Telnet is a client/server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main goal was to connect terminal devices and terminal-oriented processes.

A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window.
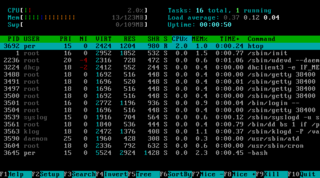
ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control cursor location, color, font styling, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with an ASCII escape character and a bracket character, are embedded into text. The terminal interprets these sequences as commands, rather than text to display verbatim.

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. Starting in the mid-1970s with machines such as the Sphere 1, Sol-20, and Apple I, terminal circuitry began to be integrated into personal and workstation computer systems, with the computer handling character generation and outputting to a CRT display such as a computer monitor or, sometimes, a consumer TV.
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97. The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console and network file transfer application. It supports several network protocols, including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can also connect to a serial port. The name "PuTTY" has no official meaning.
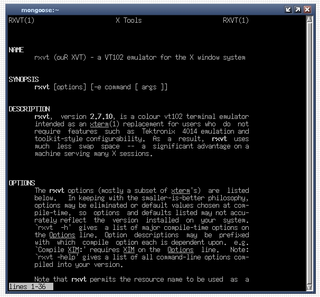
Rxvt is a terminal emulator for the X Window System, and in the form of a Cygwin port, for Windows.
Synchronet is a multiplatform BBS software package, with current ports for Microsoft Windows, Linux, and BSD variants. Past versions also ran on MS-DOS and OS/2, but support for those platforms were dropped in version 3.0.

xterm is the standard terminal emulator for the X Window System. It allows users to run programs which require a command-line interface.
Mystic BBS is a bulletin board system software program that began in 1995 and was first released to the public in December 1997 for MS-DOS. It has been ported to Microsoft Windows, OS/2, OS X, and Linux. Mystic was designed to be a spiritual successor to the Renegade (BBS) and Telegard bulletin board systems.
ProTERM is a terminal emulator and modem program for the Apple II and Macintosh lines of personal computers, published by Intrec Software. Most popular in the late 1980s and 1990s, it was most commonly used for calling bulletin board systems (BBSes) via a computer's modem, experienced users could also Telnet into Unix server and shell account thereon and FTP and tunneling to various destinations therefrom, and once logged into a Unix shell account, other forms of telecom all across the pre-Web Internet; via VT100 terminal emulator or ANSI art, this later ushered in Graphics to the scene.
An SSH client is a software program which uses the secure shell protocol to connect to a remote computer. This article compares a selection of notable clients.

A 3270 Emulator is a terminal emulator that duplicates the functions of an IBM 3270 mainframe computer terminal on a computer, usually a PC or similar microcomputer.
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.
NCSA Telnet is an implementation of the Telnet protocol developed at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, first released in 1986 and continuously developed until 1995. The initial implementation ran under Mac OS and Microsoft MS-DOS, and provided basic DEC VT102 terminal emulation with support for multiple simultaneous connections and an internal FTP server. NCSA Telnet was the first implementation of telnet for the Macintosh or PC that provided the ability to connect to multiple hosts simultaneously.
AbsoluteTelnet is a software terminal client for Windows that implements Telnet, SSH 1 and 2, SFTP, TAPI Dialup and direct COM port connections. It is commercial software, originally released in 1999 and is still in regular development by Brian Pence of Celestial Software.

SecureCRT is a commercial SSH and Telnet client and terminal emulator by VanDyke Software. Originally a Windows product, VanDyke later added a Mac OS X version in 2010 with release v6.6 and a Linux version in 2011 with release v6.7.
The MacintoshCommunications Toolbox, generally shortened to CommToolbox or CTB, was a suite of application programming interfaces, libraries and dynamically loaded code modules for the classic Mac OS that implemented a wide variety of serial and network communication protocols, as well as file transfer protocols and terminal emulations.
AlphaCom is a commercial SSH, Telnet and RS-232/modem client and terminal emulator by OmniCom Technologies. It is a Windows product but has been known to also run on Linux via emulation.






