
A superhero or superheroine is a stock character that typically possesses superpowers, abilities beyond those of ordinary people, and fits the role of the hero, typically using their powers to help the world become a better place, or dedicating themselves to protecting the public and fighting crime. Superhero fiction is the genre of fiction that is centered on such characters, especially, since the 1930s, in American comic books, as well as in Japanese media.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors with Internet connectivity for their mobile devices.
Ultra-wideband is a radio technology that can use a very low energy level for short-range, high-bandwidth communications over a large portion of the radio spectrum. UWB has traditional applications in non-cooperative radar imaging. Most recent applications target sensor data collection, precise locating, and tracking. UWB support started to appear in high-end smartphones in 2019.

Bizarro is a supervillain/anti-hero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by writer Otto Binder and artist George Papp as a "mirror image" of Superman, and first appeared in Superboy #68 (1958). Debuting in the Silver Age of Comic Books, the character has often been portrayed as an antagonist to Superman, though on occasion he also takes on an antihero role.
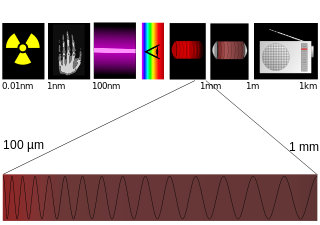
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency (THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of frequencies from 0.3 to 3 terahertz (THz), although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and is considered by some sources as 30 THz. One terahertz is 1012 Hz or 1000 GHz. Wavelengths of radiation in the terahertz band correspondingly range from 1 mm to 0.1 mm = 100 µm. Because terahertz radiation begins at a wavelength of around 1 millimeter and proceeds into shorter wavelengths, it is sometimes known as the submillimeter band, and its radiation as submillimeter waves, especially in astronomy. This band of electromagnetic radiation lies within the transition region between microwave and far infrared, and can be regarded as either.

X: The Man with the X-ray Eyes is a 1963 American science fiction horror film in Pathécolor, produced and directed by Roger Corman, from a script by Ray Russell and Robert Dillon. The film stars Ray Milland as a scientist who develops a method to extend the range of his vision, which results in unexpected complications. Comedian Don Rickles co-stars in one of his few dramatic roles. Diana Van der Vlis and veteran character actor Morris Ankrum also make appearances.

A hotspot is a physical location where people can obtain Internet access, typically using Wi-Fi technology, via a wireless local-area network (WLAN) using a router connected to an Internet service provider.

Gesture recognition is a topic in computer science and language technology with the goal of interpreting human gestures via mathematical algorithms. It is a subdiscipline of computer vision. Gestures can originate from any bodily motion or state, but commonly originate from the face or hand. Focuses in the field include emotion recognition from face and hand gesture recognition since they are all expressions. Users can make simple gestures to control or interact with devices without physically touching them. Many approaches have been made using cameras and computer vision algorithms to interpret sign language, however, the identification and recognition of posture, gait, proxemics, and human behaviors is also the subject of gesture recognition techniques. Gesture recognition can be seen as a way for computers to begin to understand human body language, thus building a better bridge between machines and humans than older text user interfaces or even GUIs, which still limit the majority of input to keyboard and mouse and interact naturally without any mechanical devices.

X-ray specs or X-ray glasses are an American novelty item, purported to allow users to see through or into solid objects. In reality, the spectacles merely create an optical illusion; no X-rays are involved. The current paper version is sold under the name "X-Ray Spex"; a similar product is sold under the name "X-Ray Gogs".

Legion of Super Heroes is an American animated television series produced by Warner Bros. Animation, adapted from the DC Comics series of the same name. It debuted on September 23, 2006, and centers on a young Superman's adventures in the 31st century, fighting alongside the eponymous group of superheroes. The show was produced by one of its main character designers James Tucker, a co-producer of the Justice League Unlimited series, for the Kids' WB line on The CW network.
In Greek mythology, Lynceus was a Messenian prince and one of the Argonauts who served as a lookout on the Argo. He also participated in the hunt for the Calydonian boar.
WirelessHD, also known as UltraGig, is a proprietary standard owned by Silicon Image for wireless transmission of high-definition video content for consumer electronics products. The consortium currently has over 40 adopters; key members behind the specification include Broadcom, Intel, LG, Panasonic, NEC, Samsung, SiBEAM, Sony, Philips and Toshiba. The founders intend the technology to be used for Consumer Electronic devices, PCs, and portable devices.

Captain Dynamo is a fictional character, a comic book superhero, created by writer Jay Faerber and artist Fran Bueno, who first appeared as a supporting character in Noble Causes: Extended Family #2 by Image Comics.
Wi-Fi positioning system is a geolocation system that uses the characteristics of nearby Wi-Fi hotspots and other wireless access points to discover where a device is located.
Mobile data offloading is the use of complementary network technologies for delivering data originally targeted for cellular networks. Offloading reduces the amount of data being carried on the cellular bands, freeing bandwidth for other users. It is also used in situations where local cell reception may be poor, allowing the user to connect via wired services with better connectivity.

Victor Bahl is an Indian Technical Fellow and CTO of Azure for Operators at Microsoft. He started networking research at Microsoft. He is known for his research contributions to white space radio data networks, radio signal-strength based indoor positioning systems, multi-radio wireless systems, wireless network virtualization, edge computing, and for bringing wireless links into the datacenter. He is also known for his leadership of the mobile computing community as the co-founder of the ACM Special Interest Group on Mobility of Systems, Users, Data, and Computing (SIGMOBILE). He is the founder of international conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services Conference (MobiSys), and the founder of ACM Mobile Computing and Communications Review, a quarterly scientific journal that publishes peer-reviewed technical papers, opinion columns, and news stories related to wireless communications and mobility. Bahl has received important awards; delivered dozens of keynotes and plenary talks at conferences and workshops; delivered over six dozen distinguished seminars at universities; written over hundred papers with more than 65,000 citations and awarded over 100 US and international patents. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery, IEEE, and American Association for the Advancement of Science.
A WiTrack is a 3-D motion tracking sensor that is capable of monitoring human body movements. This sensor is able to serve three main purposes, such functions being the following: turning on/off home appliances, tracking a lethal fall, and improving gaming experience. This new piece of technology, currently in its developing stages, was developed primarily by Fadel Adib and Dina Katabi at MIT. The WiTrack functions through the use of radio signals, which help perform the task of finding a person's current location, the radio signals not been affected at all by walls and other physical obstacles present.

Moustafa Youssef is an Egyptian computer scientist who was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2019 for contributions to wireless location tracking technologies and a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in 2019 for contributions to location tracking algorithms. He is the first and only ACM Fellow in the Middle East and Africa.
Yasamin Mostofi is an Iranian-American Scientist and a Professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of California Santa Barbara. Yasamin’s research is multi-disciplinary, expanding wireless communications, sensing, and control/robotics.
WiFi Sensing uses existing Wi-Fi signals to detect events or changes such as motion, gesture recognition, and biometric measurement. WiFi Sensing is a combination of Wi-Fi and RADAR sensing technology working in tandem to enable usage of the same Wi-Fi transceiver hardware and RF spectrum for both communication and sensing.











