
Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called epoxy. The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane.

Varnish is a clear transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not to be confused with wood stain. It usually has a yellowish shade due to the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired. It is sold commercially in various shades.

In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.

Polyurea is a type of elastomer that is derived from the reaction product of an isocyanate component and an amine component. The isocyanate can be aromatic or aliphatic in nature. It can be monomer, polymer, or any variant reaction of isocyanates, quasi-prepolymer or a prepolymer. The prepolymer, or quasi-prepolymer, can be made of an amine-terminated polymer resin, or a hydroxyl-terminated polymer resin.
Polyamide-imides are either thermosetting or thermoplastic, amorphous polymers that have exceptional mechanical, thermal and chemical resistant properties. Polyamide-imides are used extensively as wire coatings in making magnet wire. They are prepared from isocyanates and TMA in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). A prominent distributor of polyamide-imides is Solvay Specialty Polymers, which uses the trademark Torlon.
Chemical Agent Resistant Coating (CARC) is a paint commonly applied to military vehicles to provide protection against chemical and biological weapons.
Fusion bonded epoxy coating, also known as fusion-bond epoxy powder coating and commonly referred to as FBE coating, is an epoxy-based powder coating that is widely used to protect steel pipe used in pipeline construction from corrosion. It is also commonly used to protect reinforcing bars and on a wide variety of piping connections, valves etc. FBE coatings are thermoset polymer coatings. They come under the category of protective coatings in paints and coating nomenclature. The name fusion-bond epoxy is due to resigning cross-link and the application method, which is different from a conventional paint. In 2020 the market size was quoted at 12 billion dollars.
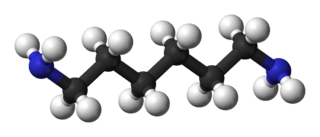
Hexamethylenediamine is the organic compound with the formula H2N(CH2)6NH2. The molecule is a diamine, consisting of a hexamethylene hydrocarbon chain terminated with amine functional groups. The colorless solid (yellowish for some commercial samples) has a strong amine odor. About 1 billion kilograms are produced annually.
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as glass-reinforced plastic radar domes on aircraft and graphite-epoxy payload bay doors on the Space Shuttle.
In polymer chemistry, the term prepolymer or pre-polymer, refers to a monomer or system of monomers that have been reacted to an intermediate-molecular mass state. This material is capable of further polymerization by reactive groups to a fully cured, high-molecular-mass state. As such, mixtures of reactive polymers with un-reacted monomers may also be referred to as pre-polymers. The term "pre-polymer" and "polymer precursor" may be interchanged.
Polyaspartic ester chemistry was first introduced in the early 1990s making it a relatively new technology. The patents were issued to Bayer in Germany and Miles Corporation in the United States. It utilizes the aza-Michael addition reaction. These products are then used in coatings, adhesives, sealants and elastomers. Pure polyurea reacts extremely quickly making them almost unusable without plural component spray equipment. Polyaspartic technology utilizes a partially blocked amine to react more slowly with the isocyanates and thus produce a modified polyurea. The amine/diamine or even triamine functional coreactant for aliphatic polyisocyanate is typically reacted with a maleate. Polyaspartic esters (PAE) initially found use in conventional solvent-borne two-component polyurethane coatings.
4,4'-Diaminodicyclohexylmethane is the name for organic compounds with the formula CH2(C6H10NH2)2. It is classified as a diamine. In the epoxy industry it is often referred to as PACM, short for para-diaminodicyclohexylmethane. It is used as a curing agent for epoxy resins It finds particular use in epoxy flooring. Another use is to produce diisocyanates, which are precursors to polyurethanes. The mixture is a colorless solid, but typical samples are yellowish and oily. The compound is produced as a mixture of three isomers by the hydrogenation of methylenedianiline. These isomers are, in decreasing order of their yield from the hydrogenation, trans-trans, cis-trans, and a small amount of cis-cis.
Polyurethane dispersion, or PUD, is understood to be a polyurethane polymer resin dispersed in water, rather than a solvent, although some cosolvent maybe used. Its manufacture involves the synthesis of polyurethanes having carboxylic acid functionality or nonionic hydrophiles like PEG incorporated into, or pendant from, the polymer backbone. Two component polyurethane dispersions are also available.
Waterborne resins are sometimes called water-based resins. They are resins or polymeric resins that use water as the carrying medium as opposed to solvent or solvent-less. Resins are used in the production of coatings, adhesives, sealants, elastomers and composite materials. When the phrase waterborne resin is used, it usually describes all resins which have water as the main carrying solvent. The resin could be water-soluble, water reducible or water dispersed.
Hydrogenated MDI (H12MDI or 4,4′-diisocyanato dicyclohexylmethane) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is a water white liquid at room temperature and is manufactured in relatively small quantities. It is also known as 4,4'-methylenedi(cyclohexyl isocyanate) or methylene bis(4-cyclohexylisocyanate) and has the formula CH2[(C6H10)NCO]2.
In organic chemistry, amine value is a measure of the nitrogen content of an organic molecule. Specifically, it is usually used to measure the amine content of amine functional compounds. It may be defined as the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide (KOH) equivalent to one gram of epoxy hardener resin. The units are thus mg KOH/g.

Diethyl toluene diamine (DETDA) is a liquid aromatic organic molecule with formula C11H18N2. It is chemically an aromatic diamine and has the CAS Registry number of 68479-98-1. It has more than one isomer and the mixture of the two main isomers is given a different CAS number of 75389-89-8. It is often marketed as a less toxic version of 4,4'-methylenedianiline (MDA). It is also used to replace the more toxic 4,4'-methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) (MOCA). The toxicology is reasonably well understood.
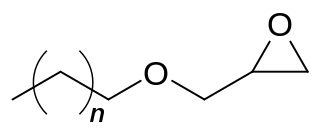
C12-C13 alcohol glycidyl ether is a mixture of organic chemicals in the glycidyl ether family. It is a mixture of mainly 12 and 13 carbon chain alcohols, also called fatty alcohols that have been glycidated. It is an industrial chemical used as a surfactant but primarily for epoxy resin viscosity reduction. It has the CAS number 120547-52-6.












