Related Research Articles

In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition which is suspected to be true due to preliminary supporting evidence, but for which no proof or disproof has yet been found. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis or Fermat's Last Theorem, have shaped much of mathematical history as new areas of mathematics are developed in order to prove them.
Enrico Bombieri is an Italian mathematician, known for his work in analytic number theory, Diophantine geometry, complex analysis, and group theory. He won a Fields Medal in 1974. Bombieri is currently Professor Emeritus in the School of Mathematics at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey.
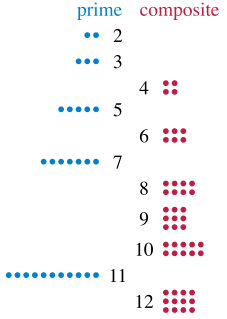
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.

Goldbach's conjecture is one of the oldest and best-known unsolved problems in number theory and all of mathematics. It states:

In number theory, Goldbach's weak conjecture, also known as the odd Goldbach conjecture, the ternary Goldbach problem, or the 3-primes problem, states that
The Riemann hypothesis is one of the most important conjectures in mathematics. It is a statement about the zeros of the Riemann zeta function. Various geometrical and arithmetical objects can be described by so-called global L-functions, which are formally similar to the Riemann zeta-function. One can then ask the same question about the zeros of these L-functions, yielding various generalizations of the Riemann hypothesis. Many mathematicians believe these generalizations of the Riemann hypothesis to be true. The only cases of these conjectures which have been proven occur in the algebraic function field case.

John Edensor Littlewood was a British mathematician. He worked on topics relating to analysis, number theory, and differential equations, and had a lengthy collaboration with G. H. Hardy and Mary Cartwright.

In mathematics, an L-function is a meromorphic function on the complex plane, associated to one out of several categories of mathematical objects. An L-series is a Dirichlet series, usually convergent on a half-plane, that may give rise to an L-function via analytic continuation. The Riemann zeta function is an example of an L-function, and one important conjecture involving L-functions is the Riemann hypothesis and its generalization.
In mathematics, analytic number theory is a branch of number theory that uses methods from mathematical analysis to solve problems about the integers. It is often said to have begun with Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet's 1837 introduction of Dirichlet L-functions to give the first proof of Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions. It is well known for its results on prime numbers and additive number theory.

Hilbert's eighth problem is one of David Hilbert's list of open mathematical problems posed in 1900. It concerns number theory, and in particular the Riemann hypothesis, although it is also concerned with the Goldbach Conjecture. The problem as stated asked for more work on the distribution of primes and generalizations of Riemann hypothesis to other rings where prime ideals take the place of primes. This problem has yet to be resolved.
In mathematics, the Lindelöf hypothesis is a conjecture by Finnish mathematician Ernst Leonard Lindelöf about the rate of growth of the Riemann zeta function on the critical line. This hypothesis is implied by the Riemann hypothesis. It says that, for any ε > 0,
In mathematics, a colossally abundant number is a natural number that, in a particular, rigorous sense, has many divisors. Formally, a number n is colossally abundant if and only if there is an ε > 0 such that for all k > 1,
In number theory, the Elliott–Halberstam conjecture is a conjecture about the distribution of prime numbers in arithmetic progressions. It has many applications in sieve theory. It is named for Peter D. T. A. Elliott and Heini Halberstam, who stated the conjecture in 1968.
In mathematics, the Bombieri–Vinogradov theorem is a major result of analytic number theory, obtained in the mid-1960s, concerning the distribution of primes in arithmetic progressions, averaged over a range of moduli. The first result of this kind was obtained by Mark Barban in 1961 and the Bombieri–Vinogradov theorem is a refinement of Barban's result. The Bombieri–Vinogradov theorem is named after Enrico Bombieri and A. I. Vinogradov, who published on a related topic, the density hypothesis, in 1965.
In number theory, Vinogradov's theorem is a result which implies that any sufficiently large odd integer can be written as a sum of three prime numbers. It is a weaker form of Goldbach's weak conjecture, which would imply the existence of such a representation for all odd integers greater than five. It is named after Ivan Matveyevich Vinogradov who proved it in the 1930s. Hardy and Littlewood had shown earlier that this result followed from the generalized Riemann hypothesis, and Vinogradov was able to remove this assumption. The full statement of Vinogradov's theorem gives asymptotic bounds on the number of representations of an odd integer as a sum of three primes.
Multiplicative number theory is a subfield of analytic number theory that deals with prime numbers and with factorization and divisors. The focus is usually on developing approximate formulas for counting these objects in various contexts. The prime number theorem is a key result in this subject. The Mathematics Subject Classification for multiplicative number theory is 11Nxx.

In mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis is a conjecture that the Riemann zeta function has its zeros only at the negative even integers and complex numbers with real part 1/2. Many consider it to be the most important unsolved problem in pure mathematics. It is of great interest in number theory because it implies results about the distribution of prime numbers. It was proposed by Bernhard Riemann (1859), after whom it is named.
A timeline of number theory.

Jean-Marc Deshouillers is a French mathematician, specializing in analytic number theory. He is a professor at the University of Bordeaux.
References
- ↑ Deshouillers, J.-M.; Effinger, G.; te Riele, H.; Zinoviev, D. (1997). "A complete Vinogradov 3-primes theorem under the Riemann Hypothesis". Electr. Res. Ann. of AMS. 3: 99–104.