Related Research Articles

A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.

The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against market manipulation.
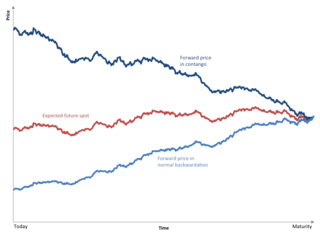
Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.

In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.

Financial regulation is a form of regulation or supervision, which subjects financial institutions to certain requirements, restrictions and guidelines, aiming to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system. This may be handled by either a government or non-government organization. Financial regulation has also influenced the structure of banking sectors by increasing the variety of financial products available. Financial regulation forms one of three legal categories which constitutes the content of financial law, the other two being market practices and case law.

In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.

A futures exchange or futures market is a central financial exchange where people can trade standardized futures contracts defined by the exchange. Futures contracts are derivatives contracts to buy or sell specific quantities of a commodity or financial instrument at a specified price with delivery set at a specified time in the future. Futures exchanges provide physical or electronic trading venues, details of standardized contracts, market and price data, clearing houses, exchange self-regulations, margin mechanisms, settlement procedures, delivery times, delivery procedures and other services to foster trading in futures contracts. Futures exchanges can be organized as non-profit member-owned organizations or as for-profit organizations. Futures exchanges can be integrated under the same brand name or organization with other types of exchanges, such as stock markets, options markets, and bond markets. Non-profit member-owned futures exchanges benefit their members, who earn commissions and revenue acting as brokers or market makers. For-profit futures exchanges earn most of their revenue from trading and clearing fees.

An investor is a person who allocates financial capital with the expectation of a future return (profit) or to gain an advantage (interest). Through this allocated capital most of the time the investor purchases some species of property. Types of investments include equity, debt, securities, real estate, infrastructure, currency, commodity, token, derivatives such as put and call options, futures, forwards, etc. This definition makes no distinction between the investors in the primary and secondary markets. That is, someone who provides a business with capital and someone who buys a stock are both investors. An investor who owns stock is a shareholder.

The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, Hong Kong, Tokyo, Dallas and Salt Lake City, and additional offices in other international financial centers. Goldman Sachs is the second largest investment bank in the world by revenue and is ranked 55th on the Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. It is considered a systemically important financial institution by the Financial Stability Board.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.

The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) is an independent agency of the US government created in 1974 that regulates the U.S. derivatives markets, which includes futures, swaps, and certain kinds of options.

The Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000 (CFMA) is United States federal legislation that ensured financial products known as over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives remained unregulated. It was signed into law on December 21, 2000 by President Bill Clinton. It clarified the law so most OTC derivative transactions between "sophisticated parties" would not be regulated as "futures" under the Commodity Exchange Act of 1936 (CEA) or as "securities" under the federal securities laws. Instead, the major dealers of those products would continue to have their dealings in OTC derivatives supervised by their federal regulators under general "safety and soundness" standards. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission's (CFTC) desire to have "functional regulation" of the market was also rejected. Instead, the CFTC would continue to do "entity-based supervision of OTC derivatives dealers". The CFMA's treatment of OTC derivatives such as credit default swaps has become controversial, as those derivatives played a major role in the financial crisis of 2008 and the subsequent 2008–2012 global recession.

The Korea Composite Stock Price Index or KOSPI (코스피지수) is the index of all common stocks traded on the Stock Market Division—previously, Korea Stock Exchange—of the Korea Exchange. It is the representative stock market index of South Korea, like the S&P 500 in the United States.

Henry "Hank" Merritt Paulson Jr. is an American banker and financier who served as the 74th United States Secretary of the Treasury from 2006 to 2009. Prior to his role in the Department of the Treasury, Paulson was the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of major investment bank Goldman Sachs.
The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, often called the "bank bailout of 2008" or the "Wall Street bailout", was proposed by Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, passed by the 110th United States Congress, and signed into law by President George W. Bush. It became law as part of Public Law 110-343 on October 3, 2008, in the midst of the financial crisis of 2007–2008. It created the $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) to purchase toxic assets from banks. The funds were mostly redirected to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions while the Treasury continued to examine the usefulness of targeted asset purchases.
AIG Financial Products Corporation (AIGFP) is a subsidiary of the American International Group, headquartered in New York, New York, with major operations in London. The collapse of AIG Financial Products, headquartered in Wilton, Connecticut, is considered to have played a pivotal role in the global financial crisis of 2008–2009.
The subprime mortgage crisis reached a critical stage during the first week of September 2008, characterized by severely contracted liquidity in the global credit markets and insolvency threats to investment banks and other institutions.

Jill E. Sommers was sworn in as a commissioner of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission on August 8, 2007 to a term that expired April 13, 2009. She was nominated on July 20, 2009 by President Barack Obama to serve a five-year second term., and confirmed by the United States Senate on October 8, 2009.

The Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) is a United States federal government organization, established by Title I of the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, which was signed into law by President Barack Obama on July 21, 2010. The Office of Financial Research is intended to provide support to the council.

Goldman Sachs controversies are the controversies surrounding the American multinational investment bank Goldman Sachs. The bank and its activities have generated substantial controversy and legal issues around the world and is the subject of speculation about its involvement in global finance and politics. In a widely publicized story in Rolling Stone, Matt Taibbi characterized Goldman Sachs as a "great vampire squid" sucking money instead of blood, allegedly engineering "every major market manipulation since the Great Depression."
References
- 1 2 "Executive Orders" (published August 15, 2016). March 18, 1988. Retrieved August 10, 2018., which appears and purports to be a copy of the original: National Archives And Records Administration (March 18, 1988). "Executive Order 12631 of March 18 1988: Working Group on Financial Markets". Federal Register. Library of Congress (published March 22, 1988). 53 (55): 9421. FR Doc. 88-6380. Retrieved August 10, 2018.
- ↑ "Plunge Protection Team". The Washington Post. February 23, 1997.
- ↑ Evans-Pritchard, Ambrose (October 30, 2006). "Monday view: Paulson re-activates secretive support team to prevent markets meltdown" . London: Telegraph UK. Retrieved September 15, 2008.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Wachman, Richard; Jamie Doward Observer (September 16, 2001). "Fed to prop up Wall St". London: Guardian Unlimited. Retrieved September 15, 2008.
- ↑ Fromson, Brett. D. (February 23, 1997). "Plunge Protection Team". Washington Post. Retrieved September 15, 2008.
- ↑ Baum, Carolyn (July 31, 2007). "Rubin Should Teach Paulson Secret PPT Handshake". Bloomberg. Retrieved September 15, 2008.
- ↑ Gross, Daniel (August 3, 2008). "Riches to Rags". The New York Times.
- ↑ Bennett, Drake (September 21, 2008). "The Operators Behind a seductive Wall Street conspiracy theory" . The Boston Globe. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ↑ Crawshaw, Julie (January 10, 2010). "Biderman: Fed, Gov't Likely Rigging Market Rally". Money News. Retrieved April 24, 2012.
- ↑ "Sprott Asset Management" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 31, 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ↑ "Federal Government Manipulating Equities Market?". Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved August 29, 2007.
- 1 2 Phillips, K. (2008). Bad Money: Reckless Finance, Failed Politics, and the Global Crisis of American Capitalism . Viking. ISBN 978-0-670-01907-6.
