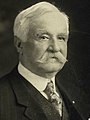William McKinley was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party, he led a realignment that made Republicans largely dominant in the industrial states and nationwide for decades. He presided over victory in the Spanish–American War of 1898; gained control of Hawaii, Puerto Rico, the Philippines and Cuba; restored prosperity after a deep depression; rejected the inflationary monetary policy of free silver, keeping the nation on the gold standard; and raised protective tariffs.
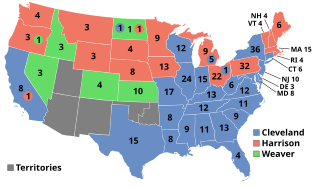
The 1892 United States presidential election was the 27th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1892. In a rematch of the closely contested 1888 presidential election, former Democratic President Grover Cleveland defeated incumbent Republican President Benjamin Harrison. Cleveland's victory made him the first and, to date, the only person in American history to be elected to a non-consecutive second presidential term. It was also the first of two times incumbents were defeated in consecutive elections—the second being Jimmy Carter's defeat of Gerald Ford in 1976, followed by Carter's subsequent loss to Ronald Reagan in 1980.

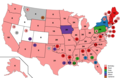
The 1896 United States presidential election was the 28th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1896. Former Governor William McKinley, the Republican nominee, defeated former Representative William Jennings Bryan, the Democratic nominee. The 1896 campaign, which took place during an economic depression known as the Panic of 1893, was a political realignment that ended the old Third Party System and began the Fourth Party System.

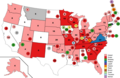
The 1900 United States presidential election was the 29th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1900. In a re-match of the 1896 race, incumbent Republican President William McKinley defeated his Democratic challenger, William Jennings Bryan. McKinley's victory made him the first president to win a consecutive re-election since Ulysses S. Grant accomplished the same feat in 1872. Until 1956, this would be the last time in which an incumbent Republican president would win re-election after serving a full term in office. This election saw the fifth rematch in presidential history, something that would also not occur again until 1956. This was also the first rematch to produce the same winner both times.

Garret Augustus Hobart was the 24th vice president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his death in 1899. Prior to serving as vice president, Hobart was an influential New Jersey businessman, politician and political operative.

Levi Parsons Morton was the 22nd vice president of the United States from 1889 to 1893. He also served as United States ambassador to France, as a U.S. representative from New York, and as the 31st governor of New York.

Marcus Alonzo Hanna was an American businessman and Republican politician who served as a United States Senator from Ohio as well as chairman of the Republican National Committee. A friend and political ally of President William McKinley, Hanna used his wealth and business skills to successfully manage McKinley's presidential campaigns in 1896 and in 1900.

The 1892 Republican National Convention was held at the Industrial Exposition Building, Minneapolis, Minnesota, from June 7 to June 10, 1892. The party nominated President Benjamin Harrison for re-election on the first ballot and Whitelaw Reid of New York for vice president.

Joseph Benson Foraker was an American politician of the Republican Party who served as the 37th governor of Ohio from 1886 to 1890 and as a United States senator from Ohio from 1897 until 1909.

Arthur Sewall was an American shipbuilder from Maine, best known as the Democratic nominee for Vice President of the United States in 1896, running mate to William Jennings Bryan. From 1888 to 1896, he served as a member of the Democratic National Committee and unsuccessfully ran for Maine's Senate seat against Eugene Hale. The only elective offices Sewall held were as councilman and alderman in the town of Bath, Maine.

The 1904 Republican National Convention was held in the Chicago Coliseum, Chicago, Cook County, Illinois, on June 21 to June 23, 1904.
The 1896 Democratic National Convention, held at the Chicago Coliseum from July 7 to July 11, was the scene of William Jennings Bryan's nomination as the Democratic presidential candidate for the 1896 U.S. presidential election.

The 1900 Republican National Convention was held June 19 to June 21 in the Exposition Auditorium, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The Exposition Auditorium was located south of the University of Pennsylvania, and the later Convention Hall was constructed along the building's east wall. It was demolished in 2006.

The 1876 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio on June 14–16, 1876. President Ulysses S. Grant had considered seeking a third term, but with various scandals, a poor economy and heavy Democratic gains in the House of Representatives that led many Republicans to repudiate him, he declined to run. The convention resulted in the nomination of Governor Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio for president and Representative William A. Wheeler of New York for vice president.

The 1888 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Auditorium Building in Chicago, Illinois, on June 19–25, 1888. It resulted in the nomination of former Senator Benjamin Harrison of Indiana for president and Levi P. Morton of New York, a former Representative and Minister to France, for vice president. During the convention, Frederick Douglass was invited to speak and became the first African-American to have his name put forward for a presidential nomination in a major party's roll call vote; he received one vote from Kentucky on the fourth ballot.

In 1896, William Jennings Bryan ran unsuccessfully for president of the United States. Bryan, a former Democratic congressman from Nebraska, gained his party's presidential nomination in July of that year after electrifying the Democratic National Convention with his Cross of Gold speech. He was defeated in the general election by the Republican candidate, former Ohio governor William McKinley.

On January 12, 1898, the Ohio General Assembly met in joint convention to elect a United States Senator. The incumbent, Mark Hanna, had been appointed by Governor Asa Bushnell on March 5, 1897, to fill the vacancy caused by the resignation of John Sherman to become Secretary of State to President William McKinley. Hanna's appointment was only good until the legislature met and made its own choice. The legislature elected Hanna over his fellow Republican, Cleveland Mayor Robert McKisson, both for the remainder of Sherman's original term and for a full six-year term to conclude in 1905.

In 1896, William McKinley was elected President of the United States. McKinley, a Republican and former Governor of Ohio, defeated the joint Democratic and Populist nominee, William Jennings Bryan, as well as minor-party candidates. McKinley's decisive victory in what is sometimes seen as a realigning election ended a period of close presidential contests, and ushered in an era of dominance for the Republican Party.

The 1896 United States presidential election in Wyoming took place on November 3, 1896, as part of the 1896 United States presidential election. State voters chose three representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1896 United States presidential election in Oregon took place on November 3, 1896. All contemporary 45 states were part of the 1896 United States presidential election. State voters chose four electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.