Microsoft Windows is a product line of proprietary graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and sub-families that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry -- Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Defunct families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone, and Windows Embedded Compact.

Microsoft Office, or simply Office, is a family of client software, server software, and services developed by Microsoft. It was first announced by Bill Gates on August 1, 1988, at COMDEX in Las Vegas. Initially a marketing term for an office suite, the first version of Office contained Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint. Over the years, Office applications have grown substantially closer with shared features such as a common spell checker, Object Linking and Embedding data integration and Visual Basic for Applications scripting language. Microsoft also positions Office as a development platform for line-of-business software under the Office Business Applications brand.

Palm OS was a mobile operating system initially developed by Palm, Inc., for personal digital assistants (PDAs) in 1996. Palm OS was designed for ease of use with a touchscreen-based graphical user interface. It was provided with a suite of basic applications for personal information management. Later versions of the OS were extended to support smartphones. The software appeared on the company's line of Palm devices while several other licensees have manufactured devices powered by Palm OS.

A Pocket PC is a class of personal digital assistant (PDA) that runs the Windows Mobile or Windows Embedded Compact operating system that has some of the abilities of modern desktop PCs. The name was introduced by Microsoft in 2000 as a rebranding of the Palm-size PC category. Some of these devices also had integrated phone and data capabilities, which were called Pocket PC Phone Edition. Windows "Smartphone" is another Windows CE based platform for non-touch flip phones or dumber phones.

Xandros, Inc. was a software company which sold Xandros Desktop, a Linux distribution. The name Xandros was derived from the X Window System and the Greek island of Andros. Xandros was founded in May 2001 by Linux Global Partners. The company was headquartered in New York City with its development office in Ottawa, Canada.

The iPAQ is a discontinued Pocket PC and personal digital assistant which was first unveiled by Compaq in April 2000.
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is a discontinued operating system developed by Microsoft for mobile and embedded devices. It was part of the Windows Embedded family and served as the foundation of several classes of devices including the Handheld PC, Pocket PC, Auto PC, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 and others.
Windows Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.

A handheld personal computer (PC), typically built around either a clamshell form factor or a gaming form factor with a gamepad integrated for video games, is a mobile device that is significantly smaller than any standard personal computer (PC), but based on the same principles as PCs. The clamshell form factor is sometimes referred to as a palmtop computer, not to be confused with Palmtop PC which was a name used mainly by Hewlett-Packard.

Internet Explorer Mobile was a mobile version of Internet Explorer developed by Microsoft, based on versions of the MSHTML (Trident) layout engine. IE Mobile comes loaded by default with Windows Phone and Windows CE. Later versions of Internet Explorer Mobile are based on the desktop version of Internet Explorer. Older versions however, called Pocket Internet Explorer, are not based on the same layout engine.

Microsoft Reader is a discontinued Microsoft application for reading e-books, first released in August 2000, that used its own .LIT format. It was available for Windows computers and Pocket PC PDAs. The name was also used later for an unrelated application for reading PDF and XPS files, first released with Windows 8 - this app was discontinued in 2018.
Windows Mobile 5.0, originally codenamed "Magneto", was released at Microsoft's Mobile and Embedded Developers Conference 2005 in Las Vegas, May 9–12, 2005. Microsoft offered mainstream support for Windows Mobile 5 through October 12, 2010, and extended support through October 13, 2015. It was first offered on the Dell Axim x51. It used the .NET Compact Framework 1.0 SP3, an environment for programs based on .NET. Windows Mobile 5.0 included Microsoft Exchange Server "push" functionality improvements that worked with Exchange 2003 SP2. The "push" functionality also required vendor/device support With AKU2 software upgrades all WM 5.0 devices supported DirectPush. This version featured increased battery life due to Persistent storage capability. Previously up to 50% of battery power was reserved just to maintain data in volatile RAM. This continued the trend of Windows-based devices moving from using RAM as their primary storage medium to the use of a combination of RAM and flash memory. Programs and frequently accessed data run in RAM, while most storage is in the flash memory. The OS seamlessly moves data between the two as needed. Everything is backed up in the flash memory, so unlike prior devices, WM5 devices lose no data if power is lost. New to 5.0, OS updates were released as Adaptation kit upgrades, with AKU 3.5 being the final released.

