
The administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".
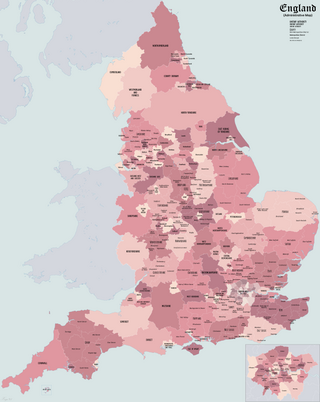
The subdivisions of England constitute a hierarchy of administrative divisions and non-administrative ceremonial areas.

The districts of England are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the structure of local government in England is not uniform, there are currently four principal types of district-level subdivision. There are a total of 296 districts made up of 36 metropolitan boroughs, 32 London boroughs, 164 two-tier non-metropolitan districts and 62 unitary authorities, as well as the City of London and the Isles of Scilly which are also districts, but do not correspond to any of these other categories. Some districts are styled as cities, boroughs or royal boroughs; these are purely honorific titles and do not alter the status of the district or the powers of their councils. All boroughs and cities are led by a mayor who in most cases is a ceremonial figure elected by the district council, but—after local government reform—is occasionally a directly elected mayor who makes most of the policy decisions instead of the council.
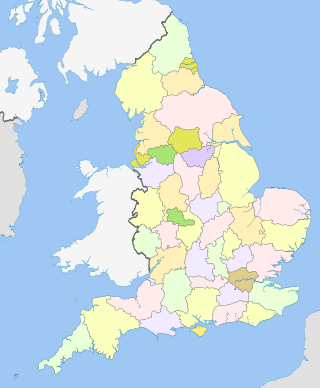
The counties of England are divisions of England. Counties have been used as administrative areas in England since Anglo-Saxon times. There are two main legal definitions of the counties in modern usage: the 84 counties for the purposes of local government, and the 48 counties for the purposes of lieutenancy, also termed the ceremonial counties.

Local government in England broadly consists of three layers: civil parishes, local authorities, and regional authorities. Every part of England is governed by at least one local authority, but parish councils and regional authorities do not exist everywhere. In addition, there are 31 police and crime commissioners, four police, fire and crime commissioners, and ten national park authorities with local government responsibilities. Local government is not standardised across the country, with the last comprehensive reform taking place in 1974.

The Metropolitan Borough of Wigan is a metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It is named after its largest town, Wigan but covers a far larger area which includes the towns of Atherton, Ashton-in-Makerfield, Golborne, Hindley, Ince-in-Makerfield, Leigh and Tyldesley. The borough also covers the villages and suburbs of Abram, Aspull, Astley, Bryn, Hindley Green, Lowton, Mosley Common, Orrell, Pemberton, Shevington, Standish, Winstanley and Worsley Mesnes. The borough is also the second-most populous district in Greater Manchester.

In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, which for centuries were the principal unit of secular and religious administration in most of England and Wales. Civil and religious parishes were formally split into two types in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894, which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry.
GSS codes are nine-character geocodes maintained by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics (ONS) to represent a wide range of geographical areas of the UK, for use in tabulating census and other statistical data. GSS refers to the Government Statistical Service of which ONS is part.
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74.
The counties of the United Kingdom are subnational divisions of the United Kingdom, used for the purposes of administrative, geographical and political demarcation. The older term, shire is historically equivalent to county. By the Middle Ages, county had become established as the unit of local government, at least in England. By the early 17th century, all of England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland had been separated into counties. In Scotland shire was the only term used until after the Act of Union 1707.

The Local Government Act 1888 was an Act of Parliament which established county councils and county borough councils in England and Wales. It came into effect on 1 April 1889, except for the County of London, which came into existence on 21 March at the request of the London County Council.

The Borough of Hartlepool is a local government district with borough status in County Durham, England. Since 1996 Hartlepool Borough Council has been a unitary authority, which gives it both district-level and county-level functions; it is independent of Durham County Council. It is named after its largest settlement, Hartlepool, where the council is based. The borough also includes a rural area to the west of the town. The population of the borough at the 2021 census was 92,571, of which over 95% (87,995) lived in the built-up area of Hartlepool itself.

The unitary authorities of England are a type of local authority responsible for all local government services in an area. They combine the functions of a non-metropolitan county council and a non-metropolitan district council, which elsewhere in England provide two tiers of local government.

The Council of the Isles of Scilly is a sui generis local government authority covering the Isles of Scilly off the west coast of Cornwall, England. It is currently made up of 16 seats, with all councillors being independents. The council was created in 1891 as the Isles of Scilly Rural District Council and was renamed in 1974.
This article documents the strengths of political parties in the 317 local authorities of England, 32 local authorities of Scotland, 22 principal councils of Wales and 11 local councils of Northern Ireland.

A civil parish is a country subdivision, forming the lowest unit of local government in England. There are 218 civil parishes in the ceremonial county of Cornwall, which includes the Isles of Scilly. The county is effectively parished in its entirety; only the unpopulated Wolf Rock is unparished. At the 2001 census, there were 501,267 people living in the current parishes, accounting for the whole of the county's population. The final unparished areas of mainland Cornwall, around St Austell, were parished on 1 April 2009 to coincide with the structural changes to local government in England.

North Lincolnshire Council is the local authority of North Lincolnshire, England. It is a unitary authority, having the powers of a county council and district council combined. It provides a full range of local government services including Council Tax billing, libraries, social services, town planning, and waste collection and disposal. It is also a local education authority. The council is based in Scunthorpe.

Southend-on-Sea City Council is the local authority of the Southend-on-Sea district in Essex, England. It is a unitary authority, having the powers of a non-metropolitan county and district council combined. It is a member of the East of England Local Government Association. It is based at Southend Civic Centre in Southend-on-Sea.
The Index of Place Names (IPN) in Great Britain is published by the Office for National Statistics.













