Related Research Articles

Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, fisheries and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the twentieth century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output.

Organic farming, also known as ecological farming or biological farming, is an agricultural system that uses fertilizers of organic origin such as compost manure, green manure, and bone meal and places emphasis on techniques such as crop rotation and companion planting. It originated early in the 20th century in reaction to rapidly changing farming practices. Certified organic agriculture accounts for 70 million hectares globally, with over half of that total in Australia. Organic farming continues to be developed by various organizations today. Biological pest control, mixed cropping, and the fostering of insect predators are encouraged. Organic standards are designed to allow the use of naturally-occurring substances while prohibiting or strictly limiting synthetic substances. For instance, naturally-occurring pesticides such as pyrethrin are permitted, while synthetic fertilizers and pesticides are generally prohibited. Synthetic substances that are allowed include, for example, copper sulfate, elemental sulfur, and ivermectin. Genetically modified organisms, nanomaterials, human sewage sludge, plant growth regulators, hormones, and antibiotic use in livestock husbandry are prohibited. Organic farming advocates claim advantages in sustainability, openness, self-sufficiency, autonomy and independence, health, food security, and food safety.

Precision agriculture (PA) is a farming management strategy based on observing, measuring and responding to temporal and spatial variability to improve agricultural production sustainability. It is used in both crop and livestock production. Precision agriculture often employs technologies to automate agricultural operations, improving their diagnosis, decision-making or performing. First conceptual work on PA and practical applications go back in the late 1980s. The goal of precision agriculture research is to define a decision support system for whole farm management with the goal of optimizing returns on inputs while preserving resources.

Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of Sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace".
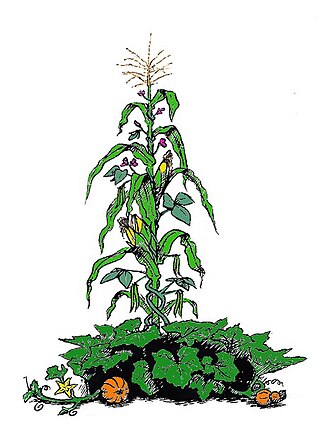
The Three Sisters are the three main agricultural crops of various Indigenous peoples of North America: squash, maize ("corn"), and climbing beans. In a technique known as companion planting, the maize and beans are often planted together in mounds formed by hilling soil around the base of the plants each year; squash is typically planted between the mounds. The cornstalk serves as a trellis for climbing beans, the beans fix nitrogen in their root nodules and stabilize the maize in high winds, and the wide leaves of the squash plant shade the ground, keeping the soil moist and helping prevent the establishment of weeds.

Dryland farming and dry farming encompass specific agricultural techniques for the non-irrigated cultivation of crops. Dryland farming is associated with drylands, areas characterized by a cool wet season followed by a warm dry season. They are also associated with arid conditions, areas prone to drought and those having scarce water resources.
Soil survey, soil mapping, is the process of classifying soil types and other soil properties in a given area and geo-encoding such information. It applies the principles of soil science, and draws heavily from geomorphology, theories of soil formation, physical geography, and analysis of vegetation and land use patterns. Primary data for the soil survey are acquired by field sampling and by remote sensing. Remote sensing principally uses aerial photography, but LiDAR and other digital techniques are steadily gaining in popularity. In the past, a soil scientist would take hard-copies of aerial photography, topo-sheets, and mapping keys into the field with them. Today, a growing number of soil scientists bring a ruggedized tablet computer and GPS into the field with them. The tablet may be loaded with digital aerial photos, LiDAR, topography, soil geodatabases, mapping keys, and more.

Genetically modified crops are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, reduction of spoilage, resistance to chemical treatments, or improving the nutrient profile of the crop. Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.
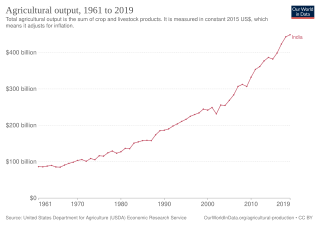
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

Strip-till is a conservation system that uses a minimum tillage. It combines the soil drying and warming benefits of conventional tillage with the soil-protecting advantages of no-till by disturbing only the portion of the soil that is to contain the seed row. This type of tillage is performed with special equipment and can require the farmer to make multiple trips, depending on the strip-till implement used, and field conditions. Each row that has been strip-tilled is usually about eight to ten inches wide.

Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they tow or operate. Diverse arrays of equipment are used in both organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed. Agricultural machinery can be regarded as part of wider agricultural automation technologies, which includes the more advanced digital equipment and robotics. While agricultural robots have the potential to automate the three key steps involved in any agricultural operation, conventional motorized machinery is used principally to automate only the performing step where diagnosis and decision-making are conducted by humans based on observations and experience.
The genetically modified brinjal is a suite of transgenic brinjals created by inserting a crystal protein gene (Cry1Ac) from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis into the genome of various brinjal cultivars. The insertion of the gene, along with other genetic elements such as promoters, terminators and an antibiotic resistance marker gene into the brinjal plant is accomplished using Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. The Bt brinjal has been developed to give resistance against lepidopteron insects, in particular the Brinjal Fruit and Shoot Borer (FSB) by forming pores in the digestive system. Mahyco, an Indian seed company based in Jalna, Maharashtra, has developed the Bt brinjal.

Red Hen Systems, Inc. is a technology company that develops integrated hardware and software solutions for multimedia asset mapping. Their spatial digital video recorders (DVRs) and still cameras instantly geotag video and still photos at the time of data collection. Corresponding mapping software provides the capability to view photographs, video, and audio using GPS coordinates.

Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It has been used to improve the quality of nutrition in products for humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce crop varieties that boast unique and superior traits for a variety of applications. The most frequently addressed agricultural traits are those related to biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, grain or biomass yield, end-use quality characteristics such as taste or the concentrations of specific biological molecules and ease of processing.

A driverless tractor is an autonomous farm vehicle that delivers a high tractive effort at slow speeds for the purposes of tillage and other agricultural tasks. It is considered driverless because it operates without the presence of a human inside the tractor itself. Like other unmanned ground vehicles, they are programmed to independently observe their position, decide speed, and avoid obstacles such as people, animals, or objects in the field while performing their task. The various driverless tractors are split into full autonomous technology and supervised autonomy. The idea of the driverless tractor appears as early as 1940, but the concept has significantly evolved in the last few years. The tractors use GPS and other wireless technologies to farm land without requiring a driver. They operate simply with the aid of a supervisor monitoring the progress at a control station or with a manned tractor in lead.
The combine grain yield monitor is a device coupled with other sensors to calculate and record the crop yield or grain yield as a modern-day combine harvester operates. Yield monitors are a part of the precision agriculture products available to producers today that provide producers with the tools to reduce costs, increase yields, and increase efficiency. The present day grain yield monitor is designed to measure the harvested grain mass flow, moisture content, and speed to determine total grain harvested. In most cases today this is coupled with global positioning system to record yield and other spatially variable information across a field. This allows for the creation of a grain yield map which provides information on spatial variability and supports management decisions for producers.

The production of corn plays a major role in the economy of the United States. The US is the largest corn producer in the world, with 96,000,000 acres (39,000,000 ha) of land reserved for corn production. Corn growth is dominated by west/north central Iowa and east central Illinois. Approximately 13% of its annual yield is exported.
Phytogeomorphology is the study of how terrain features affect plant growth. It was the subject of a treatise by Howard and Mitchell in 1985, who were considering the growth and varietal temporal and spatial variability found in forests, but recognized that their work also had application to farming, and the relatively new science of precision agriculture. The premise of Howard and Mitchell is that landforms, or features of the land's 3D topography significantly affect how and where plants grow. Since that time, the ability to map and classify landform shapes and features has increased greatly. The advent of GPS has made it possible to map almost any variable one might wish to measure. Thus, a very increased awareness of the spatial variability of the environment that plants grow in has arisen. The development of technology like airborne LiDAR has enabled the detailed measurement of landform features to better than sub-meter, and when combined with RTK-GPS enables the creation of very accurate maps of where these features are. Comparison of these landform maps with mapping of variables related to crop or plant growth show a strong correlation.

Agricultural technology or agrotechnology is the use of technology in agriculture, horticulture, and aquaculture with the aim of improving yield, efficiency, and profitability. Agricultural technology can be products, services or applications derived from agriculture that improve various input/output processes.
Digital agriculture, sometimes known as smart farming or e-agriculture, is tools that digitally collect, store, analyze, and share electronic data and/or information in agriculture. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has described the digitalization process of agriculture as the digital agricultural revolution. Other definitions, such as those from the United Nations Project Breakthrough, Cornell University, and Purdue University, also emphasize the role of digital technology in the optimization of food systems.
References
- ↑ "Precision agriculture tools and information for Nebraska". CropWatch. University of Nebraska Lincoln. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ↑ Franzen, Dave; Casey, Francis; Derby, Nathan. "Yield Mapping and Use of Yield Map Data" (PDF). University of North Dakota. Retrieved August 13, 2013.