Windows SideShow was a feature by Microsoft introduced in Windows Vista to supply information such as e-mail, instant messages, and RSS feeds from a personal computer to a local or remote peripheral device or display. SideShow was intended to enhance the Windows experience by enabling new mobility scenarios for the Windows platform and by providing power saving benefits as part of Microsoft's broader efforts regarding a mobile initiative.

Nokia PC Suite is a discontinued software package used to establish an interface between Nokia mobile devices and computers that run the Microsoft Windows operating system. Its first release was in 1997, originally called Nokia Data Suite. It was replaced by Nokia Suite and integrated into the Ovi service suite.

Windows Mobile 6, formerly codenamed "Crossbow", is the version of Windows Mobile released on February 12, 2007 at the 3GSM World Congress 2007. It comes in three different versions: "Windows Mobile 6 Standard" for Smartphones, "Windows Mobile 6 Professional" for Pocket PCs with phone functionality, and "Windows Mobile 6 Classic" for Pocket PCs without cellular radios.
Pocket PC 2002, originally codenamed "Merlin", was a member of the Windows Mobile family of mobile operating systems, released on October 4, 2001. Like Pocket PC 2000, it was based on Windows CE 3.0.

Windows Mobile Device Center is a synchronization software program developed by Microsoft, and the successor to ActiveSync. It is designed to synchronize various content including music, video, contacts, calendar events, web browser favorites, and other files between Windows Mobile devices and the Microsoft Windows operating system.

The Motorola Q9c was a smartphone first released in 2007. Initially released as an upgrade to Motorola's Q Series, the Q9C contained a Windows Mobile 6 operating system, push email and instant messaging capabilities, a 1.3 megapixel camera, stereo sound, as well as Bluetooth and GPS navigation.
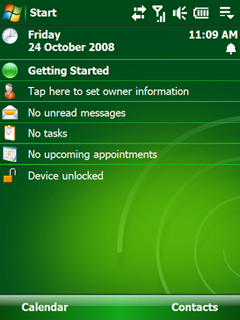
Windows Mobile 6.1 is a version of the Windows Mobile operating system, released on April 1, 2008. It is a minor upgrade to the Windows Mobile 6 platform with various performance enhancements and a redesigned Home screen featuring horizontal tiles that expand on clicking to display more information, although this new home screen is featured only on Windows Mobile Standard edition. This was not supported in the Professional edition. Several other changes such as threaded SMS, full page zooming in Internet Explorer and 'Domain Enroll' were also added, along with a "mobile" version of the Microsoft OneNote program and an interactive "Getting Started" wizard. Domain Enroll is functionality to connect the device to System Center Mobile Device Manager 2008, a product to manage mobile devices. The most apparent of the other differences is that the Standard version still creates automatic links for telephone numbers in Tasks and Appointments, which allows for the easier click and dial of stored telephone numbers within these Outlook items. This feature is not supported in the Professional version. Windows Mobile 6.1 also had improved bandwidth efficiency in its push-email protocol "Activesync" of "up to 40.02%"; this considerably improved battery life in many devices.
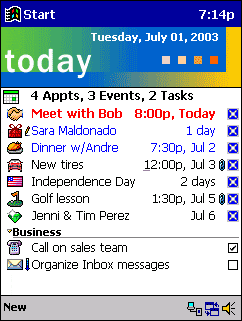
Pocket PC 2000 was the first member of the Windows Mobile family of mobile operating systems that was released on April 19, 2000, and was based on Windows CE 3.0. It is the successor to the operating system aboard Palm-size PCs. Backwards compatibility was retained with such Palm-size PC applications.