
Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors.
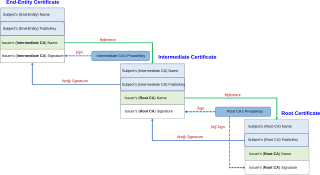
In cryptography and computer security, a root certificate is a public key certificate that identifies a root certificate authority (CA). Root certificates are self-signed and form the basis of an X.509-based public key infrastructure (PKI). Either it has matched Authority Key Identifier with Subject Key Identifier, in some cases there is no Authority Key identifier, then Issuer string should match with Subject string. For instance, the PKIs supporting HTTPS for secure web browsing and electronic signature schemes depend on a set of root certificates.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) are the three security certification programs developed after 2000 by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks. The Alliance defined these in response to serious weaknesses researchers had found in the previous system, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).

Baidu, Inc. is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in Internet-related services, products, and artificial intelligence (AI), headquartered in Beijing's Haidian District. It is one of the largest AI and Internet companies in the world. The holding company of the group is incorporated in the Cayman Islands. Baidu was incorporated in January 2000 by Robin Li and Eric Xu. Baidu has origins in RankDex, an earlier search engine developed by Robin Li in 1996, before he founded Baidu in 2000.
Shanda Group is a privately-owned multinational investment firm. With offices in Shanghai, Singapore, Hong Kong, New York and Redwood City, the firm invests in public markets, real estate and venture capital, focusing on companies in the fields of healthcare, financial services, media, and technology. The company was established in December 1999 as Shanda Interactive Entertainment Limited, an online gaming company known for publishing and operating games such as The World of Legend and Magical Land. By 2004 Shanda was the largest online game company in China, and its listing on the NASDAQ that year under ticker SNDA was the largest IPO for a Chinese internet company in the United States. Shanda Interactive later diversified and its gaming unit spun off in 2009, raising $1.04 billion in an IPO (GAME). Shanda Group was taken private in 2012 by its founders, and by 2017 it had $8 billion in net assets under management.

Line 1 of the Guangzhou Metro runs from Xilang to Guangzhou East Railway Station. Apart from Kengkou and Xilang, all stations in Line 1 are underground. The first section, from Xilang to Huangsha, opened on 28 June 1997, making Guangzhou the fourth city in mainland China to have a metro system. Construction took a total of 66 months. The total investment is 12.2616 billion yuan with an average cost per kilometer of 662.9 million yuan. The full line started operation on 28 June 1999. Line 1 is coloured yellow.
Shengqu Games is a publisher and operator of online games based in Shanghai, China. Founded in 1999 as Shanda Interactive Entertainment Limited, it spun off from Shanda Interactive in 2009 and is currently owned by Zhejiang Century Huatong. Shanda's published and operated games include AION, MapleStory, The World of Legend, The Age, Magical Land, Ragnarok Online, Dungeons & Dragons Online, Crazy Arcade, GetAmped and Final Fantasy XIV among others.

AirDrop is a proprietary wireless ad hoc service in Apple Inc.'s iOS, macOS, and visionOS operating systems, introduced in Mac OS X Lion and iOS 7, which can transfer files among supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices by means of close-range wireless communication. This communication takes place over Apple Wireless Direct Link 'Action Frames' and 'Data Frames' using generated link-local IPv6 addresses instead of the Wi-Fi chip's fixed MAC address.
WeChat or Weixin in Chinese ; lit. 'micro-message') is a Chinese instant messaging, social media, and mobile payment app developed by Tencent. First released in 2011, it became the world's largest standalone mobile app in 2018 with over 1 billion monthly active users. WeChat has been described as China's "app for everything" and a super-app because of its wide range of functions. WeChat provides text messaging, hold-to-talk voice messaging, broadcast (one-to-many) messaging, video conferencing, video games, mobile payment, sharing of photographs and videos and location sharing.

