
The Arctic fox, also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small species of fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in cold environments, and is best known for its thick, warm fur that is also used as camouflage. It has a large and very fluffy tail. In the wild, most individuals do not live past their first year but some exceptional ones survive up to 11 years. Its body length ranges from 46 to 68 cm, with a generally rounded body shape to minimize the escape of body heat.

Canidae is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid. The family includes three subfamilies: the Caninae, the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae. The Caninae are known as canines, and include domestic dogs, wolves, coyotes, foxes, jackals and other species.

Vulpes is a genus of the sub-family Caninae. The members of this genus are colloquially referred to as true foxes, meaning they form a proper clade. The word "fox" occurs in the common names of all species of the genus, but also appears in the common names of other canid species. True foxes are distinguished from members of the genus Canis, such as domesticated dogs, wolves, jackals and coyotes, by their smaller size (5–11 kg), longer, bushier tail, and flatter skull. They have black, triangular markings between their eyes and nose, and the tip of their tail is often a different color from the rest of their pelt. The typical lifespan for this genus is between two and four years, but can reach up to a decade.

The Tibetan people are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live in the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan, as well as in India, Nepal, and Bhutan.

The Tibetan Plateau, also known as Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and Qing–Zang Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South, and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres (970,000 sq mi). With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft) and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World".

The Tibetan fox, also known as the Tibetan sand fox, is a species of true fox endemic to the high Tibetan Plateau, Ladakh plateau, Nepal, China, Sikkim, and Bhutan, up to elevations of about 5,300 m (17,400 ft). It is listed as Least Concern in the IUCN Red List, on account of its widespread range in the Tibetan Plateau's steppes and semi-deserts.

The corsac fox, also known simply as a corsac, is a medium-sized fox found in steppes, semi-deserts and deserts in Central Asia, ranging into Mongolia and northern China. Since 2004, it has been classified as least concern by IUCN, but populations fluctuate significantly, and numbers can drop tenfold within a single year. It is also known as the steppe fox. The word "corsac" is derived from the Russian name for the animal, "korsák" (корса́к), derived ultimately from Turkic "karsak".

The Himalayan wolf is a canine of debated taxonomy. It is distinguished by its genetic markers, with mitochondrial DNA indicating that it is genetically basal to the Holarctic grey wolf, genetically the same wolf as the Tibetan and Mongolian wolf, and has an association with the African wolf. No striking morphological differences are seen between the wolves from the Himalayas and those from Tibet. The Himalayan wolf lineage can be found living in Ladakh in the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the mountains of Central Asia predominantly above 4,000 m (13,000 ft) in elevation because it has adapted to a low-oxygen environment, compared with other wolves that are found only at lower elevations.

The Caninae, known as canines, are one of three subfamilies found within the canid family. The other two canid subfamilies are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae. The Caninae includes all living canids and their most recent fossil relatives. Their fossils were first found in North America and dated to the Oligocene era, then spreading to Asia at the end of the Miocene era, some 7 million to 8 million years ago.

A hypercarnivore is an animal which has a diet that is more than 70% meat, either via active predation or by scavenging. The remaining non-meat diet may consist of non-animal foods such as fungi, fruits or other plant material. Some extant examples of hypercarnivorous animals include crocodilians, owls, shrikes, eagles, vultures, felids, most wild canids, cetaceans, snakes, spiders, scorpions, mantises, marlins, groupers, piranhas and most sharks. Every species in the family Felidae, including the domesticated cat, is a hypercarnivore in its natural state. Additionally, this term is also used in paleobiology to describe taxa of animals which have an increased slicing component of their dentition relative to the grinding component. In domestic settings, e.g. cats may have a diet designed from only plant and synthetic sources using modern processing methods. Feeding farmed animals such as alligators and crocodiles mostly or fully plant-based feed is sometimes done to save costs or as an evironmentally friendly alternative. Hypercarnivores need not be apex predators. For example, salmon are exclusively carnivorous, yet they are prey at all stages of life for a variety of organisms.

