
Scientific studies have investigated the causes of climate change. They have found that the main cause and driver of recent climate change is elevated levels of greenhouse gases produced by human activities. Natural forces add climate variability as well. Based on many scientific studies, it is "unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land since pre-industrial times." Studies on attribution have focused on changes observed during the period of instrumental temperature record, particularly in the last 50 years. This is the period when human activity has grown fastest and observations of the atmosphere above the surface have become available. Some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are: (a) increasing atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, for a warming effect; (b) global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect; and (c) increasing atmospheric concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.

Global warming potential (GWP) is an index to measure of how much infrared thermal radiation a greenhouse gas would absorb over a given time frame after it has been added to the atmosphere. The GWP makes different greenhouse gases comparable with regards to their "effectiveness in causing radiative forcing". It is expressed as a multiple of the radiation that would be absorbed by the same mass of added carbon dioxide, which is taken as a reference gas. Therefore, the GWP is one for CO2. For other gases it depends on how strongly the gas absorbs infrared thermal radiation, how quickly the gas leaves the atmosphere, and the time frame being considered.

Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (CO2). This is achieved by reacting the feedstock material at high temperatures (typically >700 °C), without combustion, via controlling the amount of oxygen and/or steam present in the reaction. The resulting gas mixture is called syngas (from synthesis gas) or producer gas and is itself a fuel due to the flammability of the H2 and CO of which the gas is largely composed. Power can be derived from the subsequent combustion of the resultant gas, and is considered to be a source of renewable energy if the gasified compounds were obtained from biomass feedstock.

A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated due to their toxicity, flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change.
Eastman Chemical Company is an American company primarily involved in the chemical industry. Once a subsidiary of Kodak, today it is an independent global specialty materials company that produces a broad range of advanced materials, chemicals and fibers for everyday purposes. Founded in 1920 and based in Kingsport, Tennessee, the company now has more than 50 manufacturing sites worldwide and employs approximately 14,000 people.
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCF are superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Also, near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned".

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

Bioenergy is energy made or generated from biomass, which consists of recently living organisms, mainly plants. Types of biomass commonly used for bioenergy include wood, food crops such as corn, energy crops and waste from forests, yards, or farms. The IPCC defines bioenergy as a renewable form of energy. Bioenergy can either mitigate or increase greenhouse gas emissions. There is also agreement that local environmental impacts can be problematic.

1,1,1,2,3,3,3-Heptafluoropropane, also called heptafluoropropane, HFC-227ea, HFC-227 or FM-200, as well as apaflurane (INN), is a colourless, odourless gaseous halocarbon commonly used as a gaseous fire suppression agent.

Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process in which a relatively pure stream of carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial sources is separated, treated and transported to a long-term storage location. For example, the carbon dioxide stream that is to be captured can result from burning fossil fuels or biomass. Usually the CO2 is captured from large point sources, such as a chemical plant or biomass plant, and then stored in an underground geological formation. The aim is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and thus mitigate climate change. The IPCC's most recent report on mitigating climate change describes CCS retrofits for existing power plants as one of the ways to limit emissions from the electricity sector and meet Paris Agreement goals.
Trifluoroiodomethane, also referred to as trifluoromethyl iodide is a halomethane with the formula CF3I. It is an experimental alternative to Halon 1301 (CBrF3) in unoccupied areas. It would be used as a gaseous fire suppression flooding agent for in-flight aircraft and electronic equipment fires.
Enhanced oil recovery, also called tertiary recovery, is the extraction of crude oil from an oil field that cannot be extracted otherwise. Although the primary and secondary recovery techniques rely on the pressure differential between the surface and the underground well, enhanced oil recovery functions by altering the chemical composition of the oil itself in order to make it easier to extract. EOR can extract 30% to 60% or more of a reservoir's oil, compared to 20% to 40% using primary and secondary recovery. According to the US Department of Energy, carbon dioxide and water are injected along with one of three EOR techniques: thermal injection, gas injection, and chemical injection. More advanced, speculative EOR techniques are sometimes called quaternary recovery.

Biomass, in the context of energy production, is matter from recently living organisms which is used for bioenergy production. Examples include wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues including straw, and organic waste from industry and households. Wood and wood residues is the largest biomass energy source today. Wood can be used as a fuel directly or processed into pellet fuel or other forms of fuels. Other plants can also be used as fuel, for instance maize, switchgrass, miscanthus and bamboo. The main waste feedstocks are wood waste, agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, and manufacturing waste. Upgrading raw biomass to higher grade fuels can be achieved by different methods, broadly classified as thermal, chemical, or biochemical.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2017 were 425±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 180±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2017, coal 32%, oil 25%, and gas 10%.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However, the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020, 27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation, 25% from electricity, 24% from industry, 13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021, the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States, as well as worldwide.

Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4. It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it poses technical challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure.

A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but has since also been applied to other sources of heat energy, such as nuclear energy.
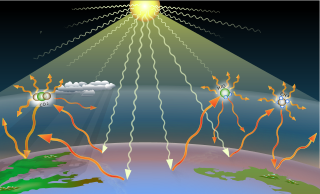
Greenhouse gases are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).
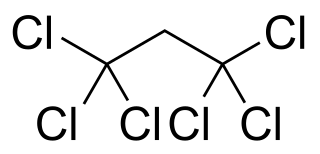
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexachloropropane is a compound of chlorine, hydrogen, and carbon, with chemical formula C3Cl6H2, specifically Cl3C−CH2−CCl3. Its molecule can be described as that of propane with chlorine atoms substituted for the six hydrogen atoms on the extremal carbons.


















