exist. HabEx would aim to understand how common terrestrial worlds beyond the Solar System may be and determine the range of their characteristics. It would be an optical, UV and infrared telescope that would also use spectrographs to study planetary atmospheres and eclipse starlight with either an internal coronagraph or an external starshade.




















