
North Cascades National Park is an American national park in the state of Washington. At more than 500,000 acres (200,000 ha), it is the largest of the three National Park Service units that comprise the North Cascades National Park Complex. North Cascades National Park consists of a northern and southern section, bisected by the Skagit River that flows through the reservoirs of Ross Lake National Recreation Area. Lake Chelan National Recreation Area lies on the southern border of the south unit of the park. In addition to the two national recreation areas, other protected lands including several national forests and wilderness areas, as well as Canadian provincial parks in British Columbia, nearly surround the park. North Cascades National Park features the rugged mountain peaks of the North Cascades Range, the most expansive glacial system in the contiguous United States, the headwaters of numerous waterways, and vast forests with the highest degree of flora biodiversity of any American national park.
Lushootseed, also Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish or Skagit-Nisqually, is a language made up of a dialect continuum of several Salish tribes of modern-day Washington state. Lushootseed is one of the Coast Salish languages, one of two main divisions of the Salishan language family.

The Skagit River is a river in southwestern British Columbia in Canada and northwestern Washington in the United States, approximately 150 mi (240 km) long. The river and its tributaries drain an area of 1.7 million acres (690,000 hectares) of the Cascade Range along the northern end of Puget Sound and flows into the sound.

The Sauk River is a tributary of the Skagit River, approximately 45 miles (72 km) long, in northwestern Washington in the United States. It drains an area of the high Cascade Range in the watershed of Puget Sound north of Seattle. The river is a popular destination for fly fishing. It is a National Wild and Scenic River.

The Stillaguamish River is a river in the northwestern region of the U.S. state of Washington. It is mainly composed of two forks, the longer North Fork Stillaguamish and the South Fork Stillaguamish. The two forks join near Arlington. From there the Stillaguamish River proper flows for 22 miles (35 km) to Puget Sound. The river's watershed drains part of the Cascade Range north of Seattle.

The Skagit Valley lies in the northwestern corner of the state of Washington, United States. Its defining feature is the Skagit River, which snakes through local communities which include the seat of Skagit County, Mount Vernon, as well as Sedro-Woolley, Concrete, Lyman-Hamilton, and Burlington.

The Northwest School was an American art movement established in the Seattle area. It flourished in the 1930s–40s.

Ivan Doig was an American author and novelist, widely known for his sixteen fiction and non-fiction books set mostly in his native Montana, celebrating the landscape and people of the post-war American West.
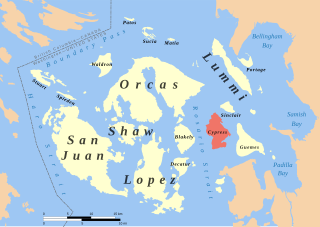
Cypress Island is the westernmost part of Skagit County, Washington and is about halfway between the mainland and offshore San Juan County. It is separated from Blakely Island to the west by Rosario Strait and from Guemes Island to the east by Bellingham Channel. The island has a land area of 5,500 acres (22 km2), and a population of 40 persons as of the 2000 United States Census.

The Pacific Northwest Trail (PNT) is a 1200-mile hiking trail running from the Continental Divide in Montana to the Pacific Ocean on Washington's Olympic Coast. Along the way, the PNT crosses three national parks, seven national forests, and two other national scenic trails. It travels against the grain of several mountain ranges, including the Continental Divide, Whitefish Divide, Purcells, Selkirks, Kettles, Cascades, and Olympics. It was designated as the Pacific Northwest National Scenic Trail by Congress in 2009.
Nard Jones (1904–1972) was an American writer, best known for his novels set in Oregon and the Pacific Northwest.

Fir Island is bounded by North and South Forks of the Skagit River and Skagit Bay of Puget Sound in the southwestern corner of Skagit County, Washington. Triangular in outline, 5.3 miles (8.5 km) east–west by 6.5 miles (10.5 km) north–south with an area of nearly 9,900 acres (40 km2), Fir Island is occupied by 195 families. The island is connected by bridge to the village of Conway, located on the east shore of the South Fork of the Skagit River. A second bridge, across the North Fork of the Skagit River, leads to La Conner, 3.7 miles (6.0 km) northwest. Near the northeast tip of Fir Island is the site of the 19th-century town of Skagit City which declined after upstream log jams were removed in 1877.