Ursoidea is a superfamily of arctoid carnivoran mammals that includes the families Subparictidae, Amphicynodontidae, and Ursidae. The last family includes the extant lineages of bears, as well as the extinct Hemicyoninae and Ursavinae.

The Trans himalaya, or "Gangdise – Nyenchen Tanglha range", is a 1,600-kilometre-long (990 mi) mountain range in China, India and Nepal, extending in a west–east direction parallel to the main Himalayan range. Located north of Yarlung Tsangpo river on the southern edge of the Tibetan Plateau, the Transhimalaya is composed of the Gangdise range to the west and the Nyenchen Tanglha range to the east.
Prototocyon is an extinct genus of small omnivorous canid that lived during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. It is closely related to the living bat-eared fox (Otocyon).

Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, in water, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at such altitudes challenging, though many species have been successfully adapted via considerable physiological changes. As opposed to short-term acclimatisation, high-altitude adaptation means irreversible, evolved physiological responses to high-altitude environments, associated with heritable behavioural and genetic changes. Among vertebrates, only few mammals and certain birds are known to have completely adapted to high-altitude environments.

Coelodonta thibetana, the Tibetan woolly rhinoceros, is an extinct species of the genus Coelodonta native to western Himalayas that lived during the middle Pliocene epoch. C. thibetana is known from the holotype IVPP V15908, a partially complete skull including incomplete lower jaw preserved with full dentition. It was first named by Tao Deng, Xiaoming Wang, Mikael Fortelius, Qiang Li, Yang Wang, Zhijie J. Tseng, Gary T. Takeuchi, Joel E. Saylor, Laura K. Säilä and Guangpu Xie in 2011.

The wild yak is a large, wild bovine native to the Himalayas. It is the ancestor of the domestic yak.

Amphimachairodus is an extinct genus of large machairodonts. It is also a member of the tribe Homotherini within Machairodontinae and is most closely related to such species as Xenosmilus, Homotherium itself, and Nimravides. It inhabited Eurasia, Northern Africa and North America during the late Miocene epoch.
Deng Tao is a Chinese palaeontologist at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, who has made important fossil discoveries on Cenozoic mammals. He is a professor of vertebrate palaeontology, deputy director of the Academic Committee, and deputy director of Key Laboratory of Evolutionary Systematics of Vertebrates at IVPP.
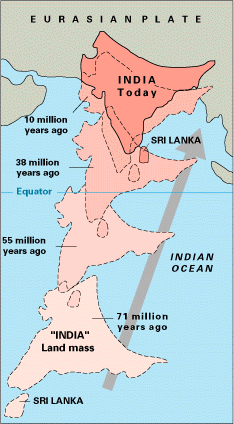
The paleogeography of the India–Asia collision system is the reconstructed geological and geomorphological evolution within the collision zone of the Himalayan orogenic belt. The continental collision between the Indian and Eurasian plate is one of the world's most renowned and most studied convergent systems. However, many mechanisms remain controversial. Some of the highly debated issues include the onset timing of continental collision, the time at which the Tibetan plateau reached its present elevation and how tectonic processes interacted with other geological mechanisms. These mechanisms are crucial for the understanding of Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution, paleoclimate and paleontology, such as the interaction between the Himalayas orogenic growth and the Asian monsoon system, as well as the dispersal and speciation of fauna. Various hypotheses have been put forward to explain how the paleogeography of the collision system could have developed. Important ideas include the synchronous collision hypothesis, the Lhasa-plano hypothesis and the southward draining of major river systems.

Cerdocyonina is an extant subtribe of the canines and is exclusively endemic to the Americas. Often described to be "fox-like" in appearance and behavior, they are more closely related to the wolf-like canids such as Canis than they are to the fox genus Vulpes. Its members are colloquially known as the South American canids and there are 10 extant species. They are sometimes referred to as South American foxes in the older literature, but the term zorro has been recommended by mammalogists to avoid confusion with the true foxes of the tribe Vulpini, which includes the genus Vulpes.

















