The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dynamics at an assembly plant located in Kearny Mesa. Atlas became operational as an ICBM in October 1959 and was quickly obsoleted by new development, being retired as a missile by 1965. However, Atlas-derived launch vehicles have a long history as space launchers.

The PGM-17A Thor was the first operational ballistic missile of the U.S. Air Force (USAF). Named after the Norse god of thunder, it was deployed in the United Kingdom between 1959 and September 1963 as an intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with thermonuclear warheads. Thor was 65 feet (20 m) in height and 8 feet (2.4 m) in diameter. It was later augmented in the U.S. IRBM arsenal by the Jupiter.
Red Snow was the British developed thermonuclear weapon. Its physics package was shared with the United States and was used in the development of the United States W28 nuclear warhead used in the B28 nuclear bomb and AGM-28 Hound Dog missile, with an explosive yield of approximately 1.8 megaton.

The B28, originally Mark 28, was a thermonuclear bomb carried by U.S. tactical fighter bombers, attack aircraft and bomber aircraft. From 1962 to 1972 under the NATO nuclear weapons sharing program, American B28s also equipped six Europe-based Canadian CF-104 squadrons known as the RCAF Nuclear Strike Force. It was also supplied for delivery by UK-based Royal Air Force Valiant and Canberra aircraft assigned to NATO under the command of SACEUR. In addition, certain U.S. Navy carrier based attack aircraft such as the A3D Skywarrior, A4D Skyhawk, and A3J Vigilante were equipped to carry the MK 28.

The W54 was one of the smallest nuclear warheads deployed by the United States. It was a very compact implosion-type nuclear weapon design, designed for tactical use and had a very low yield for a nuclear weapon, in the range of 10 to 1,000 tons TNT equivalent.
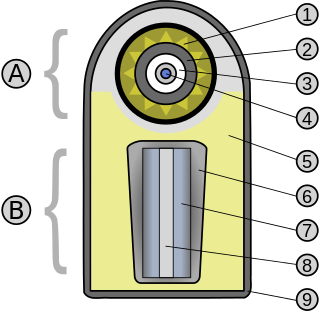
A thermonuclear weapon, or fusion weapon, is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation atomic bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material.
The LIM-49A Spartan was a United States Army anti-ballistic missile, designed to intercept attacking nuclear warheads from Intercontinental ballistic missiles at long range and while still outside the atmosphere. For actual deployment, a five-megaton thermonuclear warhead was planned to destroy the incoming ICBM warheads. It was part of the Safeguard Program.

The W-71 nuclear warhead was a US thermonuclear warhead developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and deployed on the LIM-49A Spartan missile, a component of the Safeguard Program, an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defense system briefly deployed by the US in the 1970s.
The W49 was an American thermonuclear warhead, used on the Thor, Atlas, Jupiter, and Titan I ballistic missile systems. W49 warheads were manufactured starting in 1958 and were in service until 1963, with a few warheads being retained until 1975.

The W47 was an American thermonuclear warhead used on the Polaris A-1 sub-launched ballistic missile system. Various models were in service from 1960 through the end of 1974. The warhead was developed by the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory between 1957 and 1960.
The W56 was an American thermonuclear warhead produced starting in 1963 which saw service until 1993, on the Minuteman I and II ICBMs.

The W59 was an American thermonuclear warhead used on some Minuteman I ICBM missiles from 1962-1969, and planned to be used on the cancelled GAM-87 Skybolt air-launched ballistic missile.
The W38 was an American thermonuclear warhead used in the early to mid-1960s as a warhead for Atlas E and F, and LGM-25 Titan I ICBMs. It was first built in 1961 and was in service from 1961 to 1965. 70 were deployed on Titan I missiles and 110 on Atlas missiles. It used the Avco Mark 4 reentry vehicle.
The W31 was an American nuclear warhead used for two US missiles and as an atomic demolition munition.
The Mark 27 nuclear bomb and closely related W27 warhead were two American thermonuclear bomb designs from the late 1950s.

The Mark 15 nuclear bomb, or Mk-15, was a 1950s American thermonuclear bomb, the first relatively lightweight thermonuclear bomb created by the United States.
The W21 was an hydrogen bomb design for the US military. It would have used the physics package of the TX-21 bomb. The TX-21 was a weaponized version of the "Shrimp" device tested in the Bravo shot of Operation Castle. A TX-21C was tested as the Navajo shot, Operation Redwing. The TX-21, was a scaled-down version of the Runt device. Smaller in size and weight to the Mk-17, the Mk-21 was considered as a potential missile warhead. Far more powerful than the TX-13, which was a high-yield atomic bomb developed from the Mk-6 bomb, the XW21 was to replace the XW13 in the weapons pod of the B-58 bomber and for the SM-64 Navaho missile.