The Puget Sound region is a coastal area of the Pacific Northwest in the U.S. state of Washington, including Puget Sound, the Puget Sound lowlands, and the surrounding region roughly west of the Cascade Range and east of the Olympic Mountains. It is characterized by a complex array of saltwater bays, islands, and peninsulas carved out by prehistoric glaciers.
Skagit City was a town on the western bank of the South Fork Skagit River, less than a mile southeast of where the river forks north and south, in the U.S. state of Washington. The Barker's Trading Post along the river, opened in 1869, was partially or fully responsible for drawing people to settle at the townsite, which became an important river transportation center during the late 1800s, most notably in 1872. The city prospered until shortly before the 1880s, after river access to the upstream community of Mount Vernon, Washington was established and Mount Vernon began to prosper. By 1906, only one business remained in the entire town, and soon after World War II the town disappeared entirely. Today, the unincorporated community of Cedardale is the closest community to the former townsite at 2.4 miles (3.9 km) distance, and the name "Skagit City" has become simply a placename on the northeastern tip of Fir Island near where two distributaries diverge and carry Skagit River water into Skagit Bay, which branches off the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Skagit City is sometimes confused with the nearby tiny hamlet of Skagit Forks, which was just to the northwest at the divergence of the North and South Forks of the Skagit River. The town played an integral part in the settlement of Skagit County.

Tony Angell is an American wildlife artist, environmental educator, and writer. He has lived in Seattle, Washington, since 1959.
Eugene Nicolas Kozloff was an American marine biologist and botanist at Shannon Point Marine Center on Fidalgo Island, Washington. He was an emeritus professor of the Friday Harbor Laboratories, University of Washington, and is best known for writing field guides for the Pacific Northwest Region of the United States.

The Swinomish Indian Tribal Community, also known as the Swinomish Tribe, is a federally recognized Tribe located on Puget Sound in Washington. They are an Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest that includes the Central and Coast Salish peoples who lived in the Samish and Skagit River valleys, nearby coasts, and islands. The Tribe's population includes Swinomish, Lower Skagit, Upper Skagit, Kikiallus, and Samish peoples.

The Satsop Hills are foothills of the Olympic Mountains in Mason County, Washington north of Matlock, Washington, between Wynoochee Lake to the west and Lake Cushman to the east.

Fishtown was an informal artists' community housed in a cluster of old cabins and fishing shacks on the Skagit River delta in Skagit County, Washington, USA, from the late 1960s to the mid 1980s. It was part of the larger Skagit Valley arts community, centered on the town of La Conner, but was rustic and isolated, without electricity or plumbing, and tended to attract younger and more eccentric artists. It was home to several noted painters, poets, and sculptors. Charles Krafft, who went on to international attention and controversy as a ceramicist, was for over ten years the "self-proclaimed Mayor of Fishtown"; another longtime resident was Robert Sund, who, along with several other poets, developed a recognizable Pacific Northwest style of poetry. Scholar, painter, and poet Paul Hansen, who became a professor of Chinese languages and noted translator of early Chinese poetry lived in Fishtown for several years, and best-selling author Tom Robbins was a frequent visitor.

Yellow Aster Butte is a 6,241-foot (1,902-metre) Skagit Range summit located three miles south of the Canada–United States border, in Whatcom County of Washington state. It is situated within the Mount Baker Wilderness, on land managed by Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest. The nearest higher neighbor is Winchester Mountain, 1.77 miles (2.85 km) to the east, and Mount Larrabee is set 2.3 miles (3.7 km) to the northeast. The summit offers views of Mount Larrabee, Tomyhoi Peak, American Border Peak, Canadian Border Peak, Mount Shuksan, and Mount Baker. Precipitation runoff on the north side of the mountain drains into Tomyhoi Creek, whereas the west side of the mountain drains into Damfino Creek, and the south slope is drained by Swamp Creek.















