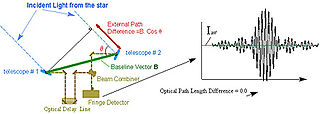
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.

The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere.

Yrjö Väisälä was a Finnish astronomer and physicist.

A Ritchey–Chrétien telescope is a specialized variant of the Cassegrain telescope that has a hyperbolic primary mirror and a hyperbolic secondary mirror designed to eliminate off-axis optical errors (coma). The RCT has a wider field of view free of optical errors compared to a more traditional reflecting telescope configuration. Since the mid 20th century, a majority of large professional research telescopes have been Ritchey–Chrétien configurations; some well-known examples are the Hubble Space Telescope, the Keck telescopes and the ESO Very Large Telescope.

A telescope mount is a mechanical structure which supports a telescope. Telescope mounts are designed to support the mass of the telescope and allow for accurate pointing of the instrument. Many sorts of mounts have been developed over the years, with the majority of effort being put into systems that can track the motion of the fixed stars as the Earth rotates.

Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments.

The Southern African Large Telescope (SALT) is a 9.2-metre optical telescope designed mainly for spectroscopy. It consists of 91 hexagonal mirror segments each with a 1-metre inscribed diameter, resulting in a total hexagonal mirror of 11.1 by 9.8 m. However, its effective aperture is only 9.2 m. It is located close to the town of Sutherland in the semi-desert region of the Karoo, South Africa. It is a facility of the South African Astronomical Observatory, the national optical observatory of South Africa.

The Gaithersburg Latitude Observatory is a historic astronomical observatory on DeSellum Avenue in Gaithersburg, Maryland. It was established in 1899 as part of a system of six International Latitude Observatories to precisely measure the wobble of the Earth's rotating axis. The observatory building and adjacent monuments were designated a National Historic Landmark in 1989 as a testament to international scientific cooperation. The observatory was taken out of service in 1982 after automation eliminated the need for human observations; the property is now owned by the city.

An altazimuth mount or alt-azimuth mount is a simple two-axis mount for supporting and rotating an instrument about two perpendicular axes – one vertical and the other horizontal. Rotation about the vertical axis varies the azimuth of the pointing direction of the instrument. Rotation about the horizontal axis varies the altitude angle of the pointing direction.

ROSAT was a German Aerospace Center-led satellite X-ray telescope, with instruments built by West Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States. It was launched on 1 June 1990, on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral, on what was initially designed as an 18-month mission, with provision for up to five years of operation. ROSAT operated for over eight years, finally shutting down on 12 February 1999.

Liquid-mirror telescopes are telescopes with mirrors made with a reflective liquid. The most common liquid used is mercury, but other liquids will work as well. The liquid and its container are rotated at a constant speed around a vertical axis, which causes the surface of the liquid to assume a paraboloidal shape. This parabolic reflector can serve as the primary mirror of a reflecting telescope. The rotating liquid assumes the same surface shape regardless of the container's shape; to reduce the amount of liquid metal needed, and thus weight, a rotating mercury mirror uses a container that is as close to the necessary parabolic shape as feasible. Liquid mirrors can be a low-cost alternative to conventional large telescopes. Compared to a solid glass mirror that must be cast, ground, and polished, a rotating liquid-metal mirror is much less expensive to manufacture.
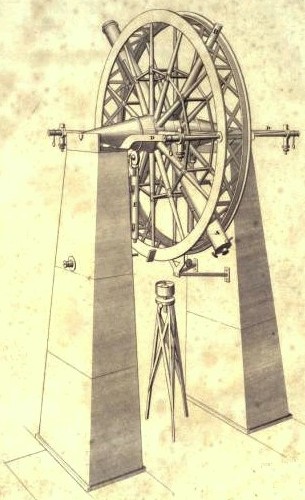
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis.

The Large Zenith Telescope (LZT) was a 6.0-meter diameter liquid-mirror telescope located in the University of British Columbia's Malcolm Knapp Research Forest, about 70 km (43 mi) east from Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It was one of the largest optical telescopes in the world, but still quite inexpensive. The telescope was completed in the spring of 2003 and decommissioned in 2016.

The Mirasteilas Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Falera in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland. With its 90-centimeter telescope it is the largest publicly accessible observatory in Switzerland.

NASA Orbital Debris Observatory (NODO) was an astronomical observatory located in the Lincoln National Forest near Cloudcroft, New Mexico approximately 23 kilometers (14 mi) northeast of Alamogordo. From 1995 to 2002 it hosted two telescopes funded and operated by NASA that were dedicated to detecting orbital debris. The facility was initially called the Cloudcroft Electro-Optical Research Facility when it was completed in 1962, and was also known as the Cloudcroft Observatory. It is now privately owned by Embry-Riddle University.

A balloon-borne telescope is a type of airborne telescope, a sub-orbital astronomical telescope that is suspended below one or more stratospheric balloons, allowing it to be lifted above the lower, dense part of the Earth's atmosphere. This has the advantage of improving the resolution limit of the telescope at a much lower cost than for a space telescope. It also allows observation of frequency bands that are blocked by the atmosphere.

Cloudcroft Observatory, is an astronomical observatory located in the Lincoln National Forest near Cloudcroft, New Mexico, approximately 23 kilometers (14 mi) northeast of Alamogordo. It is owned by the Tzec Maun Foundation, a private astronomical organization.
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth. The field of astronomy features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.



















