Related Research Articles

Mercia was one of the three main Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Domesday Book – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name Liber de Wintonia, meaning "Book of Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him.

The Kingdom of the South Saxons, today referred to as the Kingdom of Sussex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Heptarchy of Anglo-Saxon England. On the south coast of the island of Great Britain, it was originally a sixth-century Saxon colony and later an independent kingdom. The kingdom remains one of the least known of the Anglo-Saxon polities, with no surviving king-list, several local rulers and less centralisation than other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. The South Saxons were ruled by the kings of Sussex until the country was annexed by Wessex, probably in 827, in the aftermath of the Battle of Ellendun.
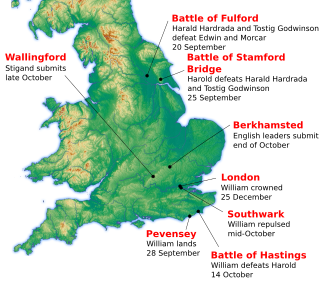
The Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror.

The history of Cheshire can be traced back to the Hoxnian Interglacial, between 400,000 and 380,000 years BP. Primitive tools that date to that period have been found. Stone Age remains have been found showing more permanent habitation during the Neolithic period, and by the Iron Age the area is known to have been occupied by the Celtic Cornovii tribe and possibly the Deceangli.

The Harrying of the North was a series of military campaigns waged by William the Conqueror in the winter of 1069–1070 to subjugate Northern England, where the presence of the last Wessex claimant, Edgar Ætheling, had encouraged Anglo-Saxon Northumbrian, Anglo-Scandinavian and Danish rebellions. William paid the Danes to go home, but the remaining rebels refused to meet him in battle, and he decided to starve them out by laying waste to the Northern shires using scorched earth tactics, especially in the historic county of Yorkshire and the city of York, before relieving the English aristocracy of their positions, and installing Norman aristocrats throughout the region.
The hide was an English unit of land measurement originally intended to represent the amount of land sufficient to support a household. It was traditionally taken to be 120 acres , but was in fact a measure of value and tax assessment, including obligations for food-rent, maintenance and repair of bridges and fortifications, manpower for the army, and (eventually) the geld land tax.

Anglo-Saxon England or Early Medieval England, existing from the 5th to the 11th centuries from soon after the end of Roman Britain until the Norman conquest in 1066, consisted of various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms until 927, when it was united as the Kingdom of England by King Æthelstan. It became part of the short-lived North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway in the 11th century.

Enham Alamein is a village and civil parish about 2+1⁄2 miles north of Andover in the north of Hampshire, England. It was named Enham until 1945.

Wigmore is a village and civil parish in the northwest part of the county of Herefordshire, England. It is located on the A4110 road, about 8 miles (13 km) west of the town of Ludlow, in the Welsh Marches. In earlier times, it was also an administrative district, called a hundred.

The civil parish of Chalvington with Ripe, in the Wealden District of East Sussex, England, is made up of the two villages, Chalvington and Ripe. They are located in the upper Rivers Cuckmere and Ouse joint valley north of the South Downs, between the A27 and the A22 roads, and some 15 miles (24 km) north-west of Eastbourne. Ripe is the larger of the two ecclesiastical parishes with 1,120 acres, compared to the 729 acres of Chalvington. The civil parish was formed on 1 April 1999 from "Chalvington" and "Ripe" parishes.

Riccall is a village and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England, lying 3.5 miles (6 km) to the north of Selby and 9 miles (14 km) south of York. Riccall is noted for being the place where Harold Hardrada's force of invaders landed in 1066, just before the Battle of Stamford Bridge. In the Second World War, an RAF base was built north of the village, and between the late 1970s and the early 2000s, coal was mined from beneath the village as Riccall Mine, part of the Selby Coalfield.

Coldred is a settlement and former civil parish, now in the parish of Shepherdswell with Coldred, in the Dover district of Kent, England. The main part of the village is Coldred Street which lies 1⁄2 mile (0.80 km) to the south-west. In 1961 the parish had a population of 153.
Henry Royston Loyn, FBA, was a British historian specialising in the history of Anglo-Saxon England. His eminence in his field made him a natural candidate to run the Sylloge of the Coins of the British Isles, which he chaired from 1979 to 1993. He was Professor of Medieval History in the University College of South Wales and Monmouthshire and afterwards Professor of Medieval History at Westfield College in the University of London.

Netley Marsh is a village and civil parish in Hampshire, close to the town of Totton. It lies within the New Forest District, and the New Forest National Park. It is the alleged site of the battle between an invading Anglo Saxon army, under Cerdic and a British army under Natanleod in the year 508.
Cyneweard of Laughern or simply Cyneweard was a mid-11th century Anglo-Saxon thegn and sheriff in Worcestershire, England. Probably the son of Æthelric Kiu and grand-nephew of Wulfstan Lupus, Archbishop of York (1003–1023), he was one of the leading nobles of the county at the Norman Conquest of England. On the death of Edward the Confessor he held lands in Gloucestershire and Warwickshire as well as Worcestershire.

The extent of the medieval district of Craven, in the north of England is a matter of debate. The name Craven is either pre-Celtic Britain, Britonnic or Romano-British in origin. However, its usage continued following the ascendancy of the Anglo-Saxons and the Normans – as was demonstrated by its many appearances in the Domesday Book of 1086. Places described as being In Craven in the Domesday Book fell later within the modern county of North Yorkshire, as well as neighbouring areas of West Yorkshire, Lancashire and Cumbria. Usage of Craven in the Domesday Book is, therefore, circumstantial evidence of an extinct, British or Anglo-Saxon kingdom or subnational entity.

Bondi the Staller, also known as 'Boding', was a wealthy Anglo-Danish landowner, thegn, and member of Edward the Confessor's personal household.
Sussex in the High Middle Ages includes the history of Sussex from the Norman Conquest in 1066 until the death of King John, considered by some to be the last of the Angevin kings of England, in 1216. It was during the Norman period that Sussex achieved its greatest importance in comparison with other English counties. Throughout the High Middle Ages, Sussex was on the main route between England and Normandy, and the lands of the Anglo-Norman nobility in what is now western France. The growth in Sussex's population, the importance of its ports and the increased colonisation of the Weald were all part of changes as significant to Sussex as those brought by the neolithic period, by the Romans and the Saxons. Sussex also experienced the most radical and thorough reorganisation of land in England, as the Normans divided the county into five tracts of lands called rapes. Although Sussex may have been divided into rapes earlier in its history, under the Normans they were clearly administrative and fiscal units. Before the Norman Conquest Sussex had the greatest concentration of lands belonging to the family of Earl Godwin. To protect against rebellion or invasion, the scattered Saxon estates in Sussex were consolidated into the rapes as part of William the Conqueror's 'Channel march'.
Stephen David Baxter is a British historian. He has been Barron Fellow and Tutor in Medieval History at St Peter's College, Oxford, since 2014, and in 2020 he was awarded the title of Professor of Medieval History by the University of Oxford. He specialises in lordship in late Anglo-Saxon and early Norman England, and the Domesday Book.
References
- ↑ "Domesday Book | Discover Domesday". www.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ↑ Naughton, Pete (13 May 2009). "Interview: Justin Hardy on 1066: the Battle for Middle Earth" . Retrieved 7 October 2015.