Zapya is a peer-to-peer file sharing application that allows users to transfer files of any size and of any format without the need of an Internet connection. Dewmobile, Inc. initially conceived Kuai Ya in Silicon Valley, California, USA to target the Chinese market in 2012. However, the demand for the application spread to neighboring countries such as Myanmar and Pakistan. When the international user base had grown to a reasonable size, Dewmobile created a separate application known as Zapya to publish on Apple App Store and Google Play Store. While Kuai Ya and Zapya are similar to each other, they include different APK and features in order to comply with Google Play Policies.
Ele.me is the online food delivery and local life service platform of Alibaba Group. Founded in 2008, it is now the second largest online food delivery service platform in China.

Chen Danian, also known as Danny Chen, is a notable Internet entrepreneur. He is the founder and CEO of LinkSure. The company launched the world’s largest and first-of-its-kind WiFi sharing app, WiFi Master Key.

KRACK is a replay attack on the Wi-Fi Protected Access protocol that secures Wi-Fi connections. It was discovered in 2016 by the Belgian researchers Mathy Vanhoef and Frank Piessens of the University of Leuven. Vanhoef's research group published details of the attack in October 2017. By repeatedly resetting the nonce transmitted in the third step of the WPA2 handshake, an attacker can gradually match encrypted packets seen before and learn the full keychain used to encrypt the traffic.
Wang Yan is a Chinese billionaire entrepreneur who co-founded the Chinese technology company Sina Corp. He formerly served as CEO and chairman of the company, and currently serves on the company's board of directors. As of November 2019, Wang is estimated by the Hurun Report and various Chinese media sources to have a fortune of US$8.9 billion. He is widely regarded as one of the most successful and influential figures in the Chinese technology industry, and known to be extremely private and media-shy.
Mole Manor is a massive multiplayer online game targeted at children ages 6 to 14; there is, however, no specific age or gender restriction on the game. The game was inspired by the online platform Club Penguin, where players can choose cartoon mole-avatars, decorate their virtual homes, adopt pets, and socialize with other players. They can wander through the virtual streets, chat with other users, go shopping, work, and play mini-games.

CM Browser is a web browser developed by Cheetah Mobile. The browser is based on Chromium and supports both the WebKit and Trident browser engines. Jinshan Network claims that CM Browser is the first secure dual-engine browser with a "browser intrusion prevention system".

The Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China, commonly referred to as the Chinese Cybersecurity Law, was enacted by the National People’s Congress with the aim of increasing data protection, data localization, and cybersecurity ostensibly in the interest of national security. The law is part of a wider series of laws passed by the Chinese government in an effort to strengthen national security legislation. Examples of which since 2014 have included a Law on National Intelligence, the National Security of the People’s Republic of China and laws on counter-terrorism and foreign NGO management, all passed within successive short timeframes of each other.
Tiantong is China's first mobile communications satellite system. The first satellite Tiantong-1-01 was launched on August 6, 2016 (UTC+8).
The Internet real-name system in China is a real-name system in which Internet service providers and Internet content providers in the People's Republic of China are required to collect users' real names, ID numbers, and other information when providing services. Since the implementation of the real-name system on the Internet may lead to the infringement and narrowing of the constitutionally protected speech space of Internet users, it has attracted concerns from all sides and generated much controversy in Chinese society. Only a few countries in the world, such as South Korea, have implemented a real-name system on the Internet.

Lost in the Stars is a 2022 Chinese mystery crime film directed by Cui Rui and Liu Xiang, and starring Zhu Yilong, Ni Ni and Janice Man. The film is adapted from Alexey Korenev's 1990 Soviet comedy film A Trap for Lonely Man and French playwright Robert Thomas' 1960 play Trap for a Lonely Man. It tells the story of He Fei's wife Li Muzi who disappeared mysteriously during the wedding anniversary trip. It's a film about a story of a shocking case. The film's style have been described by some critics as "Hitchcockian".











