2063 Bacchus, provisional designation 1977 HB, is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. The contact binary was discovered on 24 April 1977, by American astronomer Charles Kowal at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. It was named after Bacchus from Roman mythology.
(35396) 1997 XF11, provisional designation 1997 XF11, is a kilometer-sized asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object, Mars-crosser and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group.

2004 FH is a micro-asteroid and near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 30 meters in diameter, that passed just 43,000 km (27,000 mi) above the Earth's surface on 18 March 2004, at 22:08 UTC. It was the 11th closest approach to Earth recorded as of 21 November 2008. The asteroid was first observed on 16 March 2004, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico.
4197 Morpheus, provisional designation 1982 TA, is a highly eccentric asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 October 1982, by American astronomers Eleanor Helin and Eugene Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was later named for Morpheus from Greek mythology.
4486 Mithra, is an eccentric asteroid and suspected contact-binary, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It belongs to the Apollo group of asteroids and is a relatively slow rotator.
(68950) 2002 QF15 is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, that measures approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 27 August 2002, by the LINEAR project at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico, United States.

(480808) 1994 XL1 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, approximately 200 meters (700 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 6 December 1994, by Scottish–Australian astronomer Robert McNaught at Siding Spring Observatory in Australia. It was one of the first asteroids discovered to have a semi-major axis less than Venus.
8013 Gordonmoore, provisional designation 1990 KA, is an eccentric, stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1–2 kilometers in diameter.
3102 Krok, provisional designation 1981 QA, is a rare-type asteroid and slow rotator, classified as a near-Earth object of the Amor group, that measures approximately 1.5 kilometers in diameter.
7336 Saunders, provisional designation 1989 RS1, is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 0.5 kilometers in diameter.
(5836) 1993 MF is a highly eccentric, stony asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Amor group of asteroids, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 June 1993, by American astronomers Eleanor Helin and Kenneth Lawrence at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California.
(6037) 1988 EG, is an eccentric, stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid. It belongs to the group of Apollo asteroids and measures approximately half a kilometer in diameter. It was discovered by American astronomer Jeff T. Alu at the U.S. Palomar Observatory, California, on 12 March 1988.
(467336) 2002 LT38, is a sub-kilometer asteroid and suspected tumbler, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, approximately 240 meters (790 ft) in diameter. It was discovered on 12 June 2002, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States.
(8201) 1994 AH2 is a highly eccentric, rare-type asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group of asteroids, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 January 1994, by Australian amateur astronomer Gordon Garradd during the AANEAS survey at the Siding Spring Observatory, Australia. It has an Earth minimum orbit intersection distance of 0.1 AU (15 million km) and is associated with the Beta Taurids daytime meteor shower.
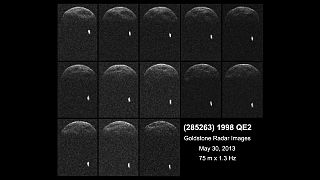
(285263) 1998 QE2, provisional designation 1998 QE2, is a dark asteroid and synchronous binary system, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 19 August 1998, by astronomers of the LINEAR program at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. Its sub-kilometer minor-planet moon was discovered by radar on 30 May 2013.

161989 Cacus is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. It was discovered on 8 February 1978, by German astronomer Hans-Emil Schuster at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile. Its orbit is confined between Venus and Mars.
(86039) 1999 NC43, is an asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. This suspected tumbler and relatively slow rotator was discovered by LINEAR in 1999.

(162058) 1997 AE12 is a stony, sub-kilometer asteroid and likely the slowest rotator known to exist. It is classified as near-Earth object of the Amor group and measures approximately 800 meters in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 10 January 1997 by the Spacewatch survey at Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona
(89830) 2002 CE, provisional designation 2002 CE, is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, approximately 3.1 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 1 February 2002, by astronomers of the LINEAR program at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. This asteroid is one of the largest potentially hazardous asteroid known to exist.

(164121) 2003 YT1, provisional designation 2003 YT1, is a bright asteroid and synchronous binary system on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 December 2003, by astronomers with the Catalina Sky Survey at the Catalina Station near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The V-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.3 hours. Its 210-meter sized minor-planet moon was discovered at Arecibo Observatory in May 2004.










